[1] NAIR PN. Apical periodontitis: a dynamic encounter between root canal infection and host response. Periodontol 2000. 1997;13:121-148.
[2] COLIĆ M, GAZIVODA D, VUCEVIĆ D, et al. Proinflammatory and immunoregulatory mechanisms in periapical lesions. Mol Immunol. 2009;47(1):101-113.
[3] MÁRTON IJ, KISS C. Overlapping protective and destructive regulatory pathways in apical periodontitis. J Endod. 2014;40(2):155-163.
[4] SHAH A, LEE D, SONG M, et al. Clastic cells are absent around the root surface in pulp-exposed periapical periodontitis lesions in mice. Oral Dis. 2018;24(1-2):57-62.
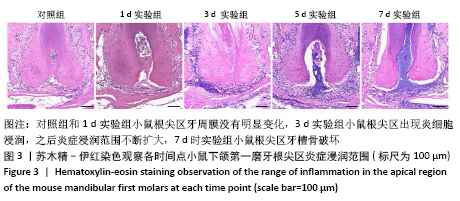
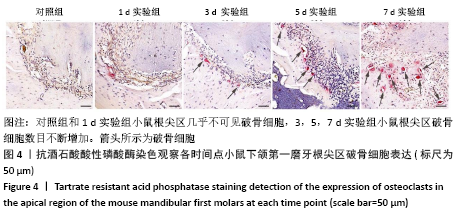
[5] 梅陵宣,刘正,张濒.实验性鼠根尖周炎组织学动态观察[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2002,18(6):500-503.
[6] DE ROSSI A, ROCHA LB, ROSSI MA. Interferon-gamma, interleukin-10, Intercellular adhesion molecule-1, and chemokine receptor 5, but not interleukin-4, attenuate the development of periapical lesions. J Endod. 2008;34(1):31-38.
[7] 陈兴兴,谷苗,吕海鹏,等.不同方法建立实验性狗根尖周炎模型的比较[J].口腔医学研究,2009,25(4):416-419.
[8] SILVA L, NELSON-FILHO P, LEONARDO MR, et al. Effect of calcium hydroxide on bacterial endotoxin in vivo. J Endod. 2002;28(2):94-98.
[9] 王青山,高艳,荣丽,等.内毒素诱导大鼠根尖周炎的X线片及组织病理学改变[J].上海口腔医学,2008,17(4):416-419.
[10] BRENNAN CA, GARRETT WS. Fusobacterium nucleatum - symbiont, opportunist and oncobacterium. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2019;17(3):156-166.
[11] 谢晓婷,王以玲,肖水清.具核梭杆菌的致病性与其可引起的口腔疾病[J].中国医学创新,2017,14(10):145-148.
[12] BOUILLAGUET S, MANOIL D, GIRARD M, et al. Root Microbiota in Primary and Secondary Apical Periodontitis. Front Microbiol. 2018;9: 2374.
[13] ZANDI H, KRISTOFFERSEN AK, ØRSTAVIK D, et al. Microbial Analysis of Endodontic Infections in Root-filled Teeth with Apical Periodontitis before and after Irrigation Using Pyrosequencing. J Endod. 2018;44(3): 372-378.
[14] 郭惠杰,王嘉德.慢性根尖周炎患牙根尖外表面的细菌生物膜[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2009,41(5):571-574.
[15] BULLMAN S, PEDAMALLU CS, SICINSKA E, et al. Analysis of Fusobacterium persistence and antibiotic response in colorectal cancer. Science. 2017;358(6369):1443-1448.
[16] 罗玉龙,葛全兴,聂玉强,等.具核梭杆菌感染与结直肠癌的关系[J].广东医学,2015,36(14):2161-2164.
[17] HAN YW, REDLINE RW, LI M, et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum induces premature and term stillbirths in pregnant mice: implication of oral bacteria in preterm birth. Infect Immun. 2004;72(4):2272-2279.
[18] SWIDSINSKI A, DÖRFFEL Y, LOENING-BAUCKE V, et al. Acute appendicitis is characterised by local invasion with Fusobacterium nucleatum/necrophorum. Gut. 2011;60(1):34-40.
[19] PETERSEN J, GLAßL EM, NASSERI P, et al. The association of chronic apical periodontitis and endodontic therapy with atherosclerosis. Clin Oral Investig. 2014;18(7):1813-1823.
[20] PAULA-SILVA FWG, RIBEIRO-SANTOS FR, PETEAN IBF, et al. Root canal contamination or exposure to lipopolysaccharide differentially modulate prostaglandin E 2 and leukotriene B 4 signaling in apical periodontitis. J Appl Oral Sci. 2020;28:e20190699.
[21] 凌均棨,韦曦,刘红艳.难治性根尖周炎的病因及防治策略[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2010,45(1):52-57.
[22] SIQUEIRA JF JR, RÔÇAS IN. Exploiting molecular methods to explore endodontic infections: Part 1--current molecular technologies for microbiological diagnosis. J Endod. 2005;31(6):411-423.
[23] XIONG H, WEI L, PENG B. The Presence and involvement of interleukin-17 in apical periodontitis. Int Endod J. 2019;52(8): 1128-1137.
[24] NAIR PN. On the causes of persistent apical periodontitis: a review. Int Endod J. 2006;39(4):249-281.
[25] SEGATA N, HAAKE SK, MANNON P, et al. Composition of the adult digestive tract bacterial microbiome based on seven mouth surfaces, tonsils, throat and stool samples. Genome Biol. 2012;13(6):R42.
[26] RICKARD AH, GILBERT P, HIGH NJ, et al. Bacterial coaggregation: an integral process in the development of multi-species biofilms. Trends Microbiol. 2003;11(2):94-100.
[27] BRADSHAW DJ, MARSH PD, WATSON GK, et al. Role of Fusobacterium nucleatum and coaggregation in anaerobe survival in planktonic and biofilm oral microbial communities during aeration. Infect Immun. 1998;66(10):4729-4732.
[28] 郭杨,张玉杰,肖水清.具核梭杆菌生物学特性及检测手段的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2012,39(6):770-774.
[29] BACHRACH G, IANCULOVICI C, NAOR R, et al. Fluorescence based measurements of Fusobacterium nucleatum coaggregation and of fusobacterial attachment to mammalian cells. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2005;248(2):235-240.
[30] 张竹砚.慢性根尖周炎动物模型的研究进展[J].口腔材料器械杂志, 2020,29(2):47-51.
[31] LUNGOVÁ V, RADLANSKI RJ, TUCKER AS, et al. Tooth-bone morphogenesis during postnatal stages of mouse first molar development. J Anat. 2011;218(6):699-716.
[32] KAKEHASHI S, STANLEY HR, FITZGERALD RJ. The effects of surgical exposures of dental pulps in germ-free and conventional laboratory rats. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1965;20:340-349.
[33] 周维君,车英林,杨瑞琨,等.根尖周炎模型小鼠DKK1,SFRP1及骨形成相关分子Runx2,Osteocalcin的表达变化[J].临床口腔医学杂志, 2017,33(12):715-719.
[34] ANDRADA AC, AZUMA MM, FURUSHO H, et al. Immunomodulation Mediated by Azithromycin in Experimental Periapical Inflammation. J Endod. 2020 Aug 5:S0099-2399(20)30574-4. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2020.07.028.
[35] 王艳青.Cyclophilin A在根尖周炎中的表达及作用研究[D].武汉:武汉大学,2019.
[36] 张琛,侯本祥.根尖周炎动物模型中CD14、TLR4的表达[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2007,42(3):148-149.
[37] PAULA-SILVA FWG, ARNEZ MFM, PETEAN IBF, et al. Effects of 5-lipoxygenase gene disruption on inflammation, osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption in polymicrobial apical periodontitis. Arch Oral Biol. 2020;112:104670.
[38] WANG L, ZHANG H, DONG M, et al. Role of the Btk-PLCγ2 Signaling Pathway in the Bone Destruction of Apical Periodontitis. Mediators Inflamm. 2019;2019:8767529.
[39] TAMMA R, ZALLONE A. Osteoblast and osteoclast crosstalks: from OAF to Ephrin. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2012;11(3):196-200.
[40] 李福军,彭彬.大鼠实验性根尖周病的酶组织化学研究[J].口腔医学研究,2003,19(2):109-111.
[41] ZUBERY Y, DUNSTAN CR, STORY BM, et al. Bone resorption caused by three periodontal pathogens in vivo in mice is mediated in part by prostaglandin. Infect Immun. 1998;66(9):4158-4162.
[42] JOHNSON L, ALMEIDA-DA-SILVA CLC, TAKIYA CM, et al. Oral infection of mice with Fusobacterium nucleatum results in macrophage recruitment to the dental pulp and bone resorption. Biomed J. 2018;41(3):184-193. |