中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (19): 3074-3079.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1253
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
过度疲劳状态模型大鼠心脏功能及心肌细胞凋亡调控因子的变化
徐 文,钱 钰,殷 劲
- (成都体育学院附属体育医院,四川省成都市 610041)
Changes of cardiac function and myocardial apoptosis regulatory factors in rat models of excessive fatigue
Xu Wen, Qian Yu, Yin Jin
- (Sports Hospital Affiliated to Chengdu Sports Institute, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
超量恢复:运动时消耗的能源物质及各器官、系统的功能恢复得超过原有的水平,该现象称为超量恢复。超量恢复保持一段时间后又回到原有水平。
超量恢复区间:糖酵解供能的“真假超量区间”理论认为,在周期性训练中,内脏器官、糖酵解供能能力、应激及运动能力等存在正叠加[(1-5)×36 h]区间,正、负叠加转折点第[(6)×36 h]区间、负叠加[(7-9) ×36 h]区间的过程。
.jpg)
文题释义:
超量恢复:运动时消耗的能源物质及各器官、系统的功能恢复得超过原有的水平,该现象称为超量恢复。超量恢复保持一段时间后又回到原有水平。
超量恢复区间:糖酵解供能的“真假超量区间”理论认为,在周期性训练中,内脏器官、糖酵解供能能力、应激及运动能力等存在正叠加[(1-5)×36 h]区间,正、负叠加转折点第[(6)×36 h]区间、负叠加[(7-9) ×36 h]区间的过程。
摘要
背景:力竭运动是超出人或动物生理极限的运动,强烈的运动刺激会打破机体原有的稳态,从而引起一系列应激反应,过度应激会出现损伤和功能异常。
目的:通过大鼠心肌细胞运动性疲劳模型分析导致运动性心脏猝死的相关因素。
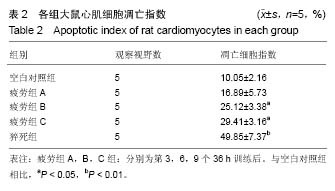
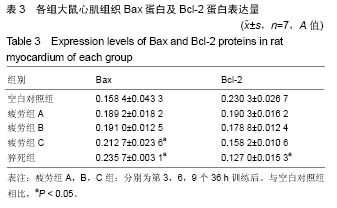
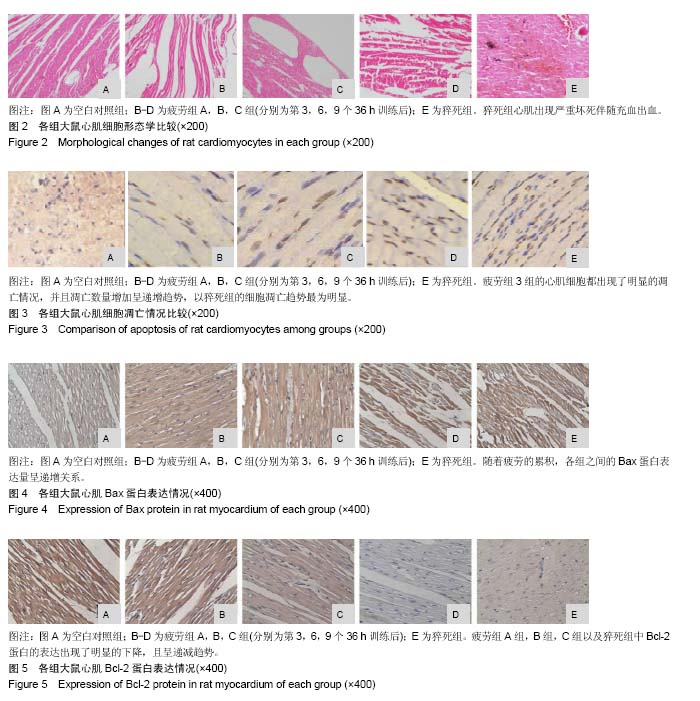
方法:130只SD大鼠购自成都达硕生物科技公司。随机选取7只大鼠作为空白组对照,其余大鼠为疲劳模型,对大鼠进行游泳训练,每36 h训练1次,连续训练致过度疲劳。建模成功后出现超量恢复的负叠加状态即为过度疲劳状态,并分别训练3×36 h,6×36 h,9×36 h后,随机处死各7只大鼠,分别记录为疲劳组 A组,疲劳组B组和疲劳组C组;训练过程中或训练结束24 h死亡的大鼠(排除因呛水死亡的大鼠)记为运动性猝死组。TUNEL法检测大鼠心肌细胞凋亡;免疫组织化学方法心肌组织Bax、Bcl-2表达;苏木精-伊红染色观察细胞形态变化。
结果与结论:①在猝死组中,心肌纤维与其余组相比较为纤细,部分肌纤维出现断裂,血管极度扩张,心肌出现严重坏死伴随充血出血;②疲劳组及猝死组心肌细胞凋亡指数、心肌细胞凋亡数量都出现明显的增长(P < 0.05);③当处于过度疲劳状态时,大鼠心脏组织中的促凋亡蛋白数量明显增加(P < 0.05),抑制凋亡蛋白Bcl-2表达明显下降(P < 0.01);④结果提示,连续训练而导致大鼠处于过度疲劳状态,会引发大鼠心肌细胞形态结构方面的变化,甚至导致损害,此时心肌组织中所含有的Bcl-2和Bax蛋白会出现异常表达情况。由于心肌细胞受到损害而导致心肌细胞凋亡,数量明显减少,进而影响整体心脏的结构以及功能,最终导致心源性运动性猝死。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-2488-6534(徐文)
背景:力竭运动是超出人或动物生理极限的运动,强烈的运动刺激会打破机体原有的稳态,从而引起一系列应激反应,过度应激会出现损伤和功能异常。
目的:通过大鼠心肌细胞运动性疲劳模型分析导致运动性心脏猝死的相关因素。
方法:130只SD大鼠购自成都达硕生物科技公司。随机选取7只大鼠作为空白组对照,其余大鼠为疲劳模型,对大鼠进行游泳训练,每36 h训练1次,连续训练致过度疲劳。建模成功后出现超量恢复的负叠加状态即为过度疲劳状态,并分别训练3×36 h,6×36 h,9×36 h后,随机处死各7只大鼠,分别记录为疲劳组 A组,疲劳组B组和疲劳组C组;训练过程中或训练结束24 h死亡的大鼠(排除因呛水死亡的大鼠)记为运动性猝死组。TUNEL法检测大鼠心肌细胞凋亡;免疫组织化学方法心肌组织Bax、Bcl-2表达;苏木精-伊红染色观察细胞形态变化。
结果与结论:①在猝死组中,心肌纤维与其余组相比较为纤细,部分肌纤维出现断裂,血管极度扩张,心肌出现严重坏死伴随充血出血;②疲劳组及猝死组心肌细胞凋亡指数、心肌细胞凋亡数量都出现明显的增长(P < 0.05);③当处于过度疲劳状态时,大鼠心脏组织中的促凋亡蛋白数量明显增加(P < 0.05),抑制凋亡蛋白Bcl-2表达明显下降(P < 0.01);④结果提示,连续训练而导致大鼠处于过度疲劳状态,会引发大鼠心肌细胞形态结构方面的变化,甚至导致损害,此时心肌组织中所含有的Bcl-2和Bax蛋白会出现异常表达情况。由于心肌细胞受到损害而导致心肌细胞凋亡,数量明显减少,进而影响整体心脏的结构以及功能,最终导致心源性运动性猝死。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-2488-6534(徐文)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg) #br#
文题释义:#br#
超量恢复:运动时消耗的能源物质及各器官、系统的功能恢复得超过原有的水平,该现象称为超量恢复。超量恢复保持一段时间后又回到原有水平。#br#
超量恢复区间:糖酵解供能的“真假超量区间”理论认为,在周期性训练中,内脏器官、糖酵解供能能力、应激及运动能力等存在正叠加[(1-5)×36 h]区间,正、负叠加转折点第[(6)×36 h]区间、负叠加[(7-9) ×36 h]区间的过程。
#br#
文题释义:#br#
超量恢复:运动时消耗的能源物质及各器官、系统的功能恢复得超过原有的水平,该现象称为超量恢复。超量恢复保持一段时间后又回到原有水平。#br#
超量恢复区间:糖酵解供能的“真假超量区间”理论认为,在周期性训练中,内脏器官、糖酵解供能能力、应激及运动能力等存在正叠加[(1-5)×36 h]区间,正、负叠加转折点第[(6)×36 h]区间、负叠加[(7-9) ×36 h]区间的过程。