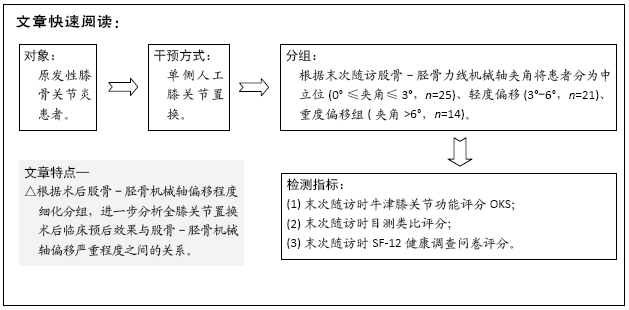
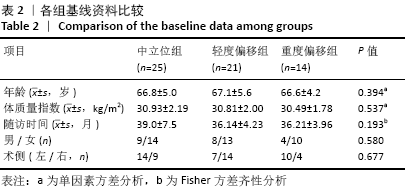
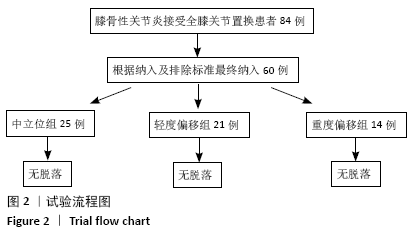
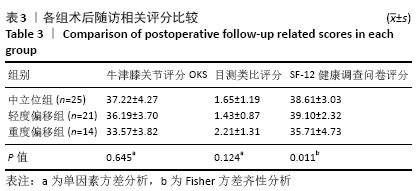
[1] CALLAHAN CM, DRAKE BG, HECK DA. Patient outcomes following tricompartmental total knee replacement.A meta-analysis. JAMA. 1994; 271(17):1349-1357
[2] SHETH NP, HUSAIN A, NELSON CL. Surgical techniques for total knee arthroplasty: measured resection, gap balancing, and hybrid. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2017;25:499-508.
[3] MATSUDA S, KAWAHARA S, OKAZAKI K, et al. Postoperative alignment and ROM affect patient satisfaction after TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(1):127.
[4] LOMBARDI AV, BEREND KR, NG VY. Neutral mechanical alignment: a requirement for successful TKA: affirms. Orthopedics. 2011;34(9):e504.
[5] Walker LC, Clement ND, Ghosh KM, et al .What is a balanced knee replacement? EFORT Open Review. 2018;3(12):614-619.
[6] DALLING JG, MATH K, SCUDERI GR. Evaluating the progression of osteolysis after total knee arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015; 23(3):173-180.
[7] SHARKEY PF, LICHSTEIN PM, SHEN C, et al. Why are total knee arthroplasties failing today--has anything changed after 10 years? J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(9):1774-1778.
[8] LUM ZC, SHIEH AK, DORR LD. Why total knees fail-A modern perspective review. World J Orthop. 2018;9(4):60-64.
[9] ABDEL MP, OUSSEDIK S, PARRATTE S, et al. Coronal alignment in total knee replacement: historical review, contemporary analysis, and future direction. Bone Joint J. 2014;96-8(7):857-862.
[10] HUANG NF, DOWSEY MM, EE E, et al. Coronal alignment correlates with outcome after total knee arthroplasty: five-year follow-up of a randomized controlled trial. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(9):1737- 1741.
[11] BURNETT RS, BARRACK RL. Computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty is currently of no proven clinical benefit: a systematic review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(1):264-276.
[12] 李杨,田华,耿霄.计算机导航系统、3D打印截骨导板与传统器械对全膝关节置换术手术时间和下肢力线恢复的影响[J].中华医学杂志,2018,98(27):2157-2161.
[13] JAMALI AA, MEEHAN JP, MOROSKI NM, et al. Do small changes in rotation affect measurements of lower extremity limb alignment? J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):77.
[14] CHOONG PF, DOWSEY MM, STONEY JD, et al .Does accurate anatomical alignment result in better function and quality of life? Comparing conventional and computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24(4):560-569.
[15] BONNER TJ, EARDLEY WGP, PATTERSON P, et al. The effect of post-operative mechanical axis alignment on the survival of primary total knee replacements after a follow-up of 15 years. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(9):1217-22
[16] MORGAN SS, BONSHAHI A, PRADHAN N, et al. The influence of postoperative coronal alignment on revision surgery in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2008;32(5):639-642.
[17] ABDEL MP, OUSSEDIK S, PARRATTE S, et al. Coronal alignment in total knee replacement: historical review, contemporary analysis, and future direction. Bone Joint J. 2014;96-B:857-862.
[18] HOPPE S, MAINZER JD, FRAUCHIGER L, et al. More accurate component alignment in navigated total knee arthroplasty has no clinical benefit at 5-year follow-up.J Acta Orthop. 2012;83(6):629-633.
[19] HOWELL SM, PAPADOPOULOS S, KUZNIK KT, et al. Accurate alignment and high function after kinematically aligned TKA performed with generic instruments. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(10): 2271-2280.
[20] HOWELL SM, HOWELL SJ, KUZNIK KT, et al. Does a kinematically aligned total knee arthroplasty restore function without failure regardless of alignment category? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(3):1000-1007.
[21] BILGIN E, BOMBACı H, TURGUT A, et al. How are clinical outcomes related to the deviation severity of the tibiofemoral mechanical axis on coronal plane following knee arthroplasty? J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2019;10(1):91-95.
[22] 王波,胡海涛,潘健,等.膝关节骨性关节炎全膝关节置换术后下肢力线与早期临床效果关系的研究[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2015,10(48):1044-1048.
[23] ANDERL W, PAUZENBERGER L, KÖLBLINGER R, et al. Patient-specific instrumentation improved mechanical alignment, while early clinical outcome was comparable to conventional instrumentation in TKA. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(1):102-111.
[24] HUANG TW, LEE CY, LIN SJ, et al. The Influence of Alignment on Midterm Outcome after Total Knee Arthroplasty in Patients With Marked Coronal Femoral Bowing. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(9):1531-1536.
[25] 朱诗白.膝关节置换术-下肢力线矫正程度与关节功能评分之间关系的早期随访研究[D].北京:北京协和医学院,2018.
[26] VANLOMMEL L, VANLOMMEL J, CLAES S, et al. Slight undercorrection following total knee arthroplasty results in superior clinical outcomes in varus knees. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(10): 2325-2330.
[27] GRAEF F, FALK R, TSITSILONIS S, et al. Correction of excessive intraarticular varus deformities in total knee arthroplasty is associated with deteriorated postoperative ankle function. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019.doi: 10.1007/s00167-019-05812-9.
[28] JAROMA A, SOININVAARA T, KRÖGER H. Periprosthetic tibial bone mineral density changes after total knee arthroplasty. Acta Orthop. 2016;87(3):268-273.
[29] MENEGHINI RM, GRANT TW, ISHMAEL MK, et al. Leaving Residual Varus Alignment After Total Knee Arthroplasty Does Not Improve Patient Outcomes. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(9S):S171-S176.
[30] 孙茂淋,何锐,张颖,等.健康人群下肢力线测量在全膝关节置换术中的应用[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2019,12(8):584-588.
[31] BRYAN S, GOLDSMITH LJ, DAVIS JC, et al. Revisiting patient satisfaction following total knee arthroplasty: a longitudinal observational study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):423.
[32] VAN ONSEM S, VERSTRAETE M, DHONT S, et al. Improved walking distance and range of motion predict patient satisfaction after TKA. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26(11):3272-3279.
[33] SIDDIQI A, WHITE PB, KAPLIN L, et al. Effects of Coronal Limb Alignment and Ligament Balance on Pain and Satisfaction Following Total Knee Arthroplasty at Short-Term Follow Up. Surg Technol Int. 2018;33: 271-276.
[34] KURODA Y, TAKAYAMA K, HAYASHI S, et al. Varus deformity in the proximal tibia and immediate postoperative varus alignment result in varus progression in limb alignment in the long term after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28(10): 3287-3293. |