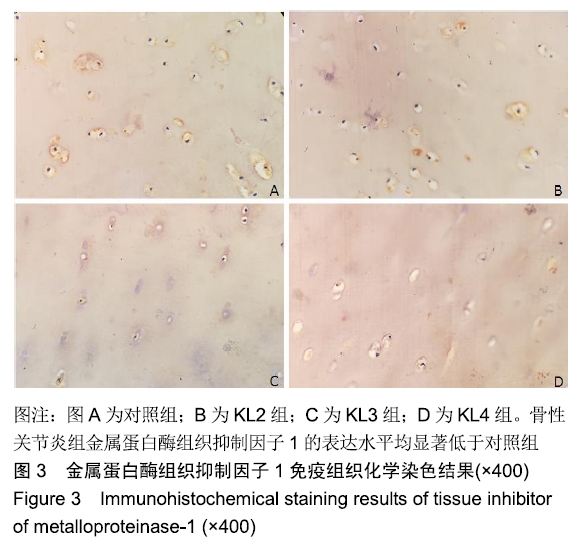
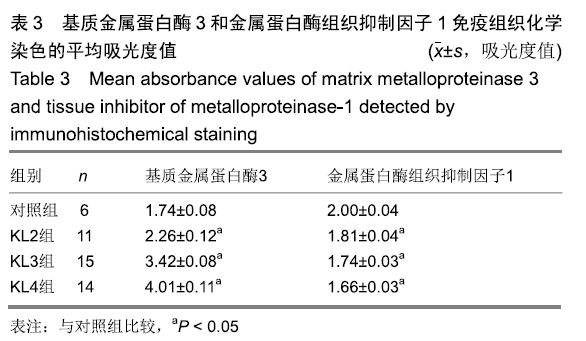
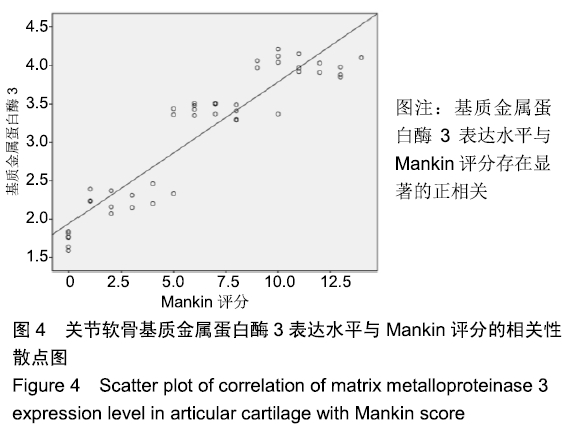
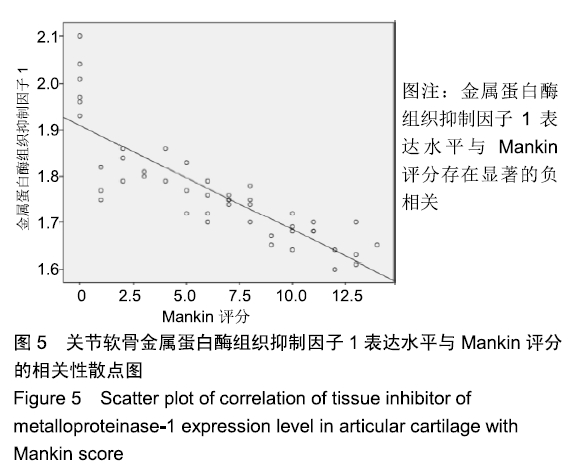
[1] 邬波,柳椰,杜明昌,等.膝关节单髁置换治疗膝内侧间室骨关节炎的疗效观察[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2017, 10(2):123-125.
[2] 赵继国.膝关节骨关节炎的治疗进展[J].中医临床研究, 2015, 7(31):144-146.
[3] ACKERMAN IN, BOHENSKY MA, DE STEIGER R, et al. Substantial rise in the lifetime risk of primary total knee replacement surgery for osteoarthritis from 2003 to 2013: an international, population-level analysis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(4): 455-461.
[4] ACKERMAN I N, ZOMER E, GILMARTIN-THOMAS JF, et al. Forecasting the future burden of opioids for osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(3):350-355.
[5] SHARIF B, KOPEC J, BANSBACK N, et al.Projecting the direct cost burden of osteoarthritis in Canada using a microsimulation model.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23: 1654-1663.
[6] PALAZZO C, NGUYEN C, LEFEVRE-COLAU MM, et al. Risk factors and burden of osteoarthritis.Ann Phys Rehabil Med.2016;59: 134-138.
[7] HÜGLE T, GEURTS J. What drives osteoarthritis?-synovial versus subchondral bone pathology. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2017;56(9):1461-1471.
[8] BERENBAUM F.Osteoarthritis as an inflammatory disease (osteoarthritis is not osteoarthrosis!). Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013; 21:16-21.
[9] GEURTS J, PATEL A, HIRSCHMANN MT, et al.Elevated marrow inflammatory cells and osteoclasts in subchondral osteosclerosis in human knee osteoarthritis.J Orthop Res. 2016; 34:262-269.
[10] BAUDART P, LOUATI K, MARCELLI C, et al.Association between osteoarthritis and dyslipidaemia: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis.RMD Open.2017;3: e000442.
[11] ZHANG YM, WANG J, LIU XG.Association between hypertension and risk of knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Medicine(Baltimore).2017;96:e7584.
[12] FRASCA D, BLOMBERG BB, PAGANELLI R.Aging, obesity, and inflammatory age-related diseases. Front Immunol.2017; 8: 1745.
[13] MARTEL-PELLETIER J, PELLETIER JP, CLOUTIER JM, et al. Neutral proteases capable of proteoglycan digesting activity in osteoarthritic and normal human articular cartilage. Arthritis Rheumatol. 1984;27(3):305e12.
[14] DEAN DD, MARTEL-PELLETIER J, PELLETIER JP, et al. Evidence for metalloproteinase and metal-loproteinase inhibitor imbalance in human osteoarthritic cartilage.J Clin Invest.1989;84(2): 678e85.
[15] DOCHERTY AJ, MURPHY G.The tissue metalloproteinase family and the inhibitor TIMP: a study using cDNAs and recombinant proteins. Ann Rheum Dis.1990;49(Suppl 1): 469e79.
[16] CHU XQ, WANG JJ, DOU LD, et al.Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein and matrix metalloproteinase-3 expression in the serum and joint fluid of a reversible osteoarthritis rabbit model. Genet Mol Res. 2015;14(4):14207-14215.
[17] QU H, LI J, WU LD, et al.Trichostatin A increases the TIMP-1/MMP ratio to protect against osteoarthritis in an animal model of the disease. Mol Med Rep. 2016;14(3): 2423-2430.
[18] DULAY GS, COOPER C, DENNISON EM.Knee pain, knee injury, knee osteoarthritis & work. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2015; 29(3):454-461.
[19] CUDEJKO T, VAN DER ESCH M, VAN DEN NOORT JC, et al. Decreased pain and improved dynamic knee instability mediate the beneficial effect of wearing a soft knee brace on activity limitations in persons with knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2018 Aug 12.
[20] ZHENG H, CHEN C.Body mass index and risk of knee osteoarthritis: systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. BMJ Open. 2015;5(12):e007568.
[21] BLAGOJEVIC M, JINKS C, JEFFERY A ,et al.Risk factors for onset of osteoarthritis of the knee in older adults: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2010;18 (1): 24-33.
[22] 叶臻,李民,陈定家.骨关节炎软骨下骨的微结构改变[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2016,22(5):624-627.
[23] 周嵘,钱齐荣.软骨下骨在骨关节炎发病中作用的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(21):1971-1973.
[24] MADRY H, DIJK C N V, MUELLER-GERBL M.The basic science of subchondral bone.Knee Surgery Sports Traumatology Arthroscopy.2010;18(4):419-433.
[25] JI JB, LI XF, LIU L, et al.Effect of low intensity pulsed ultrasound on expression of TIMP-2 in serum and expression of mmp-13 in articular cartilage of rabbits with knee osteoarthritis. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2015;8(12):1043-1048.
[26] RAI MF, SCHMIDT EJ, HASHIMOTO S, et al. Genetic loci that regulate ectopic calcification in response to knee trauma in LG/J by SM/J advanced intercross mice.J Orthop Res.2015; 33:1412-1423.
[27] SANCHEZ C, MAZZUCCHELLI G, LAMBERT C, et al. Comparison of secretome from osteoblasts derived from sclerotic versus non-sclerotic subchondral bone in OA: A pilot study.Plos One.2018;13(3):e0194591.
[28] MURPHY G, NAGASE H.Progress in matrix metalloproteinase research.Mol Aspects Med. 2008;29 : 290-308.
[29] JAVAID MA, ABDALLAH MN, AHMED AS, et al.Matrix metalloproteinases and their pathological upregulation in multiple sclerosis: an overview. Acta Neurol Belg.2013; 113:381-390.
[30] FOTOPOULOS VC, TZINIA A, TZURBAKIS M, et al. Expression levels of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 and its specific inhibitor TIMP-1, in septic and aseptic arthritis of the knee. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(6): 1159-1167.
|