中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (14): 2211-2216.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2531
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
大鼠肝脏冷缺血再灌注损伤时姜黄素后处理对肝细胞凋亡的影响
邹海波,施 鹏,孙晓峰
- 沈阳医学院附属中心医院,辽宁省沈阳市 110000
Effects of curcumin post-conditioning on hepatocyte apoptosis in rats with liver cold ischemia/reperfusion injury
Zou Haibo, Shi Peng, Sun Xiaofeng
- Affiliated Central Hospital of Shenyang Medical College, Shenyang 110000, Liaoning Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
姜黄素:是从姜科、南星科一些植物根茎中提取的一种化学成分,具有抗氧化应激、抑制炎症细胞因子释放、抗细胞凋亡等广泛的药理活性。
冷缺血再灌注:从冷缺血开始至器官重新恢复血供的时间间隔(整个过程器官都在低温环境中)称为冷缺血时间,随后发生的器官恢复血液供应,即是冷缺血再灌注。
背景:姜黄素预处理可减轻肢体缺血再灌注对肝脏的损伤,但姜黄素后处理对肝脏冷缺血再灌注损伤是否有保护作用及其机制目前研究甚少。
目的:探讨大鼠肝脏冷缺血再灌注损伤时姜黄素后处理对肝细胞凋亡的影响。
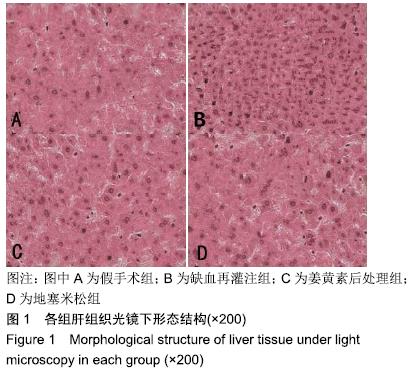
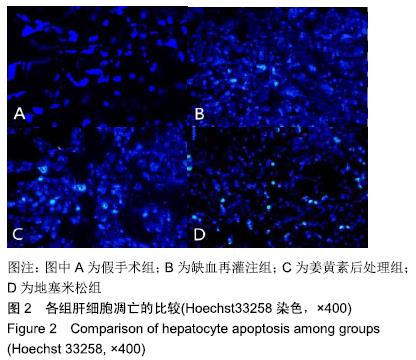
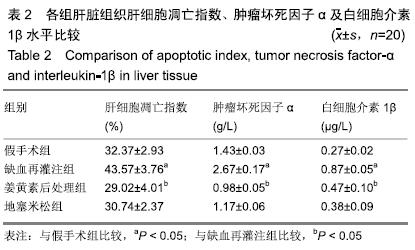
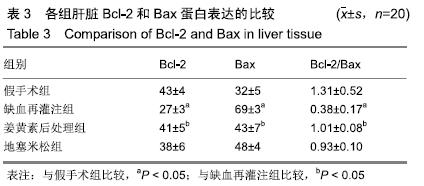
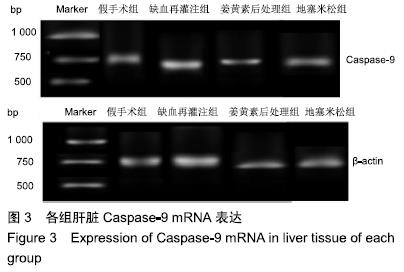
方法:选取成年雄性SD大鼠80只,采用随机数字表法将其分成4组(n=20):假手术组、冷缺血再灌注组、姜黄素后处理组、地塞米松组。使肝脏血流处于完全阻断状态,随后以脾静脉作为流入道和右肾上腺静脉作为流出道注入0 ℃复方乳酸林格液,冷灌注30 min;停止冷灌注后,结扎近端脾静脉和右肾上腺静脉,切除脾脏,随即恢复肝脏血流,完成制作冷缺血再灌注模型。在大鼠冷缺血30 min后,姜黄素后处理组经尾静脉注射姜黄素60 mg/kg,地塞米松组尾静脉注射地塞米松0.5 mg/kg,其他组以等量的生理盐水替代。再灌注6 h时经下腔静脉取血,检测血清天门冬氨酸氨基转移酶、丙氨酸转移酶水平,随后处死大鼠,取肝组织检测丙二醛水平;采用苏木精-伊红染色观察肝脏病理变化;Hoechst33258染色法检测肝细胞凋亡指数;Western blot检测肝组织Bcl-2和Bax蛋白表达;RT-PCR检测肝组织促细胞凋亡基因Caspase-9 mRNA表达;ELISA检测肝组织肿瘤坏死因子α及白细胞介素1β水平。
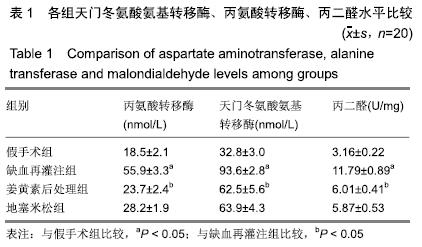
结果与结论:①与假手术组比较,冷缺血再灌注组天门冬氨酸氨基转移酶、丙氨酸转移酶、丙二醛和凋亡指数明显升高(P < 0.05);苏木精-伊红染色切片可见肝血窦内有大量炎性细胞浸润,肝细胞嗜酸性变,胞浆内疏松化,肝细胞呈气球样变,偶可见斑片状坏死,散在点状坏死灶;Bcl-2表达下降,Bax表达明显升高(P < 0.05);Caspase-9 mRNA表达、肿瘤坏死因子α及白细胞介素1β水平明显升高(P < 0.05);②与冷缺血再灌注组比较, 姜黄素后处理组天门冬氨酸氨基转移酶、丙氨酸转移酶、丙二醛和凋亡指数明显下降(P < 0.05);苏木精-伊红染色可见肝血窦内炎性浸润明显减轻,胞浆嗜酸性变和气球样变的肝细胞明显减少,但偶可见少量散在的点状坏死;Bcl-2表达升高,Bax表达明显下降(P < 0.05);Caspase-9 mRNA表达、肿瘤坏死因子α及白细胞介素1β水平明显下降(P < 0.05);③姜黄素后处理组上述各指标与地塞米松组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);④综上所述,姜黄素后处理可减轻大鼠肝脏冷缺血再灌注损伤,其作用机制可能通过上调Bcl-2/Bax比值,抑制凋亡启动子Caspase-9 mRNA的表达,减少炎性因子肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β的释放,发挥抗凋亡的肝保护作用。
ORCID: 0000-0002-8442-8113(邹海波)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: