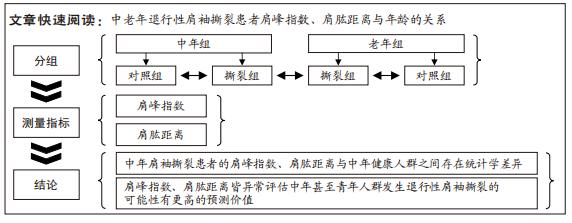
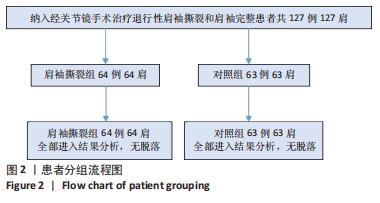
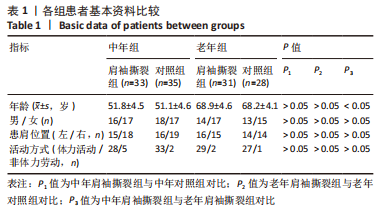
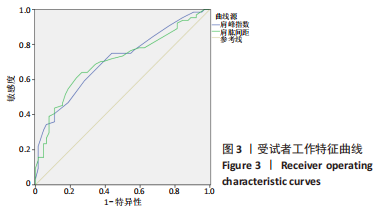
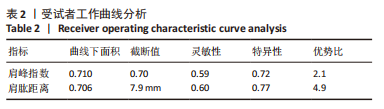
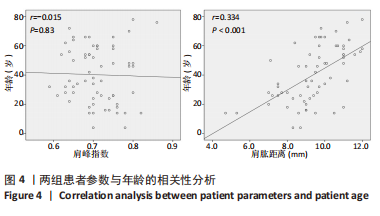
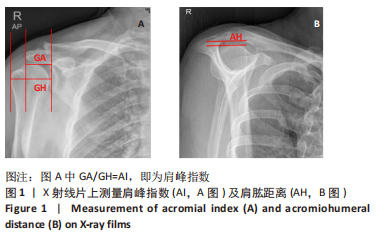
[1] NAMDARI S, YAGNIK G, EBAUGH DD, et al. Defining functional shoulder range of motion for activities of daily living. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012;21(9):1177-1183.
[2] LUGO R, KUNG P, MA CB. Shoulder biomechanics. Eur J Radiol. 2008; 68(1):16-24.
[3] LEE SE, JUNG JY, LEE SY,et al. Progression of long head of the biceps brachii tendon abnormality on magnetic resonance imaging after rotator cuff repair. Br J Radiol. 2021;94(1124):20210366.
[4] MCCRUM E. MR Imaging of the Rotator Cuff. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2020;28(2):165-179.
[5] KLEIM BD, SIEBENLIST S, SCHEIDERER B, et al. [Irreparable rotator cuff tear-reverse shoulder arthroplasty and alternative procedures]. Unfallchirurg. 2021;124(2):117-124.
[6] AGHA O, DIAZ A, DAVIES M, et al. Rotator cuff tear degeneration and the role of fibro-adipogenic progenitors. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2021; 1490(1):13-28.
[7] PLANCHER KD, SHANMUGAM J, BRIGGS K,et al. Diagnosis and Management of Partial Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears: A Comprehensive Review. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2021;29(24):1031-1043.
[8] BANDARA U, AN VVG, IMANI S, et al. Rehabilitation protocols following rotator cuff repair: a meta-analysis of current evidence. ANZ J Surg. 2021;91(12):2773-2779.
[9] BRINDISINO F, SALOMON M, GIAGIO S,et al. Rotator cuff repair vs. nonoperative treatment: a systematic review with meta-analysis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2021;30(11):2648-2659.
[10] LAWRENCE RL, BRAMAN JP, LUDEWIG PM. Shoulder kinematics impact subacromial proximities: a review of the literature. Braz J Phys Ther. 2020;24(3):219-230.
[11] NEER CS, 2ND. Anterior acromioplasty for the chronic impingement syndrome in the shoulder: a preliminary report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1972;54(1):41-50.
[12] NYFFELER RW, WERNER CM, SUKTHANKAR A, et al. Association of a large lateral extension of the acromion with rotator cuff tears. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(4):800-805.
[13] HSU TH, LIN CL, WU CW,et al. Accuracy of Critical Shoulder Angle and Acromial Index for Predicting Supraspinatus Tendinopathy. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022;12(2):283.
[14] LIU CT, MIAO JQ, WANG H, et al. The association between acromial anatomy and articular-sided partial thickness of rotator cuff tears. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):760.
[15] HAMIE QM, HUBER FA, GRUNDER V,et al. Added value of combined acromiohumeral distance and critical shoulder angle measurements on conventional radiographs for the prediction of rotator cuff pathology. Eur J Radiol Open. 2022;9:100416.
[16] HASAN SS. Editorial Commentary: Biology and Biomechanics Must Be Carefully Balanced for a Durable Rotator Cuff Repair. Arthroscopy. 2021;37(1):38-41.
[17] BJÖRNSSON HALLGREN HC, ADOLFSSON L. Neither critical shoulder angle nor acromion index were related with specific pathology 20 years later! Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021;29(8):2648-2655.
[18] TUNALI O, ERŞEN A, KIZILKURT T, et al. Are critical shoulder angle and acromion index correlated to the size of a rotator cuff tear. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2022;108(2):103122.
[19] MOOR BK, BOUAICHA S, ROTHENFLUH DA, et al. Is there an association between the individual anatomy of the scapula and the development of rotator cuff tears or osteoarthritis of the glenohumeral joint?: A radiological study of the critical shoulder angle. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-b(7):935-941.
[20] BIGLIANI LU, TICKER JB, FLATOW EL, et al. The relationship of acromial architecture to rotator cuff disease. Clin Sports Med. 1991;10(4):823-838.
[21] YILMAZTURK K, BIRINCI M, KUYUCU E, et al. Is shoulder geometry important for rotator cuff tears? Int J Clin Pract. 2021;75(12):e15005.
[22] THIESEMANN S, KIRCHNER F, FARKHONDEH FAL M, et al. Antero-lateral acromioplasty does not change the Critical Shoulder Angle and Acromion Index in a clinically relevant amount. Arthroscopy. 2022.
[23] KIM HS, JOO SH, LIM HS, et al. Feasibility of the acromion index as a reference of severity of stratified supraspinatus tendon injury: a secondary analysis. Acta Radiol. 2020;61(12):1661-1667.
[24] DE OLIVEIRA FCL, PAIROT DE FONTENAY B, BOUYER LJ, et al. Kinesiotaping for the Rehabilitation of Rotator Cuff-Related Shoulder Pain: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Sports Health. 2021;13(2):161-172.
[25] CLARK JM, HARRYMAN DT, 2ND. Tendons, ligaments, and capsule of the rotator cuff. Gross and microscopic anatomy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992;74(5):713-725.
[26] MAFFULLI N, LONGO UG, BERTON A, et al. Biological factors in the pathogenesis of rotator cuff tears. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2011; 19(3):194-201.
[27] CHOPP JN, O’NEILL JM, HURLEY K, et al. Superior humeral head migration occurs after a protocol designed to fatigue the rotator cuff: a radiographic analysis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010;19(8):1137-1144.
[28] LÓPEZ-DE-CELIS C, ESTÉBANEZ-DE-MIGUEL E, PÉREZ-BELLMUNT A, et al. The Effect of Scapular Fixation on Scapular and Humeral Head Movements during Glenohumeral Axial Distraction Mobilization. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022;58(3):454.
[29] NYFFELER RW, MEYER DC. Acromion and glenoid shape: Why are they important predictive factors for the future of our shoulders? EFORT Open Rev. 2017;2(5):141-150.
[30] XU M, LI Z, ZHOU Y, et al. Correlation between acromiohumeral distance and the severity of supraspinatus tendon tear by ultrasound imaging in a Chinese population. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020; 21(1):106.
[31] NYFFELER RW. Editorial Commentary: Does the Morphology of the Acromion Explain All Rotator Cuff Tears? Arthroscopy. 2019;35(12): 3316-3317.
[32] VÄHÄKARI M, LEPPILAHTI J, HYVÖNEN P, et al. Acromial shape in asymptomatic subjects: a study of 305 shoulders in different age groups. Acta Radiol. 2010;51(2):202-206.
[33] ALRADDADI A, ALASHKHAM A, LAMB C, et al. Examining changes in acromial morphology in relation to spurs at the anterior edge of acromion. Surg Radiol Anat. 2019;41(4):409-414.
[34] ALFARO-GOMEZ U, FUENTES-RAMIREZ LD, CHAVEZ-BLANCO KI, et al. Anatomical variations of the acromial and coracoid process: clinical relevance. Surg Radiol Anat. 2020;42(8):877-885.
[35] MAYERHOEFER ME, BREITENSEHER MJ, WURNIG C, et al. Shoulder impingement: relationship of clinical symptoms and imaging criteria. Clin J Sport Med. 2009;19(2):83-89.
[36] HOESSLY M, BOUAICHA S, JENTZSCH T, et al. Angle of approach to the superior rotator cuff of arthroscopic instruments depends on the acromial morphology: an experimental study in 3D printed human shoulders. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):435.
[37] CASIER SJ, VAN DEN BROECKE R, VAN HOUCKE J, et al. Morphologic variations of the scapula in 3-dimensions: a statistical shape model approach. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2018;27(12):2224-2231.
[38] CHANG EY, MOSES DA, BABB JS, et al. Shoulder impingement: objective 3D shape analysis of acromial morphologic features. Radiology. 2006; 239(2):497-505.
[39] BEELER S, LEOTY L, HOCHREITER B, et al. Similar scapular morphology in patients with dynamic and static posterior shoulder instability. JSES Int. 2021;5(2):181-189.
[40] HUFELAND M, BRUSIS C, KUBO H, et al. The acromiohumeral distance in the MRI should not be used as a decision criterion to assess subacromial space width in shoulders with an intact rotator cuff. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021;29(7):2085-2089. |