中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (19): 3080-3089.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1254
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
不同培养基与饲养细胞组合对多房棘球绦虫体外培养模型的影响
韩振阳,邓 子,王泽宇,张示杰
- (石河子大学医学院第一附属医院肝胆外科,新疆维吾尔自治区石河子市 832000)
Effects of different culture media and feeder cells on the culture of Echinococcus multilocularis in vitro
Han Zhenyang, Deng Zi, Wang Zeyu, Zhang Shijie
- (Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of School of Medicine, Shihezi University, Shihezi 832000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
多房棘球绦虫体外培养模型:指通过使用各种方法在体外模拟多房棘球绦虫生长环境,使其在体外完成整个生长发育全过程,主要由最初有宿主成分干扰的“组织碎片培养模型、胶原蛋白膜培养模型及大规模液体培养模型”发展到“无宿主成分干扰培养模型”以及最新的“原代细胞培养模型”几种方式构成。
泡状棘球蚴病:是由多房棘球绦虫寄生于人体引发的一种人兽共患病,该病起病隐匿,潜伏期长,发展迅速,呈侵润性增殖,被发现时一般都处在疾病晚期。
.jpg)
文题释义:
多房棘球绦虫体外培养模型:指通过使用各种方法在体外模拟多房棘球绦虫生长环境,使其在体外完成整个生长发育全过程,主要由最初有宿主成分干扰的“组织碎片培养模型、胶原蛋白膜培养模型及大规模液体培养模型”发展到“无宿主成分干扰培养模型”以及最新的“原代细胞培养模型”几种方式构成。
泡状棘球蚴病:是由多房棘球绦虫寄生于人体引发的一种人兽共患病,该病起病隐匿,潜伏期长,发展迅速,呈侵润性增殖,被发现时一般都处在疾病晚期。
摘要
背景:多房棘球绦虫原头节的体外成囊培养是提取与研究其生发层干细胞的实验基础。D-MEM与RPMI-1640是最适宜用于泡球蚴体外培养的商业培养基,HeLa细胞与大鼠肝癌细胞(ATCC No. CRL-1600)也是常用饲养细胞。
目的:构建多房棘球绦虫体外培养模型,观察泡球蚴在不同饲养细胞[HeLa细胞与大鼠肝癌细胞(ATCC No.CRL-1600)]及含有体积分数10%胎牛血清的不同培养基[D-MEM(高/低糖型)与RPMI-1640]下生长情况。
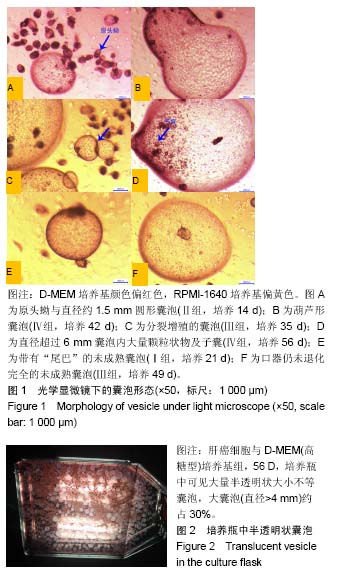
方法:预先培养HeLa细胞及大鼠肝癌细胞(ATCC No.CRL-1600),从新疆石河子大学第一附属院实验动物中心提供的感染多房棘球绦虫6个月以上的种鼠体内提取原头节后分别与不同饲养细胞及培养基体外共同培养。实验经石河子大学医学院第一附属医院医学伦理委员会批准,批准号:2015-018-01,批准时间:2017-04-07。实验根据饲养细胞与培养基组合分为6组,每组加入1×106饲养细胞与50 mL含体积分数10%胎牛血清的培养基及5 000个原头节,Ⅰ组:HeLa细胞与1640培养基培养;Ⅱ组:HeLa细胞与D-MEM(高糖型)培养基培养;Ⅲ组:大鼠肝癌细胞与1640培养基培养;Ⅳ组:大鼠肝癌细胞与D-MEM(高糖型)培养基培养;Ⅴ组:HeLa细胞与D-MEM(低糖型)培养基培养;Ⅵ组:大鼠肝癌细胞与D-MEM(低糖型)培养基培养,观察泡球蚴原头节的生存、生长和发育,每隔7 d计算原头蚴成囊率,使用目镜测微尺测量囊泡平均直径大小。
结果与结论:①原头蚴在6种组合中均可长期存活,大部分都形成囊泡,囊泡直径分布在1-6 mm;②培养第56天原头蚴成囊率和囊泡平均直径均为大鼠肝癌细胞与D-MEM(高糖型)培养基组效果最佳(P < 0.05),成囊率(72.08±1.79)%,囊泡平均直径(3.379±0.199) mm;③囊泡囊液蛋白定量检测结果显示6组囊液蛋白含量均低于体内囊泡,Ⅳ组蛋白含量高于其他5组(P < 0.05);④结果证实:同条件下D-MEM(高糖型)培养基囊泡大小与数量优于其他2种培养基。大鼠肝癌细胞(ATCC No.CRL-1600)作为饲养细胞囊泡大小与数量优于HeLa细胞。D-MEM(高糖型)与大鼠肝癌细胞(ATCC No.CRL-1600)共同作用的环境下原头蚴生长发育的成囊率及囊泡大小最佳,可作为体外培养泡球蚴原头蚴获得囊泡的最优选择。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-8307-8978(韩振阳)
背景:多房棘球绦虫原头节的体外成囊培养是提取与研究其生发层干细胞的实验基础。D-MEM与RPMI-1640是最适宜用于泡球蚴体外培养的商业培养基,HeLa细胞与大鼠肝癌细胞(ATCC No. CRL-1600)也是常用饲养细胞。
目的:构建多房棘球绦虫体外培养模型,观察泡球蚴在不同饲养细胞[HeLa细胞与大鼠肝癌细胞(ATCC No.CRL-1600)]及含有体积分数10%胎牛血清的不同培养基[D-MEM(高/低糖型)与RPMI-1640]下生长情况。
方法:预先培养HeLa细胞及大鼠肝癌细胞(ATCC No.CRL-1600),从新疆石河子大学第一附属院实验动物中心提供的感染多房棘球绦虫6个月以上的种鼠体内提取原头节后分别与不同饲养细胞及培养基体外共同培养。实验经石河子大学医学院第一附属医院医学伦理委员会批准,批准号:2015-018-01,批准时间:2017-04-07。实验根据饲养细胞与培养基组合分为6组,每组加入1×106饲养细胞与50 mL含体积分数10%胎牛血清的培养基及5 000个原头节,Ⅰ组:HeLa细胞与1640培养基培养;Ⅱ组:HeLa细胞与D-MEM(高糖型)培养基培养;Ⅲ组:大鼠肝癌细胞与1640培养基培养;Ⅳ组:大鼠肝癌细胞与D-MEM(高糖型)培养基培养;Ⅴ组:HeLa细胞与D-MEM(低糖型)培养基培养;Ⅵ组:大鼠肝癌细胞与D-MEM(低糖型)培养基培养,观察泡球蚴原头节的生存、生长和发育,每隔7 d计算原头蚴成囊率,使用目镜测微尺测量囊泡平均直径大小。
结果与结论:①原头蚴在6种组合中均可长期存活,大部分都形成囊泡,囊泡直径分布在1-6 mm;②培养第56天原头蚴成囊率和囊泡平均直径均为大鼠肝癌细胞与D-MEM(高糖型)培养基组效果最佳(P < 0.05),成囊率(72.08±1.79)%,囊泡平均直径(3.379±0.199) mm;③囊泡囊液蛋白定量检测结果显示6组囊液蛋白含量均低于体内囊泡,Ⅳ组蛋白含量高于其他5组(P < 0.05);④结果证实:同条件下D-MEM(高糖型)培养基囊泡大小与数量优于其他2种培养基。大鼠肝癌细胞(ATCC No.CRL-1600)作为饲养细胞囊泡大小与数量优于HeLa细胞。D-MEM(高糖型)与大鼠肝癌细胞(ATCC No.CRL-1600)共同作用的环境下原头蚴生长发育的成囊率及囊泡大小最佳,可作为体外培养泡球蚴原头蚴获得囊泡的最优选择。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-8307-8978(韩振阳)
中图分类号:
.jpg) #br#
文题释义:#br#
多房棘球绦虫体外培养模型:指通过使用各种方法在体外模拟多房棘球绦虫生长环境,使其在体外完成整个生长发育全过程,主要由最初有宿主成分干扰的“组织碎片培养模型、胶原蛋白膜培养模型及大规模液体培养模型”发展到“无宿主成分干扰培养模型”以及最新的“原代细胞培养模型”几种方式构成。#br#
泡状棘球蚴病:是由多房棘球绦虫寄生于人体引发的一种人兽共患病,该病起病隐匿,潜伏期长,发展迅速,呈侵润性增殖,被发现时一般都处在疾病晚期。
#br#
文题释义:#br#
多房棘球绦虫体外培养模型:指通过使用各种方法在体外模拟多房棘球绦虫生长环境,使其在体外完成整个生长发育全过程,主要由最初有宿主成分干扰的“组织碎片培养模型、胶原蛋白膜培养模型及大规模液体培养模型”发展到“无宿主成分干扰培养模型”以及最新的“原代细胞培养模型”几种方式构成。#br#
泡状棘球蚴病:是由多房棘球绦虫寄生于人体引发的一种人兽共患病,该病起病隐匿,潜伏期长,发展迅速,呈侵润性增殖,被发现时一般都处在疾病晚期。