中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (11): 1712-1716.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3089
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
表达嵌合蛋白PAcA/CTB转基因番茄疫苗可通过胃肠道吸收的方式免疫大鼠
关薇薇1,2,3,顾 瑜2,管晓燕2,3,吴家媛2,3,白国辉3,田 源2,3,刘建国2,3
- 1中南大学湘雅医学院附属海口医院·海南省口腔医学中心,海南省海口市 570208;2遵义医科大学附属口腔医院,贵州省遵义市 563099;3贵州省高等学校口腔疾病研究特色重点实验室·遵义市口腔疾病研究重点实验室,贵州省遵义市 563006
Transgenic tomato vaccine expressing chimeric protein PAcA/CTB can immunize rats through gastrointestinal absorption
Guan Weiwei1, 2, 3, Gu Yu2, Guan Xiaoyan2, 3, Wu Jiayuan2, 3, Bai Guohui3, Tian Yuan2, 3, Liu Jianguo2, 3
- 1Haikou Hospital Affiliated to Xiangya School of Medicine, Central South University · Hainan Dental Medical Center, Haikou 570208, Hainan Province, China; 2Stomatological Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563099, Guizhou Province, China; 3Key Laboratory of Oral Disease Research Characteristics of Higher Education Institutions of Guizhou Province · Zunyi Key Laboratory of Oral Disease Research, Zunyi 563006, Guizhou Province, China
摘要:
 文题释义:
文题释义:
PAcA/CTB:PAc是由pac基因编码的菌体表面蛋白,介导菌体与牙面最初的蔗糖非依赖性黏附,是变异链球菌主要的黏结素和毒力因子。其A区富集 T、B细胞表位,具有免疫原性和免疫反应性。霍乱毒素(cholera toxin,CT)B亚单位(CTB)是一种较强的免疫佐剂,其与PAc抗原联合免疫有较强的免疫防龋效果。
可食用转基因植物防龋疫苗:应用分子生物学技术将致龋病原微生物具有免疫原性及免疫反应性的基因序列植入植物载体,使其稳定表达出免疫活性蛋白,口服免疫人或动物后激发全身免疫系统及体液免疫系统,从而产生对致龋病原菌的免疫能力。
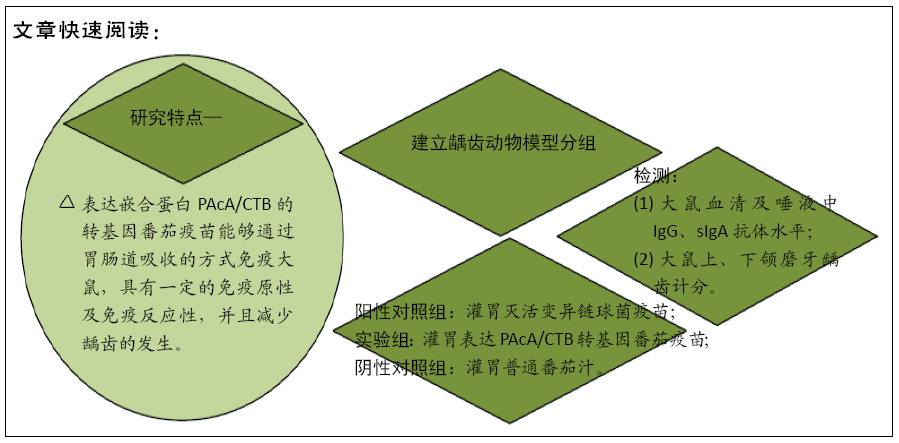
背景:转基因植物防龋疫苗因其生产工艺简单、价格低廉、有较好的免疫原性及安全有效等优点逐渐展现出其独特的优势,成为近年研究的热点。
目的:用含PAcA/CTB的转基因番茄以灌胃的方式免疫SD大鼠,观察其免疫反应性及免疫原性。
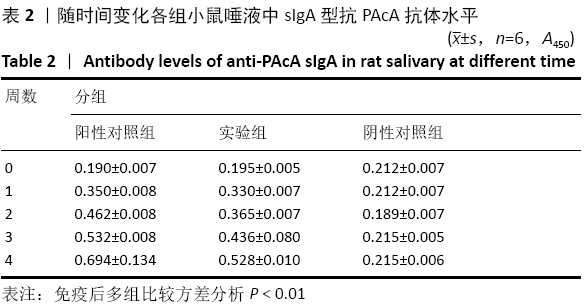
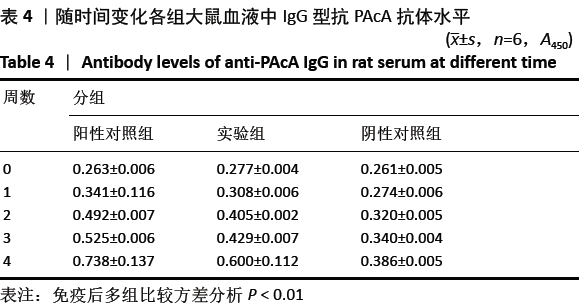
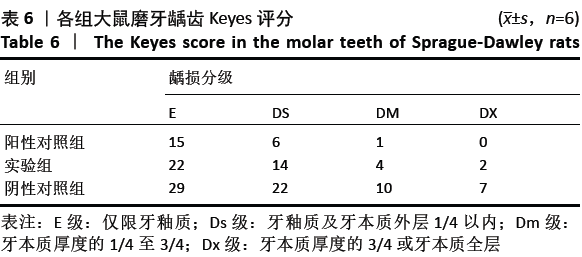
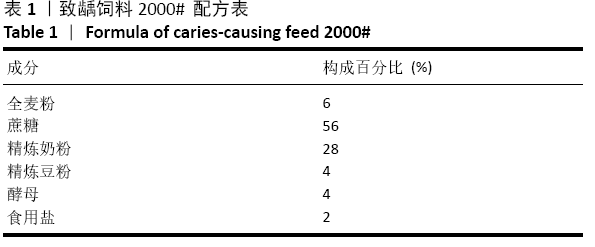
方法:将雄性SD大鼠随机分成3组,建立动物龋齿模型1周后,阳性对照组大鼠灌胃灭活变异链球菌疫苗;实验组大鼠灌胃表达PAcA/CTB转基因番茄疫苗;阴性对照组大鼠灌胃普通番茄汁,每周灌胃免疫1次,连续4周。于免疫前、免疫后1,2,3,4周采集大鼠的血液及唾液样本,用ELISA法检测血清及唾液中抗变异链球菌PAcA的IgG 、sIgA抗体水平;鼠龄 57 d 时片切大鼠上、下颌磨牙进行龋齿计分。实验方案经遵义医学院动物实验伦理委员会批准。
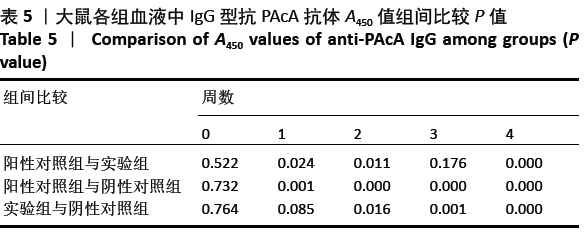
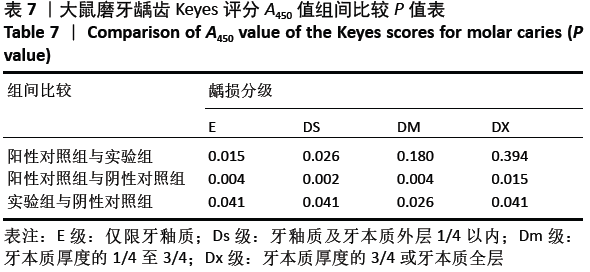
结果与结论:①阳性对照组、实验组分别与阴性对照组比较,第1,2,3,4周小鼠唾液中sIgA型抗PAcA抗体水平均显著升高 (P < 0.01);②与阴性对照组比较,阳性对照组免疫后第1-4周,实验组免疫后第2-4周小鼠血液中IgG型抗PAcA抗体水平显著升高(P < 0.05,P < 0.01);③阳性对照组牙齿的损坏程度最小,少数达牙本质浅层,龋齿数量最少;其次是实验组;阴性对照组损坏最为严重,龋损数量最多;④结果说明,表达嵌合蛋白PAcA/CTB的转基因番茄疫苗能够通过胃肠道吸收的方式免疫大鼠,具有一定的免疫原性及免疫反应性,并且减少龋齿的发生。
中图分类号: