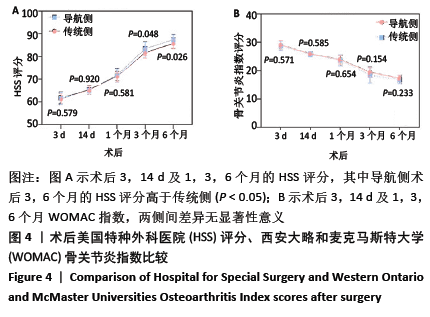
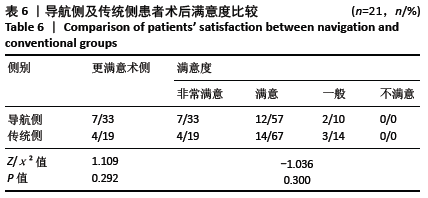
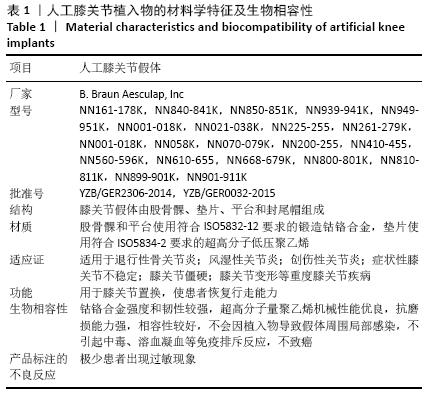
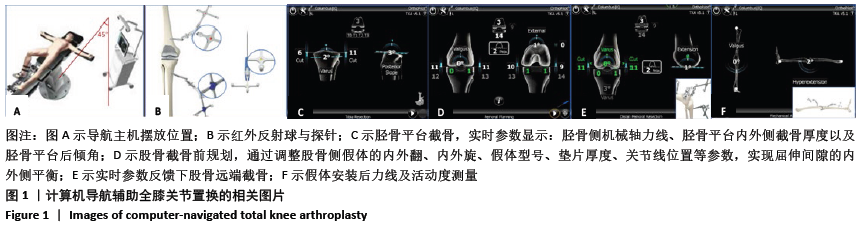
[1] INSALL JN, BINAZZI R, SOUDRY M, et al. Total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985;192:13-22.
[2] WENG YJ, HSU RW, HSU WH. Comparison of computer-assisted navigation and conventional instrumentation for bilateral total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24(5):668-673.
[3] HUANG TW, HSU WH, PENG KT, et al. Total knee arthroplasty with use of computer-assisted navigation compared with conventional guiding systems in the same patient: radiographic results in Asian patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(13):1197-1202.
[4] ZHANG GQ, CHEN JY, CHAI W, et al. Comparison between computer-assisted-navigation and conventional total knee arthroplasties in patients undergoing simultaneous bilateral procedures: a randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(13):1190-1196.
[5] STOCKL B, NOGLER M, ROSIEK R, et al. Navigation improves accuracy of rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;426:180-186.
[6] DE STEIGER RN, LIU YL, GRAVES SE. Computer navigation for total knee arthroplasty reduces revision rate for patients less than sixty-five years of age. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(8):635-642.
[7] ALLEN CL, HOOPER GJ, ORAM BJ, et al. Does computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty improve the overall component position and patient function? Int Orthop. 2014;38(2):251-257.
[8] KIM YH, PARK JW, KIM JS. The Clinical Outcome of Computer-Navigated Compared with Conventional Knee Arthroplasty in the Same Patients: A Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blind, Long-Term Study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99(12):989-996.
[9] KIM YH, PARK JW, KIM JS. Computer-navigated versus conventional total knee arthroplasty a prospective randomized trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(22):2017-2024.
[10] BAUWENS K, MATTHES G, WICH M, et al. Navigated total knee replacement. A meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(2): 261-269.
[11] 周宗科, 翁习生, 曲铁兵, 等. 中国髋、膝关节置换术加速康复--围术期管理策略专家共识 [J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志,2016,9(1): 10-15.
[12] MELHEM E, ASSI A, EL RACHKIDI R, et al. EOS((R)) biplanar X-ray imaging: concept, developments, benefits, and limitations. J Child Orthop. 2016;10(1):1-14.
[13] PARRATTE S, PAGNANO MW, TROUSDALE RT, et al. Effect of postoperative mechanical axis alignment on the fifteen-year survival of modern, cemented total knee replacements . J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(12):2143-2149.
[14] KIM YH, PARK JW, KIM JS, et al. The relationship between the survival of total knee arthroplasty and postoperative coronal, sagittal and rotational alignment of knee prosthesis. Int Orthop. 2014;38(2): 379-385.
[15] PITTA M, ESPOSITO CI, LI Z, et al. Failure After Modern Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Prospective Study of 18,065 Knees. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(2):407-414.
[16] RHEE SJ, KIM HJ, LEE CR, et al. A Comparison of Long-Term Outcomes of Computer-Navigated and Conventional Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019;101(20):1875-1885.
[17] ARBAB D, REIMANN P, BRUCKER M, et al. Alignment in total knee arthroplasty - A comparison of patient-specific implants with the conventional technique. Knee. 2018;25(5):882-887.
[18] AUSTRALIAN ORTHOPAEDIC ASSOCIATION NATIONAL JOINT REPLACEMENT REGISTRY (AOANJRR). Hip, Knee & Shoulder Arthroplasty: 2019 Annual Report. Adelaide: AOA, 2019.
[19] CHOONG PF, DOWSEY MM, STONEY JD. Does accurate anatomical alignment result in better function and quality of life? Comparing conventional and computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24(4):560-569.
[20] HERNANDEZ-VAQUERO D, SUAREZ-VAZQUEZ A, IGLESIAS-FERNANDEZ S. Can computer assistance improve the clinical and functional scores in total knee arthroplasty? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(12): 3436-3442.
[21] BEREND ME, RITTER MA, MEDING JB, et al. Tibial component failure mechanisms in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004; 428:26-34.
[22] RITTER MA, DAVIS KE, MEDING JB, et al. The effect of alignment and BMI on failure of total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(17):1588-1596.
[23] INNOCENTI B, BELLEMANS J, CATANI F. Deviations From Optimal Alignment in TKA: Is There a Biomechanical Difference Between Femoral or Tibial Component Alignment? J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(1): 295-301.
[24] SLEVIN O, HIRSCHMANN A, SCHIAPPARELLI FF, et al. Neutral alignment leads to higher knee society scores after total knee arthroplasty in preoperatively non-varus patients: a prospective clinical study using 3D-CT . Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26(6):1602-1609.
[25] BONNER TJ, EARDLEY WG, PATTERSON P, et al. The effect of post-operative mechanical axis alignment on the survival of primary total knee replacements after a follow-up of 15 years . J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(9):1217-1222.
[26] MORGAN SS, BONSHAHI A, PRADHAN N, et al. The influence of postoperative coronal alignment on revision surgery in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2008;32(5):639-642.
[27] VANLOMMEL L, VANLOMMEL J, CLAES S, et al. Slight undercorrection following total knee arthroplasty results in superior clinical outcomes in varus knees. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(10): 2325-2330.
[28] BELLEMANS J, COLYN W, VANDENNEUCKER H, et al. The Chitranjan Ranawat award: is neutral mechanical alignment normal for all patients? The concept of constitutional varus. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(1):45-53.
[29] HOWELL SM, HOWELL SJ, KUZNIK KT, et al. Does a kinematically aligned total knee arthroplasty restore function without failure regardless of alignment category? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(3):1000-1007.
[30] FEHRING TK, MASON JB, MOSKAL J, et al. When computer-assisted knee replacement is the best alternative. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006; 452:132-136.
[31] DEMIR B, OZKUL B, SAYGILI MS, et al. Deformity correction with total knee arthroplasty for severe knee osteoarthritis accompanying extra-articular femoral deformity: the results are promising . Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26(11):3444-3451.
[32] MATASSI F, COZZI LEPRI A, INNOCENTI M, et al. Total Knee Arthroplasty in Patients With Extra-Articular Deformity: Restoration of Mechanical Alignment Using Accelerometer-Based Navigation System. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(4):676-681.
[33] DATTANI R, PATNAIK S, KANTAK A, et al. Navigation knee replacement. Int Orthop. 2009;33(1):7-10.
[34] 李晓辉, 于建华, 龚跃昆, 等. 导航辅助全膝关节置换与传统置换技术早期临床及 X 线评估 [J]. 中华医学杂志,2015,95(15):1162-1167.
[35] WEBER KL, JEVSEVAR DS, MCGRORY BJ. AAOS Clinical Practice Guideline: Surgical Management of Osteoarthritis of the Knee: Evidence-based Guideline. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2016;24(8):e94-96.
[36] SIU KK, WU KT, KO JY, et al. Effects of computer-assisted navigation versus the conventional technique for total knee arthroplasty on levels of plasma thrombotic markers: a prospective study. Biomed Eng Online. 2019;18(1):99.
[37] JUNG HJ, JUNG YB, SONG KS, et al. Fractures associated with computer-navigated total knee arthroplasty. A report of two cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(10):2280-2284. |