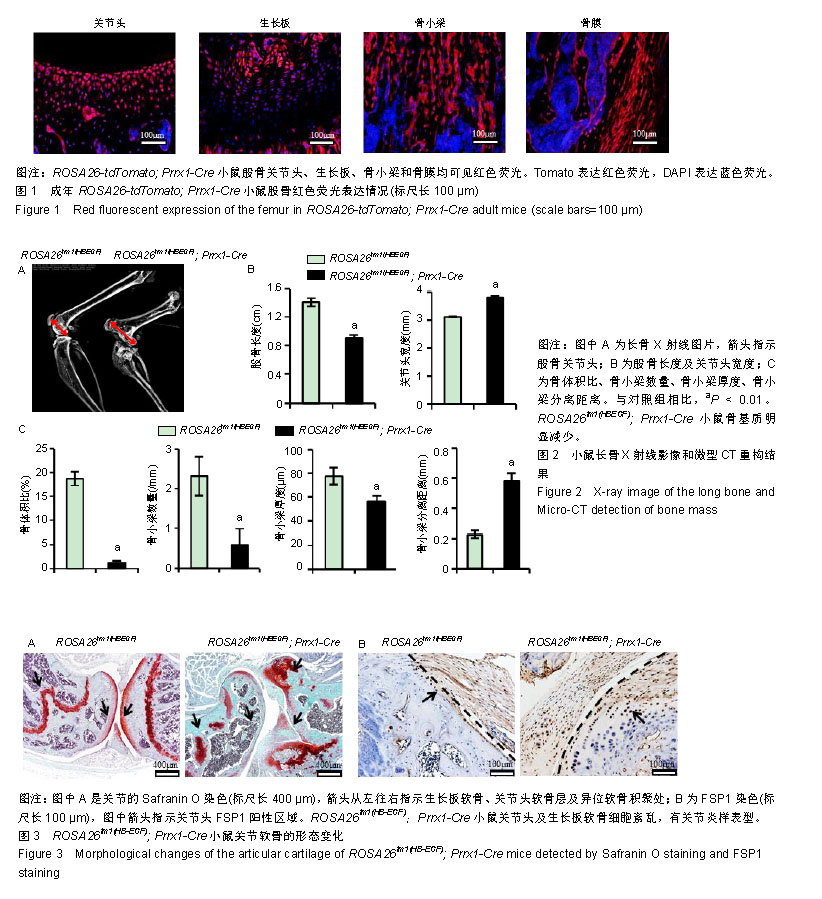
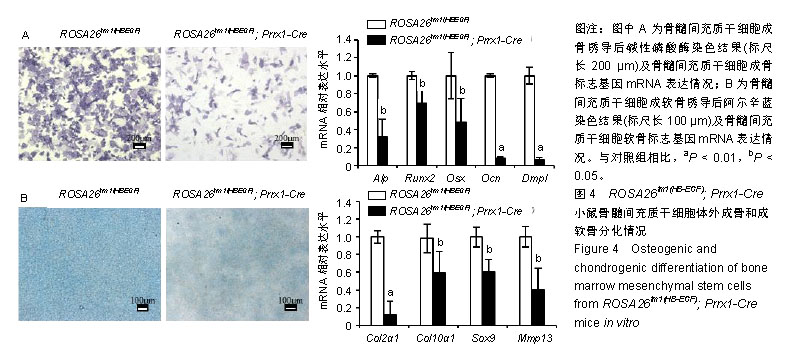
| [1]Schneider MR, Wolf E. The epidermal growth factor receptor ligands at a glance. J Cell Physiol. 2009;218(3):460-466. [2]Miyamoto S, Yagi H, Yotsumoto F, et al. Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor as a novel targeting molecule for cancer therapy. Cancer Sci. 2006;97(5):341-347[3]Falls DL. Neuregulins: functions, forms, and signaling strategies. Exp Cell Res. 2003;284(1):14-30.[4]Ming YC, Chao HC, Chu SM, et al. Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor (HB-EGF) protected intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury through JNK and p38/MAPK- dependent pathway for anti-apoptosis. Pediatr Neonatol. 2018. doi: 10.1016/j.pedneo.2018.08.003. [Epub ahead of print][5]Zhang X, Tamasi J, Lu X, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor plays an anabolic role in bone metabolism in vivo. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(5):1022-1034. [6]Roskoski R Jr. The ErbB/HER family of protein-tyrosine kinases and cancer. Pharmacol Res. 2014;79:34-74. [7]Barry FP. Biology and clinical applications of mesenchymal stem cells. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2003;69(3):250-256.[8]Ohishi M, Schipani E. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Biochem. 2010;109(2):277-282. [9]Lamplot JD, Denduluri S, Liu X, et al. Major signaling pathways regulating the proliferation and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. In: Zhao R C, ed. Essentials of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Biology and Its Clinical Translation, Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands. 2013: 75-100.[10]Chien HH, Lin WL, Cho MI. Down-regulation of osteoblastic cell differentiation by epidermal growth factor receptor. Calcif Tissue Int. 2000;67(2):141-150.[11]Zhang X, Siclari VA, Lan S, et al. The critical role of the epidermal growth factor receptor in endochondral ossification. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(11):2622-2633. [12]Vary CP, Li V, Raouf A, et al. Involvement of Ets transcription factors and targets in osteoblast differentiation and matrix mineralization. Exp Cell Res. 2000;257(1):213-222.[13]Tsuritani K, Takeda J, Sakagami J, et al. Cytokine receptor-like factor 1 is highly expressed in damaged human knee osteoarthritic cartilage and involved in osteoarthritis downstream of TGF-beta. Calcif Tissue Int. 2010;86(1):47-57. [14]Krampera M, Pasini A, Rigo A, et al. HB-EGF/HER-1 signaling in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells: inducing cell expansion and reversibly preventing multilineage differentiation. Blood. 2005;106(1):59-66. [15]Ding L, Morrison SJ. Haematopoietic stem cells and early lymphoid progenitors occupy distinct bone marrow niches. Nature. 2013;495(7440): 231-235. [16]Madisen L, Zwingman TA, Sunkin SM, et al. A robust and high-throughput Cre reporting and characterization system for the whole mouse brain. Nat Neurosci. 2010;13(1):133-140.[17]Logan M, Martin JF, Nagy A, et al. Expression of Cre Recombinase in the developing mouse limb bud driven by a Prxl enhancer. Genesis. 2002;33(2):77-80.[18]Buch T, Heppner FL, Tertilt C, et al. A Cre-inducible diphtheria toxin receptor mediates cell lineage ablation after toxin administration. Nat Methods. 2005;2(6):419-426.[19]常晓朋,陈涛,赵寅,等.骨形态发生蛋白2和转化生长因子β2协同促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(1):1-6.[20]张文.SkyScan 1176 Micro-CT在骨科研究中的应用[J].数字化用户, 2017,23(51):272,266.[21]Higashiyama S, Abraham JA, Miller J, et al. A heparin-binding growth factor secreted by macrophage-like cells that is related to EGF. Science. 1991;251(4996):936-939.[22]Taylor SR, Markesbery MG, Harding PA. Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor (HB-EGF) and proteolytic processing by a disintegrin and metalloproteinases (ADAM): a regulator of several pathways. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014;28:22-30.[23]Iwamoto R, Mekada E. HB-EGF (Heparin-Binding EGF-Like Growth Factor). In: Choi S, ed. Encyclopedia of Signaling Molecules. Cham: Springer International Publishing. 2018: 2318-2329.[24]Adam RM. Role of HB-EGF in cancer. Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol. 2011;15(7):610-619.[25]Dao DT, Anez-Bustillos L, Adam RM, et al. Heparin-Binding Epidermal Growth Factor-Like Growth Factor as a Critical Mediator of Tissue Repair and Regeneration. Am J Pathol. 2018;188(11):2446-2456. [26]Hanoun M, Frenette PS. This niche is a maze; an amazing niche. Cell Stem Cell. 2013;12(4):391-392. d[27]Greenbaum A, Hsu YM, Day RB, et al. CXCL12 in early mesenchymal progenitors is required for haematopoietic stem-cell maintenance. Nature. 2013;495(7440):227-230. [28]Mehta VB, Besner GE. HB-EGF promotes angiogenesis in endothelial cells via PI3-kinase and MAPK signaling pathways. Growth Factors. 2007;25(4):253-263.[29]Jackson LF, Qiu TH, Sunnarborg SW, et al. Defective valvulogenesis in HB-EGF and TACE-null mice is associated with aberrant BMP signaling. EMBO J. 2003;22(11):2704-2716.[30]Mine N, Iwamoto R, Mekada E. HB-EGF promotes epithelial cell migration in eyelid development. Development. 2005;132(19): 4317-4326. [31]Berendsen AD,Olsen BR. Bone development.Bone. 2015;80:14-18. [32]Ono N, Kronenberg HM. Bone repair and stem cells. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2016;40:103-107. [33]Nakamura T, Toita H, Yoshimoto A, et al. Potential involvement of Twist2 and Erk in the regulation of osteoblastogenesis by HB-EGF-EGFR signaling. Cell Struct Funct. 2010;35(1):53-61.[34]Chan SY, Wong RW. Expression of epidermal growth factor in transgenic mice causes growth retardation. J Biol Chem. 2000; 275(49):38693-38698.[35]Loeser RF, Olex AL, McNulty MA, et al. Microarray analysis reveals age-related differences in gene expression during the development of osteoarthritis in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2012; 64(3):705-717. [36]Loeser RF, Long DL, Olex AL, et al. A systems biology approach identifies heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor as a potential mediator in OA. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2013;21:S234-S235.[37]Zhang X, Zhu J, Liu F, et al. Reduced EGFR signaling enhances cartilage destruction in a mouse osteoarthritis model. Bone Res. 2014;2:14015. [38]Long DL, Ulici V, Chubinskaya S, et al. Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor (HB-EGF) is increased in osteoarthritis and regulates chondrocyte catabolic and anabolic activities. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(9):1523-1531.[39]Sherwood J. Osteoarthritis year in review 2018: biology. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2018;27(3):365-370.[40]Vasheghani F, Monemdjou R, Fahmi H, et al. Adult cartilage-specific peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma knockout mice exhibit the spontaneous osteoarthritis phenotype. Am J Pathol. 2013;182(4):1099-1106. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)