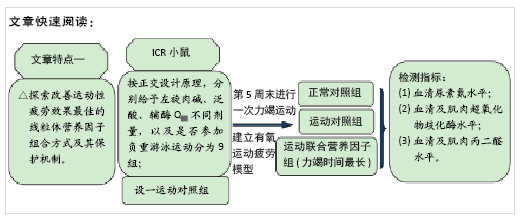
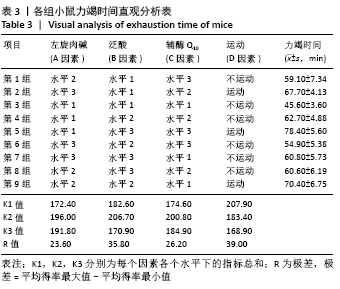
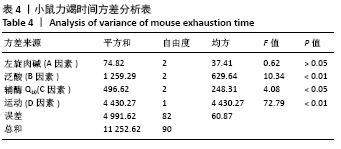
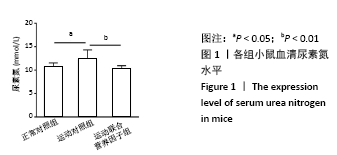
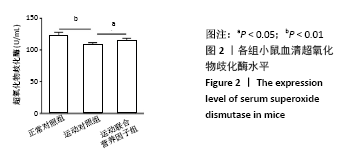
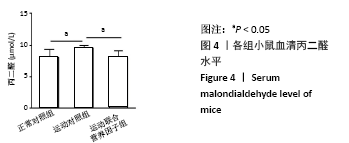
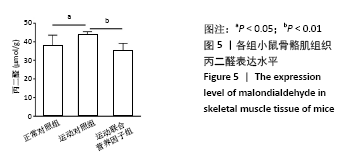
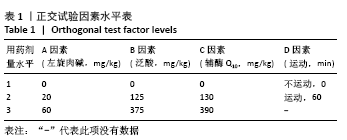
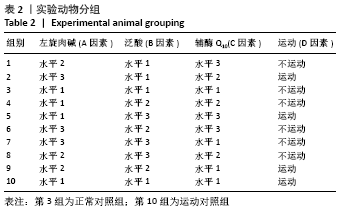
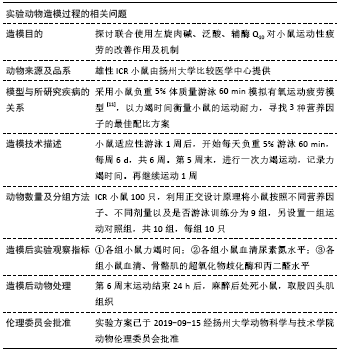
[1] 张蕴琨,丁树哲. 运动生物化学[M]. 北京:高等教育出版社, 2014:7.
[2] GNONI A, LONGO S, GNONI GV, et al. Carnitine in Human Muscle Bioenergetics: Can Carnitine Supplementation Improve Physical Exercise?. Molecules. 2020;25(1):182.
[3] SMITH CM,SONG WO. Comparative nutrition of pantothenic acid. J Nutr Biochem. 1996;7(6):312-321.
[4] MA Q, LIANG M, TANG X, et al. Vitamin B5 inhibit RANKL induced osteoclastogenesis and ovariectomy induced osteoporosis by scavenging ROS generation. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(8):5008-5018.
[5] SM S, HN S, NA E, et al. Curative role of pantothenic acid in brain damage of gamma irradiated rats. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2018;33(3): 314-321.
[6] BHAGAVAN HN, CHOPRA RK. Coenzyme Q10: Absorption, tissue uptake, metabolism and pharmacokinetics. Free Radic Res. 2006;40:445-453.
[7] 曹玉音,陈迎玉,王晖,等. 辅酶Q10在活性氧相关疾病中应用研究进展[J]. 实用医学杂志,2018,34(20):3482-3485.
[8] 耿爱莲,李保明,呙于明. L-肉碱与辅酶Q_(10)添加对腹水症肉鸡心肌细胞凋亡及抗氧化能力的影响[J]. 中国农业大学学报,2007, 12(2):21-26.
[9] 胡志刚,周蕾,丁树哲. 联合补充乙酰左旋肉碱和α-硫辛酸对耐力训练大鼠骨骼肌线粒体通透性转运孔开放的影响[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2009,28(5):564-566+569.
[10] VARGIU R, LICHERI D, CARCASSI AM, et al. Enhancement of muscular performance by a coformulation of propionyl-L-carnitine, coenzyme Q10, nicotinamide, riboflavin and pantothenic acid in the rat. Physiol Behav. 2002;76(2):257-263.
[11] XIE Y, LI Z, WANG Y, et al. Effects of moderate-versus high-intensity swimming training on inflammatory and CD4+T cell subset profiles in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice. J Neuroimmunol. 2019;328:60-67.
[12] BRUNO A, WELCH JF, GEARY CM, et al. Temporal characteristics of exercise- induced diaphragmatic fatigue. J Appl Physio. 2018;124(4): 906- 914.
[13] LI W, ZHANG R, GUO J, et al. Protective effect of R. glutinosa oligosaccharides against high L-carnitine diet-induced endothelial dysfunction and hepatic injury in mice. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016; 85:285-293.
[14] BARNETT C, COSTILL DL, VUKOVICH MD, et al. Effect of L-carnitine supplementation on muscle and blood carnitine content and lactate accumulation during high-intensity sprint cycling. Int J Sport Nutr. 1994;4(3):280-288.
[15] VUKOVICH MD, COSTILL DL, FINK WJ. Carnitine supplementation: effect on muscle carnitine and glycogen content during exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1994;26(9):1122-1129.
[16] BRASS EP. Supplemental carnitine and exercise. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000; 72(2 Suppl): 618S-623S.
[17] DEMIRCI B, DEMIR O, DOST T, et al. Protective effect of vitamin B5 (dexpanthenol) on cardiovascular damage induced by streptozocin in rats. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2014;115(4):190-196.
[18] SLYSHENKOV VS, DYMKOWSKA D, WOJTCZAK L. Pantothenic acid and pantothenol increase biosynthesis of glutathione by boosting cell energetics. FEBS Lett. 2004;569(1-3):169-172.
[19] WOJTCZAK L, SLYSHENKOV VS. Protection by pantothenic acid against apoptosis and cell damage by oxygen free radicals--the role of glutathione. Biofactors. 2003;17(1-4):61-73.
[20] EBNER F, HELLER A, RIPPKE F, et al. Topical use of dexpanthenol in skin disorders. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2002;3(6):427-433.
[21] TARDY AL, POUTEAU E, MARQUEZ D, et al. Vitamins and Minerals for Energy, Fatigue and Cognition: A Narrative Review of the Biochemical and Clinical Evidence. Nutrients. 2020;12(1):228.
[22] TANG J, ZHANG B, LIANG S, et al. Effects of pantothenic acid on growth performance and antioxidant status of growing male white Pekin ducks. Poult Sci. 2020;99(9):4436-4441.
[23] SARMIENTO A, DIAZ-CASTRO J, PULIDO-MORAN M, et al. Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation and Exercise in Healthy Humans: A Systematic Review. Curr Drug Metab. 2016;17(4):345-358.
[24] BELVIRANLı M, OKUDAN N. Effect of Coenzyme Q10 Alone and in Combination with Exercise Training on Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Rats. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2018;88(3-4):126-136.
[25] Çelik B, Sağıroğlu AA, Özdemir S. Design, optimization and characterization of coenzyme Q10- and D-panthenyl triacetate-loaded liposomes. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017;12:4869-4878.
[26] Wang Y, Branicky R, Noë A, et al. Superoxide dismutases: Dual roles in controlling ROS damage and regulating ROS signaling. J Cell Biol. 2018;217(6):1915-1928.
[27] Spirlandeli AL, Deminice R, Jordao AA. Plasma malondialdehyde as biomarker of lipid peroxidation: effects of acute exercise. Int J Sports Med. 2014;35(1):14-18. |