| [1] Hoenicka M, Schrammel S, Bursa J, et al. Development of endothelium-denuded human umbilical veins as living scaffolds for tissue-engineered small-calibre vascular grafts. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2013;7(4):324-336. [2] Seifu DG, Purnama A, Mequanint K, et al. Small-diameter vascular tissue engineering. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2013; 10(7): 410-421. [3] Desai M, Seifalian AM, Hamilton G. Role of prosthetic conduits in coronary artery bypass grafting. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2011;40(2):394-398. [4] Huang AH, Niklason LE. Engineering of arteries in vitro. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014;71(11):2103-2118. [5] Quint C, Kondo Y, Manson RJ, et al. Decellularized tissue-engineered blood vessel as an arterial conduit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(22):9214-9219. [6] Cebotari S, Tudorache I, Ciubotaru A, et al. Use of fresh decellularized allografts for pulmonary valve replacement may reduce the reoperation rate in children and young adults: early report. Circulation. 2011;124(11 Suppl):S115-S123. [7] Badylak SF, Weiss DJ, Caplan A, et al. Engineered whole organs and complex tissues. Lancet. 2012;379(9819): 943-952. [8] 蒲磊,吴剑,孟明耀,等.不同脱细胞方案制备主动脉细胞外基质支架的比较研究[Z].2014:28,1413-1421.[9] Bouten CV, Dankers PY, Driessen-Mol A, et al. Substrates for cardiovascular tissue engineering. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2011;63(4-5):221-241. [10] Conklin BS, Richter ER, Kreutziger KL, et al. Development and evaluation of a novel decellularized vascular xenograft. Med Eng Phys. 2002;24(3):173-183. [11] Gilbert T, Sellaro T, Badylak S. Decellularization of tissues and organs. Biomaterials. 2006;27(19):3675-3683. [12] Knight RL, Wilcox HE, Korossis SA, et al. The use of acellular matrices for the tissue engineering of cardiac valves. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2008;222(1):129-143. [13] Schoen FJ, Levy RJ. Calcification of tissue heart valve substitutes: progress toward understanding and prevention. Ann Thorac Surg. 2005;79(3):1072-1080. [14] Keane TJ, Londono R, Turner NJ, et al. Consequences of ineffective decellularization of biologic scaffolds on the host response. Biomaterials. 2012;33(6):1771-1781. [15] Wilczek P, Lesiak A, Niemiec-Cyganek A, et al. Biomechanical properties of hybrid heart valve prosthesis utilizing the pigs that do not express the galactose-alpha-1, 3-galactose(alpha-Gal) antigen derived tissue and tissue engineering technique. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2015;26(1): 5329. [16] Böer U, Lohrenz A, Klingenberg M, et al. The effect of detergent-based decellularization procedures on cellular proteins and immunogenicity in equine carotid artery grafts. Biomaterials. 2011;32(36):9730-9737. [17] Böeer U, Buettner FF, Klingenberg M, et al. Immunogenicity of intensively decellularized equine carotid arteries is conferred by the extracellular matrix protein collagen type VI. PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e105964. [18] Naso F, Gandaglia A, Iop L, et al. First quantitative assay of alpha-Gal in soft tissues: presence and distribution of the epitope before and after cell removal from xenogeneic heart valves. Acta Biomater. 2011;7(4):1728-1734. [19] Naso F, Gandaglia A, Iop L, et al. Alpha-Gal detectors in xenotransplantation research: a word of caution. Xenotransplantation. 2012;19(4):215-220. [20] 员海超,蒲春晓,魏强,等.组织工程细胞外基质材料研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2012,6(10):1251-1254.[21] Faulk DM, Carruthers CA, Warner HJ, et al. The effect of detergents on the basement membrane complex of a biologic scaffold material. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(1):183-193. [22] Venkatasubramanian RT, Wolkers WF, Shenoi MM, et al. Freeze-thaw induced biomechanical changes in arteries: role of collagen matrix and smooth muscle cells. Ann Biomed Eng. 2010;38(3):694-706. [23] Crapo PM, Wang Y. Physiologic compliance in engineered small-diameter arterial constructs based on an elastomeric substrate. Biomaterials. 2010;31(7):1626-1635. [24] Murase Y, Narita Y, Kagami H, et al. Evaluation of compliance and stiffness of decellularized tissues as scaffolds for tissue-engineered small caliber vascular grafts using intravascular ultrasound. ASAIO J. 2006;52(4):450-455. |
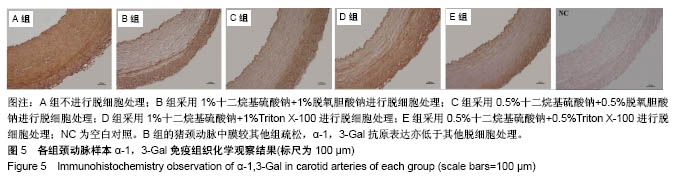
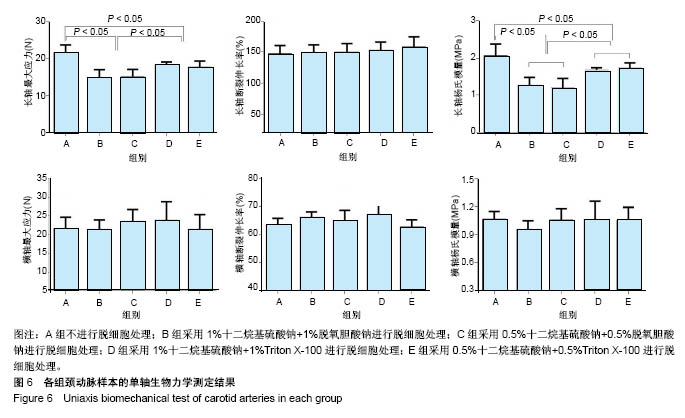
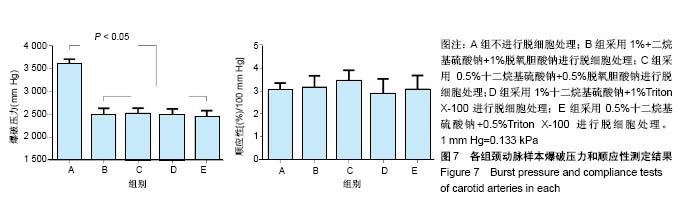
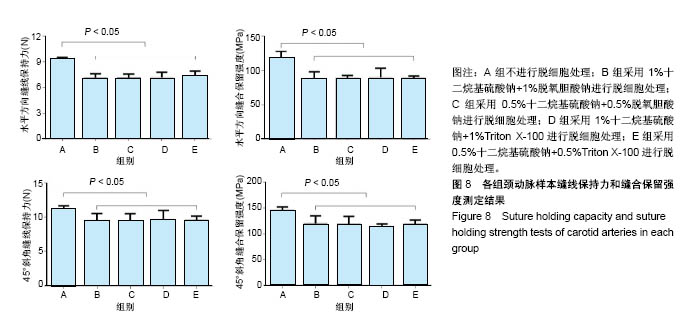
.jpg)
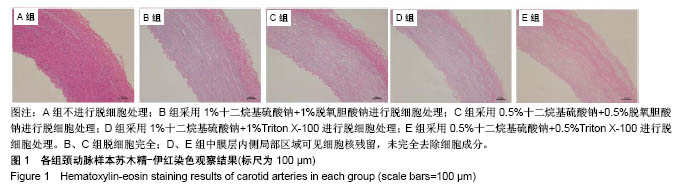
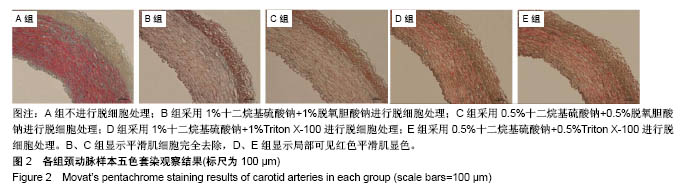
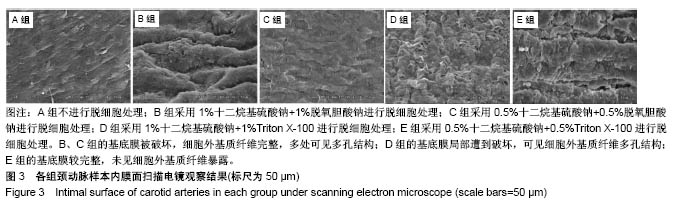
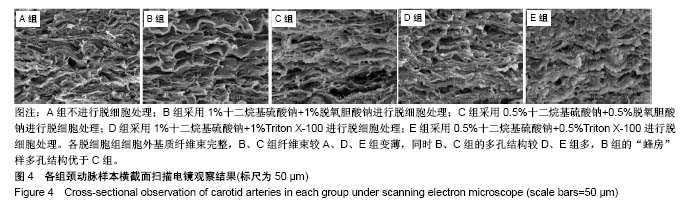

.jpg)