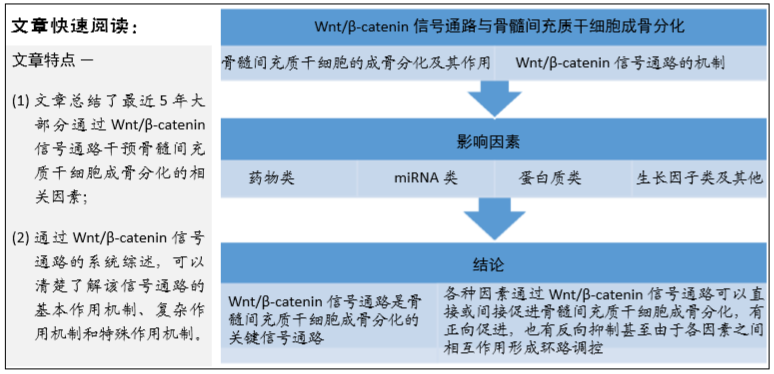
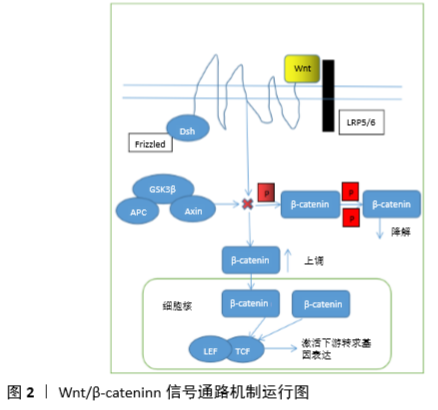
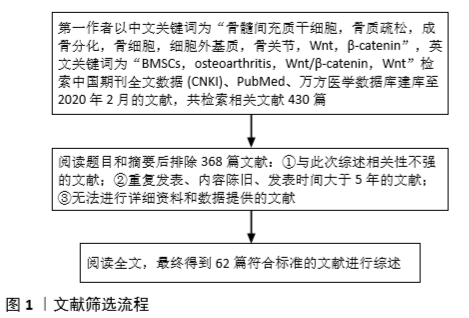
[1] BATEMAN ME, STRONG AL, MCLACHLAN JA, et al. The Effects of Endocrine Disruptors on Adipogenesis and Osteogenesis in Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Review. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2017;7:171.
[2] BAGHERI L, PELLATI A, RIZZO P,et al. Notch pathway is active during osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induced by pulsed electromagnetic fields. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(2):304-315.
[3] ZHAO C, LI Y, WANG X, et al. The Effect of Uniaxial Mechanical Stretch on Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway in Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells. J Craniofac Surg. 2017;28(1):113-117.
[4] ZHANG S, CHEN X, HU Y, et al. All-trans retinoic acid modulates Wnt3A-induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells via activating the PI3K/AKT/GSK3β signalling pathway. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2016;422:243-253.
[5] SHAO J, ZHANG Y, YANG T, et al. HIF-1α disturbs osteoblasts and osteoclasts coupling in bone remodeling by up-regulating OPG expression. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2015;51(8):808-814.
[6] CHEN Q, SHOU P, ZHENG C,et al. Fate decision of mesenchymal stem cells: adipocytes or osteoblasts? Cell Death Differ. 2016;23(7): 1128-1139.
[7] NIZIOLEK PJ, MACDONALD BT, KEDLAYA R, et al. High Bone Mass-Causing Mutant LRP5 Receptors Are Resistant to Endogenous Inhibitors In Vivo. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(10):1822-1830.
[8] 依香叫,李金诚,王松月,等.刺老苞根皮含药血清对原代成骨细胞Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的影响[J].中国中药杂志, 2017, 42(14): 2749-2753.
[9] 罗智,史可测,田锋.葛根素对成骨细胞体外增殖及Wnt/β-catenin信号通路表达的影响[J].海南医学院学报,2017,23(10):1319-1321, 1325.
[10] 齐鹏飞,尹文哲,孙奇峰,等.失重下骨碎补总黄酮抑制JNK通路促间充质干细胞增殖的研究[J].中医学报,2016,31(11):1742-1745.
[11] 陈云刚,谭国庆,任维龙,等.骨碎补含药血清经wnt/β-catenin信号通路对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的影响[J].中国药理学通报,2017,33(6):830-836.
[12] 李晨睿,孟志远,牛银波,等.黄芩苷通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的促进作用[J].中国药理学通报,2015,31(7):919-924.
[13] 张哲,徐秀娟,刘欣,等.老鹳草素通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路影响小鼠骨髓基质干细胞的增殖和成骨分化[J].中华中医药学刊, 2017,35(1):215-218.
[14] WEI Q, ZHANG J, HONG G, et al. Icariin promotes osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow stromal cells by activating the ERα-Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;84: 931-939.
[15] 李新建. 基于Wnt/β-catenin信号通路探讨补肾活血汤调控激素性股骨头缺血坏死BMSCs成骨-成脂分化的机制[D].福州:福建中医药大学,2016.
[16] 马忠平,黄健,张志峰,等.贝尼地平对小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化体外研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2016, 22(4):423-427.
[17] ZHAO XE, YANG Z, GAO Z, et al. 6-Bromoindirubin-3’-oxime promotes osteogenic differentiation of canine BMSCs through inhibition of GSK3β activity and activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. An Acad Bras Cienc. 2019;91(1):e20180459.
[18] ZHU Y, WANG Y, JIA Y,et al. Catalpol promotes the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):37.
[19] JIANG HJ, TIAN XG, HUANG SB, et al. Tenuigenin promotes the osteogenic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells in vitro and in vivo. Cell Tissue Res. 2017;367(2):257-267.
[20] RUSSO C, FERRO Y, MAUROTTI S, et al. Lycopene and bone: an in vitro investigation and a pilot prospective clinical study. J Transl Med. 2020;18(1):43.
[21] ZHANG F, LUO K, RONG Z, et al. Periostin Upregulates Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling to Promote the Osteogenesis of CTLA4-Modified Human Bone Marrow-Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Sci Rep. 2017;7:41634.
[22] WANG BX, LI KP, YU T, et al. Rosuvastatin promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in the rat model of osteoporosis by the Wnt/β-catenin signal. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(22):10161-10168.
[23] MO J, YANG R, LI F, et al. Geraniin promotes osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) via activating β-catenin: a comparative study between BMSCs from normal and osteoporotic rats. J Nat Med. 2019;73(1):262-272.
[24] YE M, ZHANG C, ZHU L, et al. Yak (Bos grunniens) bones collagen-derived peptides stimulate osteoblastic proliferation and differentiation via the activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J Sci Food Agric. 2020;100(6):2600-2609.
[25] 刘珊.树豆内酯A调节Wnt/β-catenin/runx-2信号通路促进人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的作用研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学, 2016.
[26] 农梦妮.基于Wnt/β-catenin信号通路研究黄精多糖促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化及其作用机制[D].南宁:广西医科大学, 2016.
[27] LI ZH, HU H, ZHANG XY, et al. MiR-291a-3p regulates the BMSCs differentiation via targeting DKK1 in dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2020;36(1):35-42.
[28] XU G, DING Z, SHI HF. The mechanism of miR-889 regulates osteogenesis in human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):366.
[29] LI Z, WANG Y, XIANG S, et al. Chondrocytes-derived exosomal miR-8485 regulated the Wnt/β-catenin pathways to promote chondrogenic differentiation of BMSCs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;523(2):506-513.
[30] DAI Y, ZHENG C, LI H. Inhibition of miR-23a-3p promotes osteoblast proliferation and differentiation. J Cell Biochem. 2019 Nov 6. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29497. Online ahead of print.
[31] LONG H, SUN B, CHENG L, et al. miR-139-5p Represses BMSC Osteogenesis via Targeting Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. DNA Cell Biol. 2017;36(8):715-724.
[32] WANG H, MENG Y, CUI Q, et al. MiR-101 Targets the EZH2/Wnt/β-Catenin the Pathway to Promote the Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Sci Rep. 2016;6:36988.
[33] WANG C, QIAO X, ZHANG Z, et al. MiR-128 promotes osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in rat by targeting DKK2. Biosci Rep. 2020;40(2):BSR20182121.
[34] SHEN JJ, ZHANG CH, CHEN ZW, et al. LncRNA HOTAIR inhibited osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs by regulating Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(17):7232-7246.
[35] WANG R, ZHANG Y, JIN F, et al. High-glucose-induced miR-214-3p inhibits BMSCs osteogenic differentiation in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Cell Death Discov. 2019;5:143.
[36] ZHOU P, LI Y, DI R, et al. H19 and Foxc2 synergistically promotes osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs via Wnt-β-catenin pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(8):13799-13806.
[37] 吴斯媛. MiR-590-3p在人间充质干细胞成骨向分化过程中的作用及机制研究[D].广州:南方医科大学, 2017.
[38] 周洁.核酸内切酶Dicer1在成骨分化中的作用及其上游转录调控机制研究[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2017.
[39] SEN B, PARADISE CR, XIE Z, et al. β-Catenin Preserves the Stem State of Murine Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Through Activation of EZH2. J Bone Miner Res. 2020 Feb 5. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3975. Online ahead of print.
[40] SHEN G, REN H, SHANG Q, et al. Foxf1 knockdown promotes BMSC osteogenesis in part by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway and prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss. EBioMedicine. 2020;52:102626.
[41] 彭杨茜子,刘庆梅,马彦云,等. Rspo1通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路调节成骨细胞分化的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(4): 504-507.
[42] GERLACH JP, JORDENS I, TAURIELLO DVF, et al. TMEM59 potentiates Wnt signaling by promoting signalosome formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(17):E3996-E4005.
[43] KIM H, KIM T, JEONG BC, et al. Tmem64 modulates calcium signaling during RANKL-mediated osteoclast differentiation. Cell Metab. 2013; 17(2):249-260.
[44] JEONG BC, KIM TS, KIM HS, et al. Transmembrane protein 64 reciprocally regulates osteoblast and adipocyte differentiation by modulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Bone. 2015;78:165-173.
[45] ZHANG Y, WANG H, YIN T,et al. TMEM18 inhibits osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells by inactivating β-catenin. Exp Cell Res. 2019;383(1):111491.
[46] LIU Z, YANG J. Uncarboxylated osteocalcin promotes osteogenic differentiation of mouse bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells by activating the Erk-Smad/β-catenin signalling pathways. Cell Biochem Funct. 2020;38(1):87-96.
[47] ZHANG W, CHEN E, CHEN M, et al. IGFBP7 regulates the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. FASEB J. 2018;32(4):2280-2291.
[48] LIANG T, GAO W, ZHU L, et al. TIMP-1 inhibits proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of hBMSCs through Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(1):BSR20181290.
[49] WU CC, WANG F, RONG S, et al. Enhancement of osteogenesis of rabbit bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells by transfection of human BMP-2 and EGFP recombinant adenovirus via Wnt signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(5):4030-4036.
[50] LUO Y, ZHANG Y, MIAO G,et al. Runx1 regulates osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs by inhibiting adipogenesis through Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Arch Oral Biol. 2019;97:176-184.
[51] 陈杨. Runx2对高糖环境下干细胞成骨分化作用和机制的初步研究[D].重庆:重庆医科大学, 2017.
[52] ZHAO SJ, KONG FQ, JIE J, et al. Macrophage MSR1 promotes BMSC osteogenic differentiation and M2-like polarization by activating PI3K/AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway. Theranostics. 2020;10(1):17-35.
[53] SCHIAVONE ML, MILLUCCI L, BERNARDINI G, et al. Homogentisic acid affects human osteoblastic functionality by oxidative stress and alteration of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2020 Jan 28. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29575. Online ahead of print.
[54] 王潇丽,徐丽丽,杨乃龙.尿酸对人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化过程中Wnt信号通路的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(28): 4472-4477.
[55] 岳辰,张雪,温阳阳,等. siRNA慢病毒载体介导DKK-1基因沉默对骨髓间充质干细胞分化影响的实验研究[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2018,11(2):137-142,150.
[56] 任磊,代光明,林枭,等.骨细胞Wnt/β-Catenin通过Notch信号促进BMSCs成骨分化[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(5): 600-605.
[57] 何鹏. CGRP对MC3T3-E1细胞成骨分化的影响及Wnt/β-catenin信号通路在其中的作用[D].长沙:湖南师范大学,2016.
[58] 陈坤. Wnt/β-catenin信号通路对vaspin介导的大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的影响[D].太原:山西医科大学, 2016.
[59] 齐奇.组蛋白去甲基化酶KDM4A调控骨髓基质干细胞成脂/成骨分化的作用和机制研究[D].天津:天津医科大学, 2018.
[60] LIU X, BAO C, XU HHK, et al. Osteoprotegerin gene-modified BMSCs with hydroxyapatite scaffold for treating critical-sized mandibular defects in ovariectomized osteoporotic rats. Acta Biomater. 2016;42: 378-388.
[61] HASEGAWA A, YONEZAWA T, TANIGUCHI N, et al. Role of Fibulin 3 in Aging-Related Joint Changes and Osteoarthritis Pathogenesis in Human and Mouse Knee Cartilage. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017;69(3):576-585.
[62] CHEN K, ZHANG C, WANG L, et al. Progress on strategies to promote vascularization in bone tissue engineering. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2015; 28(4):383-388. |