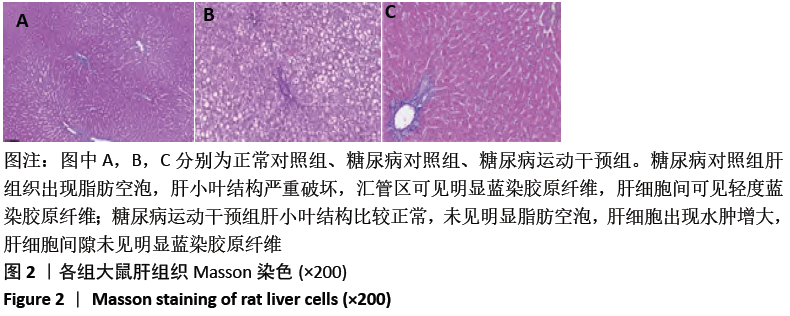
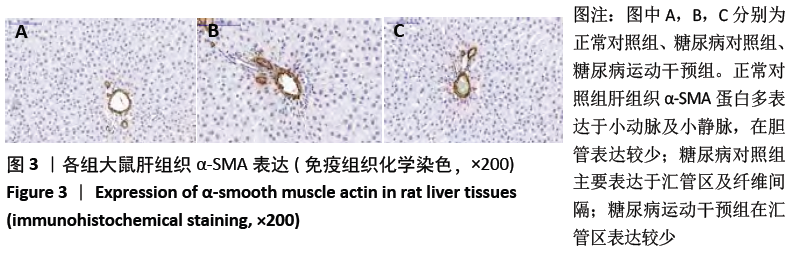
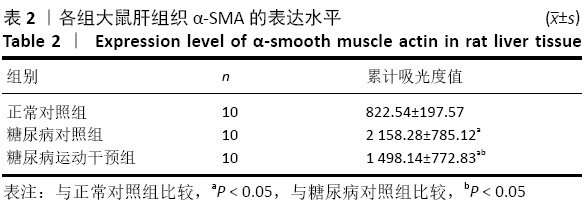
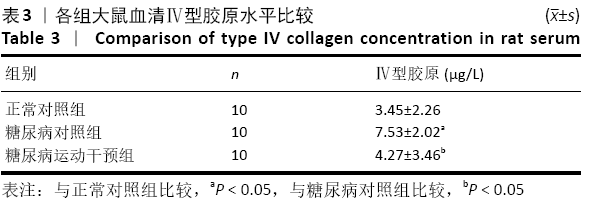
[1] GUO R, WU Z, JIANG J, et al. New mechanism of lipotoxicity in diabetic cardiomyopathy: Deficiency of Endogenous H2S Production and ER stress. Mech Ageing Dev. 2017;162:46-52.
[2] KATSURA E, ICHIKAWA T, TAURA N, et al. Elevated Fasting Plasma Glucose before Liver Transplantation is Associated with Lower Post-Transplant Survival. Med Sci Monit. 2016;22:4707-4715.
[3] 中华医学会糖尿病学分会.中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2017年版)[J].中华糖尿病杂志,2018,10(1):4-67.
[4] BELLENTANI S, SCAGLIONI F, MARINO M, et al. Epidemiology of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig Dis. 2010;28(1):155-161.
[5] BEDFORD TG, TIPTON CM, WILSON NC, et al. Maximum oxygen consumption of rats and its changes with various experimental procedures. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979;47(6): 1278-1283.
[6] 马晓雯,常芸,王世强,等.长期耐力训练对大鼠心肌细胞自噬相关 因子Beclin1和LC3的影响[J]. 体育科学,2016,36(2):66-71.
[7] TIAN F, ZHANG YJ, LI Y, et al. Celecoxib ameliorates non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in type 2 diabetic rats via suppression of the non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway expression. PLoS One. 2014;9(1): e83819.
[8] 沈婕,夏新新,邹俊杰,等.通络方剂治疗糖尿病性肝损伤的疗效及其可能机制[J].第二军医大学学报,2010,31(5):499-503.
[9] 徐国琴,林文弢,翁锡全,等.急性有氧运动对糖尿病大鼠肝脏和胰腺内质网应激蛋白和血糖的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2012, 31(7):583-589.
[10] KHAN S, JENA G. Sodium butyrate reduces insulin-resistance, fat accumulation and dyslipidemia in type-2 diabetic rat: A comparative study with metformin. Chem Biol Interact. 2016;254:124-134.
[11] GARABADU D, KRISHNAMURTHY S. Metformin attenuates hepatic insulin resistance in type-2 diabetic rats through PI3K/Akt/GLUT-4 signalling independent to bicuculline-sensitive GABAA receptor stimulation. Pharm Biol. 2017;55(1):722-728.
[12] 江洪.不同运动强度干预2型糖尿病模型大鼠的骨密度变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(27): 3963-3969.
[13] 魏占英,沈丽,冯晓慧,等.高脂饲料喂养时间和STZ剂量对建立2型糖尿病大鼠模型的影响[J].医学研究杂志,2014,43(2):42-46.
[14] 孙焕,陈广,陆付耳.介绍几种诱发性糖尿病动物模型[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2007,13(2): 65-68.
[15] MATSUNAMI T, SATO Y, ARIGA S, et al. Regulation of oxidative stress and inflammation by hepatic adiponectin receptor 2 in an animal model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2010;3(5):472-481.
[16] 柳占彪,李玉红,张少卓,等.糖脂清对高脂血症家兔糖脂代谢及肝组织的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2011,17(15):135-138.
[17] 荆西民,岳静静,吴卫东,等.有氧运动对非酒精性脂肪肝大鼠肝组织AMPK蛋白活性的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2015,34(7): 653-657.
[18] 翁锡全,徐国琴,林文弢,等.不同运动强度对糖尿病大鼠血清骨代谢生化指标的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2009,28(5):522-525.
[19] 陈璐璐,肖方喜.胰岛素抵抗与非酒精性脂肪性肝病[J].临床内科杂志,2008,25(11):725-727.
[20] KISTLER KD, BRUNT EM, CLARK JM, et al. Physical activity recommendations, exercise intensity, and histological severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011;106(3): 460-468; quiz 469.
[21] HORIUCHI S. The liver is the main site for metabolism of circulating advanced glycation end products. J Hepatol. 2002;36(1):123-125.
[22] 王付.四逆散加味辨治肝纤维化的探索与实践[J].中医药通报, 2011,10(6): 29-30.
[23] PERSEGHIN G, LATTUADA G, DE COBELLI F, et al. Habitual physical activity is associated with intrahepatic fat content in humans. Diabetes Care. 2007;30(3):683-688.
[24] 冷超,李大威,李强.不同强度的运动联合葛根素对非酒精性脂肪肝大鼠模型的治疗及其机制研究[J].中华中医药学刊,2018,36(2): 452-455.
[25] 展玉涛,陈颖伟.肝星状细胞与肝纤维化[J].临床肝胆病杂志,2000, 16(2): 71-73.
[26] SAFADI R, FRIEDMAN SL. Hepatic fibrosis-role of hepatic stellate cell activation. MedGenMed. 2002;4(3):27.
[27] PARADIS V, PERLEMUTER G, BONVOUST F, et al. High glucose and hyperinsulinemia stimulate connective tissue growth factor expression: a potential mechanism involved in progression to fibrosis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2001;34(4 Pt 1):738-744. |
 文题释义:
文题释义: