中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (2): 242-247.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1918
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
糖尿病模型小鼠拔牙后对颌牙牙合向伸长过程中根周骨密度及相关因子的变化
杨晓叶1,李文晋1,2,朱 莉2,王 瑜2,张双元1
- 1山西医科大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,山西省太原市 030001;2山西医科大学口腔医学院·口腔医院·山西医科大学第二医院,山西省太原市 030001
Changes of bone mineral density and related factors during maxillary teeth occlusion after tooth extraction in diabetic mice
Yang Xiaoye1, Li Wenjin1, 2, Zhu Li2, Wang Yu2, Zhang Shuangyuan1
- 1Shanxi Medical University Stomatological College • Stomatological Hospital, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; 2Shanxi Medical University Stomatological College • Stomatological Hospital • Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
骨连接蛋白:是一种非结构性的细胞外间质蛋白,分子质量较小,为高度进化的保守序列,基因位于人类第9号染色体,小鼠第11号染色体,由3个独立的区域组成:①末端酸性钙离子结合区域;②卵泡静止素同源的铜离子结合区域;③细胞外钙离子结合区域,其中最重要的功能是骨连接蛋白可以调节细胞外基质和基质金属蛋白酶的产生。
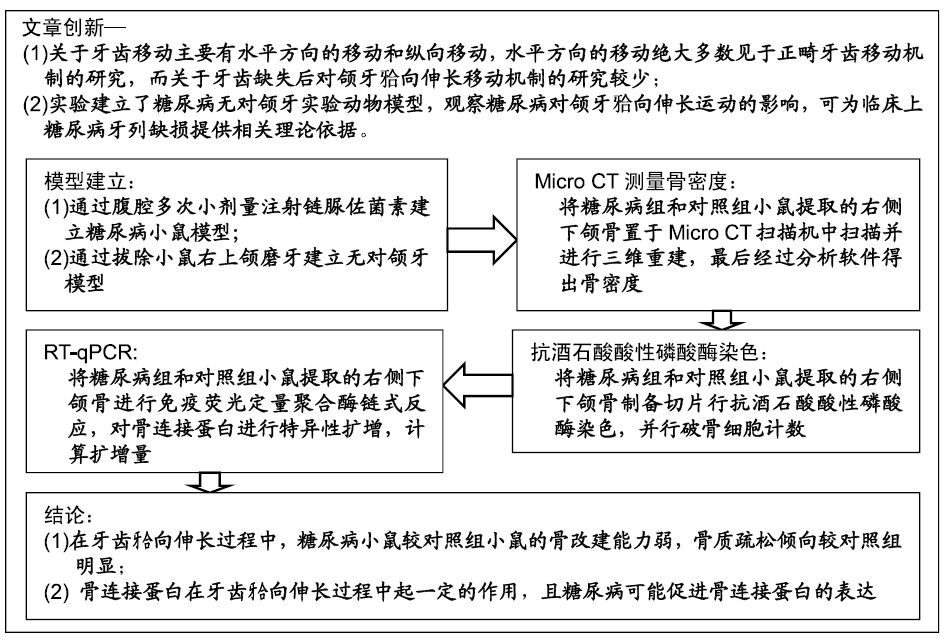
背景:牙列缺失是常见的口腔疾病,若得不到及时有效的治疗,就会出现邻牙倾斜、对颌牙伸长等不良影响,造成牙合紊乱以及牙合干扰,严重影响后期修复。尤其是糖尿病患者牙列缺失后,对颌牙在牙合向伸长过程中,糖尿病对其有何影响?骨连接蛋白在此过程如何变化?目前尚不清楚。
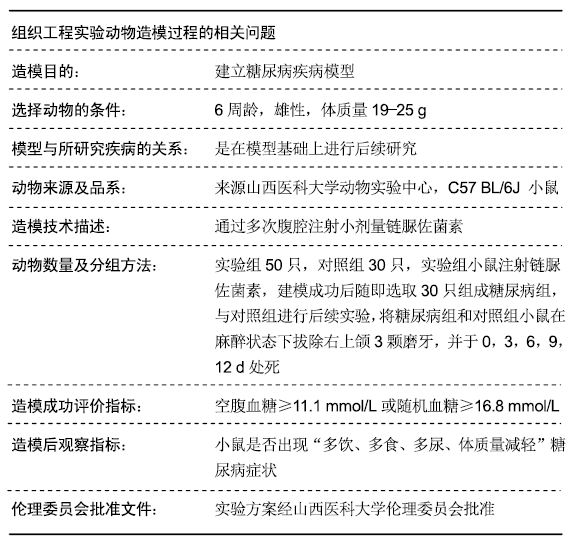
目的:通过建立糖尿病小鼠对颌牙牙合向伸长运动实验模型,研究糖尿病对小鼠牙齿牙合向伸长运动过程的影响。
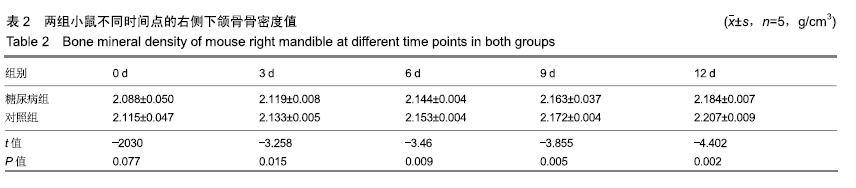
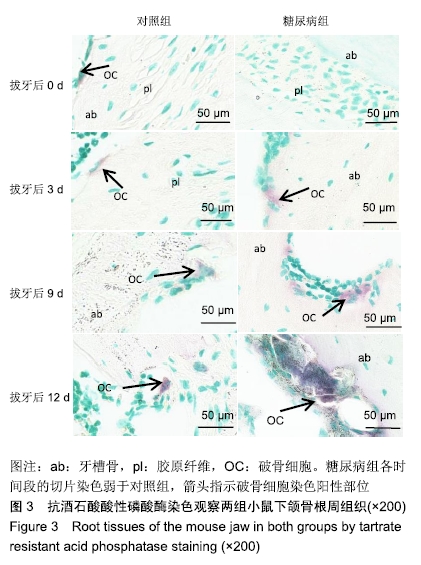
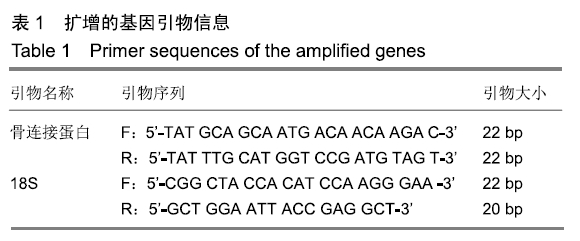
方法:向C57 BL/6J小鼠(购买于山西医科大学动物实验中心)腹腔注射链脲佐菌素建立糖尿病模型,以腹腔注射柠檬酸钠缓冲液的小鼠为对照。取建模成功的糖尿病小鼠与对照组小鼠各30只,拔除右上颌3颗磨牙建立对颌牙牙合向伸长运动实验模型,术后0,3,6,9,12 d,取右侧下颌骨,利用Micro CT测量骨密度,抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶染色计数破骨细胞数量,RT-qPCR检测骨连接蛋白基因的表达。实验方案经山西医科大学伦理委员会批准。
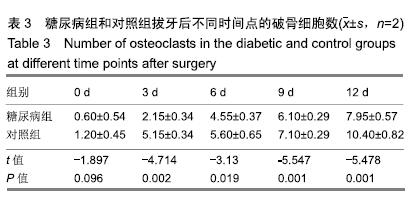
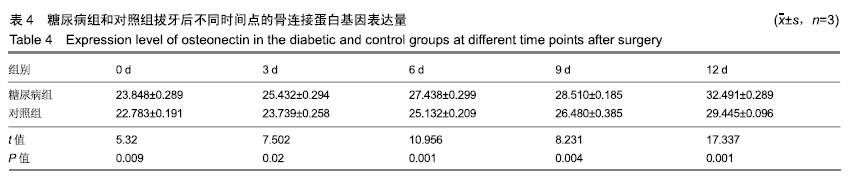
结果与结论:①随着时间的延长,两组右侧下颌骨的骨密度逐渐增加,糖尿病组术后3,6,9,12 d的骨密度低于对照组(P < 0.05);②随着时间的延长,两组右侧下颌骨的破骨细胞数量逐渐增多,糖尿病组术后3,6,9,12 d的破骨细胞数量少于对照组(P < 0.05);③随着时间的延长,两组右侧下颌骨的骨连接蛋白基因表达量逐渐升高,糖尿病组术后0,3,6,9,12 d的骨连接蛋白基因表达量高于对照组(P < 0.05);④结果表明,糖尿病可降低牙齿牙合向伸长运动过程中的骨改建能力并提高骨连接蛋白基因表达。ORCID: 0000-0003-0898-6073(杨晓叶)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: