| [1]Collins AJ, Foley RN, Chavers B, et al.'United States Renal Data System 2011 Annual Data Report: Atlas of chronic kidney disease & end-stage renal disease in the United States.Am J Kidney Dis. 2012; 59(1 Suppl 1):A7, e1-420.[2]Toth-Manikowski S, Atta MG.Diabetic Kidney Disease: Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Targets.J Diabetes Res. 2015;2015:697010.[3]Saran R, Li Y, Robinson B, et al.US Renal Data System 2014 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States.Am J Kidney Dis. 2015;66(1 Suppl 1):Svii, S1-305.[4]Checheri?? IA, Turcu F, Dragomirescu RF, et al.Chronic complications in hemodialysis: correlations with primary renal disease.Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2010;51(1):21-26.[5]Stoumpos S, Jardine AG, Mark PB.Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality after kidney transplantation.Transpl Int. 2015;28(1):10-21.[6]杜俊文,吴韬,张坤,等. 骨髓间充质干细胞移植改善糖尿病肾病大鼠血糖及尿总蛋白[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(6):855-860.[7]何文涓,何晓升,袁志坚,等. 黄芪甲苷对兔脂肪来源的间充质干细胞体外增殖和细胞周期的影响[J]. 中国生化药物杂志, 011,32(6):466-468.[8]王葳,姜燕,王巍巍,等. 黄芪甲苷对脂肪源性干细胞体外生物学行为的影响[J]. 中国药理学通报,2013,29(2):220-224.[9]王葳,姜燕,王巍巍,等.黄芪甲苷孵育脂肪源性干细胞对顺铂诱导肾小管上皮细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(28):4498-4503.[10]姜燕,王葳,李泽争,等. 黄芪甲苷孵育的脂肪源性干细胞对顺铂诱导的急性肾损伤小鼠的保护作用[J]. 中国中西医结合肾病杂志,2014,15(2):114-117.[11]高俊丽,朱赟洁,王巍巍,等. 左肾切除术联合链脲佐菌素腹腔注射诱导糖尿病肾病大鼠模型的建立[J]. 临床肾脏病杂志, 2018,18(05):306-311.[12]Coombe L, Kadri A, Martinez JF, et al. Current approaches in regenerative medicine for the treatment of diabetes: introducing CRISPR/CAS9 technology and the case for non-embryonic stem cell therapy. Am J Stem Cells. 2018;7(5):104-113.[13]Chandra V, G S, Phadnis S, et al.Generation of pancreatic hormone-expressing islet-like cell aggregates from murine adipose tissue-derived stem cells.Stem Cells. 2009;27(8):1941-1953.[14]Kajiyama H, Hamazaki TS, Tokuhara M, et al.Pdx1-transfected adipose tissue-derived stem cells differentiate into insulin-producing cells in vivo and reduce hyperglycemia in diabetic mice.Int J Dev Biol. 2010;54(4):699-705.[15]Kim D, Dressler GR.Nephrogenic factors promote differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells into renal epithelia.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16(12):3527-3534.[16]Narayanan K, Schumacher KM, Tasnim F, et al.Human embryonic stem cells differentiate into functional renal proximal tubular-like cells.Kidney Int. 2013;83(4):593-603.[17]Song B, Smink AM, Jones CV, et al.The directed differentiation of human iPS cells into kidney podocytes.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e46453.[18]Lam AQ, Freedman BS, Morizane R, et al.Rapid and efficient differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into intermediate mesoderm that forms tubules expressing kidney proximal tubular markers.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014;25(6):1211-1225.[19]Ezquer ME, Ezquer FE, Arango-Rodriguez ML, et al. MSC transplantation:a promising therapeutic strategy to manage the onset and progression of diabetic nephropathy. Biol Res. 2012;45(3): 289-296.[20]Ezquer FE, Ezquer ME, Parrau DB, et al. Systemic administration of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells reverts hyperglycemia and prevents nephropathy in type 1 diabetic mice.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2008;14(6):631-640.[21]Wu S, Li L, Wang G, et al.Ultrasound-targeted stromal cell-derived factor-1-loaded microbubble destruction promotes mesenchymal stem cell homing to kidneys in diabetic nephropathy rats.Int J Nanomedicine. 2014;9:5639-5651. [22]Nagaishi K, Mizue Y, Chikenji T, et al.Mesenchymal stem cell therapy ameliorates diabetic nephropathy via the paracrine effect of renal trophic factors including exosomes.Sci Rep. 2016;6:34842.[23]Ezquer F, Giraud-Billoud M, Carpio D, et al. Proregenerative Microenvironment Triggered by Donor Mesenchymal Stem Cells Preserves Renal Function and Structure in Mice with Severe Diabetes Mellitus.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:164703.[24]Hamza AH, Al-Bishri WM, Damiati LA, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells: a future experimental exploration for recession of diabetic nephropathy. Renal Failure. 2017;39(1):67-76.[25]Lenoir N. Europe confronts the embryonic stem cell research challenge. Science.2000;287(5457):1425-1427.[26]Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126(4):663-676.[27]Ben-David U, Benvenisty N.The tumorigenicity of human embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells.Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11(4):268-277.[28]Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H, et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies.Tissue Eng. 2001;7(2): 211-228.[29]Panés J, García-Olmo D, Van Assche G, et al.Expanded allogeneic adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (Cx601) for complex perianal fistulas in Crohn's disease: a phase 3 randomised, double-blind controlled trial.Lancet. 2016;388(10051):1281-1290.[30]Henry TD, Pepine CJ, Lambert CR, et al. The Athena trials: Autologous adipose-derived regenerative cells for refractory chronic myocardial ischemia with left ventricular dysfunction.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2017;89(2):169-177.[31]Merceron C, Portron S, Masson M, et al. TThe effect of two- and three-dimensional cell culture on the chondrogenic potential of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells after subcutaneous transplantation with an injectable hydrogel.Cell Transplant.2011; 20(10):1575-1588.[32]Aksu AE, Rubin JP, Dudas JR, et al. Role of gender and anatomical region on induction of osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells. Ann Plast Surg. 2008;60(3):306-322.[33]Wosnitza M, Hemmrich K, Groger A, et al. Plasticity of human adipose stem cells to perform adipogenic and endothelial differentiation. Differentiation. 2007;75(1):12-23.[34]Bourin P, Bunnell BA, Casteilla L, et al. Stromal cells from the adipose tissue-derived stromal vascular fraction and culture expanded adipose tissue-derived stromal/stem cells: a joint statement of the International Federation for Adipose Therapeutics and Science (IFATS) and the International Society for Cellular Therapy (ISCT). Cytotherapy. 2013; 15(6):641-648.[35]Zack-Williams SD, Butler PE, Kalaskar DM.Current progress in use of adipose derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration.World J Stem Cells. 2015;7(1):51-64.[36]Baer PC, Geiger H. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal/stem cells: tissue localization, characterization, and heterogeneity.Stem Cells Int. 2012;2012:812693.[37]Lee RH, Kim B, Choi I, et al.Characterization and expression analysis of mesenchymal stem cells from human bone marrow and adipose tissue.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2004;14(4-6):311-324.[38]Sheykhhasan M, Qomi RT, Ghiasi M.Fibrin Scaffolds Designing in order to Human Adipose-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Differentiation to Chondrocytes in the Presence of TGF-β3.Int J Stem Cells. 2015;8(2):219-227.[39]Mundra V, Gerling IC, Mahato RI. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Therapy. Molecular Pharmaceutics. 2012;10(1):77-89.[40]Valina C, Pinkernell K, Song YH, et al.Intracoronary administration of autologous adipose tissue-derived stem cells improves left ventricular function, perfusion, and remodelling after acute myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. 2007;28(21):2667-2677.[41]Zhang DZ, Gai LY, Liu HW, et al.Transplantation of autologous adipose-derived stem cells ameliorates cardiac function in rabbits with myocardial infarction.Chin Med J (Engl). 2007;120(4):300-307. |
.jpg)

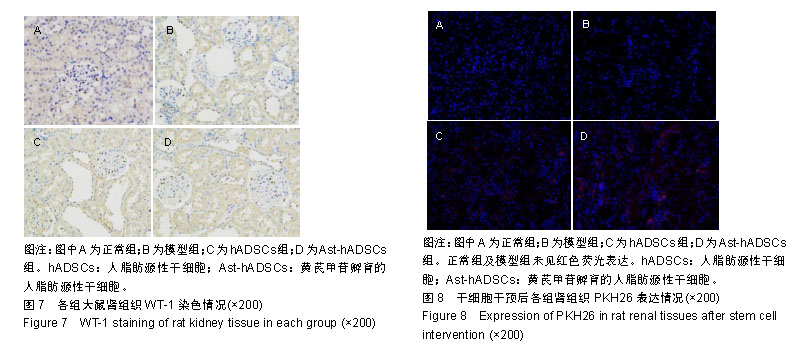

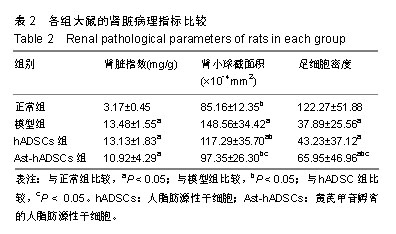
.jpg)
.jpg)