中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (2): 171-175.doi: 10.12307/2022.029
• 组织构建细胞学实验 cytology experiments in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
转基因番茄防龋疫苗中外源目的基因鉴定及表达检测
关薇薇1,2,3,顾 瑜2,管晓燕2,3,吴家媛2,3,白国辉3,田 源2,3,刘建国2,3
- 1中南大学湘雅医学院附属海口医院·海南省口腔医学中心,海南省海口市 570208;2遵义医科大学附属口腔医院,贵州省遵义市 563099;3贵州省高等学校口腔疾病研究特色重点实验室·遵义市口腔疾病研究重点实验室,贵州省遵义市 563006
Identification and expression of exogenous target genes in transgenic tomato
Guan Weiwei1, 2, 3, Gu Yu2, Guan Xiaoyan2, 3, Wu Jiayuan2, 3, Bai Guohui3, Tian Yuan2, 3, Liu Jianguo2, 3
- 1Haikou Affiliated Hospital of Central South University Xiangya School of Medicine · Hainan Stomatological Center, Haikou 570208, Hainan Province, China; 2Stomatological Hospital Affiliated to Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563099, Guizhou Province, China; 3Key Laboratory of Oral Disease Research in Guizhou Higher Education Institutions · Zunyi Key Laboratory of Oral Disease Research, Zunyi 563006, Guizhou Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
CTB免疫佐剂:CTB(霍乱毒素B亚单位,cholera toxin B unit)是一种常用的黏膜免疫佐剂,其稳定的环状五聚体结构既可以在生物体内单独表达,也能够通过化学方法或基因融合的方式与抗原偶联,增强免疫应答反应及免疫效果。例如富集 T、B细胞表位的变异链球菌表面蛋白PAc A区,没有天然蛋白质抗原的构象,因此必须联合应用CTB免疫佐剂来增强免疫防龋效果。
转基因番茄防龋疫苗:以分子生物学技术为基础,将致龋病原微生物具有免疫原性及免疫反应性的外源性基因序列植入番茄基因组,使其稳定表达出目的基因及免疫活性蛋白,当被摄入人或动物体内后激发全身免疫系统及体液免疫系统产生对致龋病原菌的免疫能力。其为下一步研发新型可食性转基因植物口服防龋疫苗提供理论支持。
背景:转基因植物可食性疫苗是以植物作为载体,将外源性基因整合到植物基因组当中,进一步激活动物或人体免疫系统以获得特异性免疫能力。但外源性基因的持续低表达量一直无法达到满意的免疫效果。
目的:用分子生物学技术检测转基因番茄植株中pacA-ctxB融合基因表达及目的蛋白的表达量,为进一步观察可食用防龋疫苗的防龋效果提供研究基础。
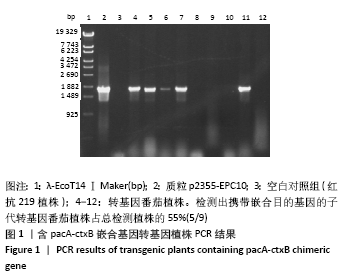
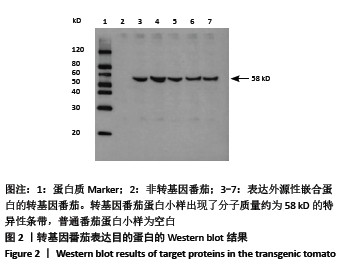
方法:①提取转基因番茄叶片总DNA,PCR检测外源性融合基因pacA-ctxB,实验分组3组:阳性对照组为质粒p2355-EPC10;空白对照组为普通番茄1株(红抗219);转基因组为转基因番茄9株;②BCA法检测转基因番茄果肉中总蛋白的水平;Western blot证实转基因番茄果实中PAcA/CTB目的蛋白的表达,目的蛋白检测分组2组:转基因组为表达外源性嵌合基因的转基因番茄5株(PCR检测阳性);空白对照组为普通番茄1株;酶联免疫吸附实验(ELISA)法检测转基因番茄果实中PAcA/CTB目的蛋白浓度。
结果与结论:①PCR扩增结果可见9株转基因番茄中有5株出现约 1.7 kb 特异性扩增条带,占总检测植株的55%;②转基因番茄总蛋白为3.15 g/L;Western blot可见PCR检测为阳性的转基因番茄蛋白提取样本在分子质量约为58 kD处均出现了高密度条带,非转基因番茄蛋白样本未见特异条带;ELISA 测得目的蛋白表达量约4.12 mg/L,占番茄可溶性总蛋白的 0.13%;③结果说明,外源性融合基因pacA-ctxB能够在番茄植株中表达及产生目的蛋白。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7238-9372 (关薇薇)
中图分类号: