中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (33): 5354-5357.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2830
• 骨与关节图像与影像 bone and joint imaging • 上一篇 下一篇
无症状成人颈胸交界区脊柱矢状面参数的相关性
曹 斌1,左玉强2,杜晗阳3,于海泉1,苏敬阳1,孟浩勇3
石家庄市第一医院,1骨三科,3放射科,河北省石家庄市 050000;2河北医科大学第二医院体检中心,河北省石家庄市 050000
Correlation of saggital parameters of cervical and thoracic junction areas in asymptomatic adults
Cao Bin1, Zuo Yuqiang2, Du Hanyang3, Yu Haiquan1, Su Jingyang1, Meng Haoyong3
1Third Department of Orthopedics, 3Department of Radiology, First Hospital of Shijiazhuang, Shijiazhuang 050000, Hebei Province, China; 2Medical Examination Center, Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050000, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
颈胸交界区:颈胸交界区系连接颈部与上纵隔、上胸腔及腋窝的特定部位,以颈根部为中心,上起自甲状腺中部,下止于主动脉弓平面,在胸部包括上纵隔、胸膜顶、双肺尖和上胸腔;在颈部包括筋膜、筋膜间隙及其包绕的肌肉、神经、血管和气管、食管、甲状腺、甲状旁腺等器官;既有颈部中线结构向上纵隔的延续,又有颈部的神经、血管及肌肉等结构向双侧腋窝区的横向延伸,其解剖结构复杂。
脊柱矢状面平衡:人体脊柱在矢状面上有4个生理弯曲,即颈椎前凸、胸椎后凸、腰椎前凸和骶椎后凸,脊柱在矢状面呈S形。人体脊柱整体的矢状面平衡,能保证人在站立及行走时以最小的能量消耗来维持视线水平和相对稳定的姿势,若各种原因导致脊柱某节段出现矢状面序列改变时,脊柱需通过其代偿机制来维持脊柱的矢状面平衡。
背景:颈胸交界区脊柱矢状面平衡不仅与全脊柱矢状面平衡相关,还与颈椎矢状面平衡相关。
目的:探讨无症状成人颈胸交界区脊柱矢状面参数的相关性。
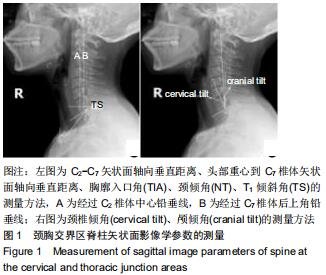
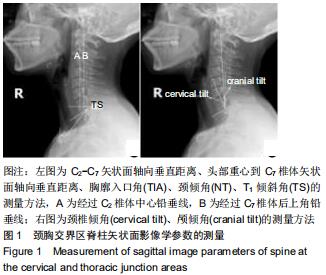
方法:选择2017年1月至2018年12月在河北医科大学第二医院体检中心行健康体检且无颈椎病相关临床症状者120名,年龄23-79岁,根据年龄分为21-40岁组、41-60岁组、61-80岁组,每组40名,均拍摄颈椎侧位DR影像,测量下面影像学参数:C2-C7矢状面轴向垂直距离、头部重心到C7椎体矢状面轴向垂直距离、胸廓入口角、颈倾角、T1倾斜角、颅倾角。
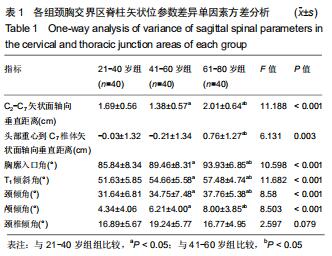
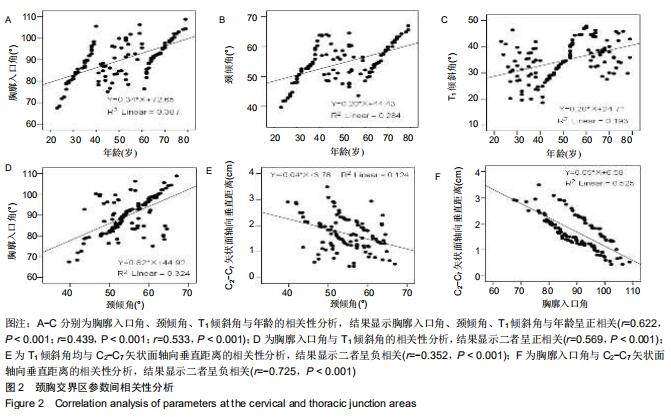
结果与结论:①3组间C2-C7矢状面轴向垂直距离、头部重心到C7椎体矢状面轴向垂直距离、胸廓入口角、颈倾角、T1倾斜角、颅倾角比较差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05),并且组间两两比较差异亦有显著性意义 (P < 0.05);胸廓入口角、颈倾角、T1倾斜角随着年龄的增大而增大;②相关性分析显示胸廓入口角、颈倾角、T1倾斜角与年龄呈正相关(r=0.622,r=0.439,r=0.533,P均< 0.001);胸廓入口角与T1倾斜角呈正相关(r=0.569,P < 0.001);胸廓入口角、T1倾斜角均与C2-C7矢状面轴向垂直距离呈负相关(r=-0.725,r=-0.352,P均< 0.001);③结果表明,无症状成人胸廓入口角、颈倾角、颅倾角、T1倾斜角呈随年龄增大而增大的趋势,且胸廓入口角、颈倾角、T1倾斜角与年龄呈正相关。
ORCID: 0000-0002-2694-3950(曹斌)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: