中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (2): 269-273.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2980
• 组织构建细胞学实验 cytology experiments in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
同型半胱氨酸致足细胞凋亡中FoxO1 DNA甲基化水平增高
刘 昆1,2,3,谢 琳2,3,4,曹 军1,2,3,丁 宁2,3,4,徐灵博2,3,4,马胜超2,3,4,李桂忠2,3,4,
姜怡邓2,3,4,卢冠军2,3,5
- 宁夏医科大学,1临床医学院,4基础医学院,宁夏回族自治区银川市 750004;2国家卫生健康委代谢性心血管疾病研究重点实验室,宁夏回族自治区银川市 750004;3宁夏血管损伤与修复研究重点实验室,宁夏回族自治区银川市 750004;5宁夏医科大学总医院,宁夏回族自治区银川市 750004
Increased FoxO1 DNA methylation level in homocysteine-induced podocyte apoptosis
Liu Kun1, 2, 3, Xie Lin2, 3, 4, Cao Jun1, 2, 3, Ding Ning2, 3, 4, Xu Lingbo2, 3, 4, Ma Shengchao2, 3, 4, Li Guizhong2, 3, 4 , Jiang Yideng2, 3, 4, Lu Guanjun2, 3, 5
- 1Clinical Medical College, 4Basic Medical College, 3Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; 2Key Laboratory of Metabolic Cardiovascular Disease Research of National Health Commission, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; 3Ningxia Key Laboratory of Vascular Injury and Repair Research, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; 5General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
足细胞:是附着于肾小球基底膜外侧一种终末分化细胞,与血管内皮细胞和肾小球基底膜共同构成肾小球滤过膜。研究发现,足细胞由细胞器、主突和足突组成,其中足突与基底膜相连形成肾小球滤过的最后屏障;足细胞还参与肾小球基底膜的基质合成和维持其正常的结构功能;因此,足细胞对于维持肾小球滤过功能的完整性有着重要的作用。
同型半胱氨酸:是蛋氨酸在氨基酸循环代谢过程中产生的中间产物,研究表明同型半胱氨酸具有广泛的生物学效应,包括加速动脉粥样硬化、损害损伤后内皮修复和功能、调节脂质代谢和诱导血栓形成;同型半胱氨酸已经被认为是心血管疾病的独立因素,而且与肾损伤有密切联系,研究旨在阐明同型半胱氨酸在肾损伤中的具体作用机制。
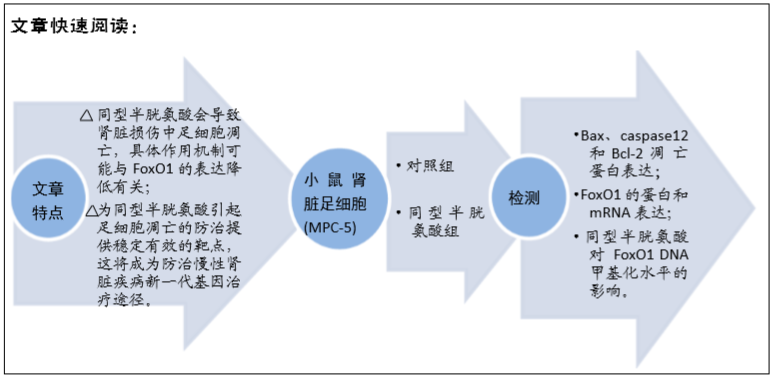
背景:同型半胱氨酸增多会引起肾损伤并导致足细胞凋亡,但是其具体机制还尚不清楚。
目的:探讨叉头框转录因子O1 (forkhead box O,FoxO1)及其DNA甲基化在同型半胱氨酸致足细胞凋亡中的作用。
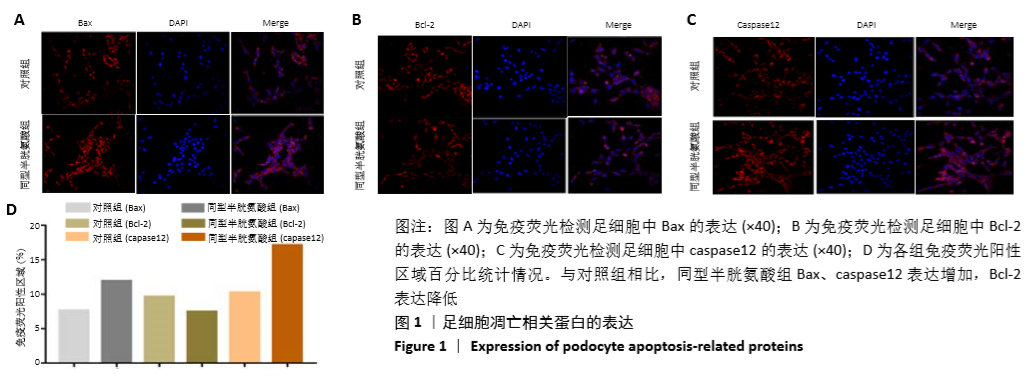
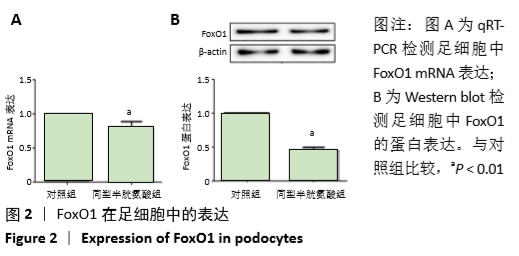
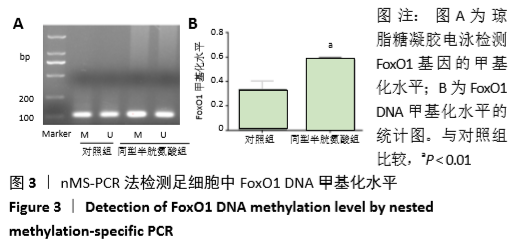
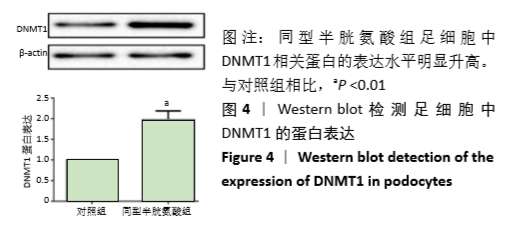
方法:体外培养小鼠肾脏足细胞(MPC-5),将其分为对照组(0 μmol/L同型半胱氨酸)和同型半胱氨酸组(80 μmol/L 同型半胱氨酸)。干预细胞48 h后,采用免疫荧光技术检验足细胞凋亡相关蛋白Bax、caspase12和Bcl-2的表达情况;采用实时荧光定量PCR(qRT-PCR)检测FoxO1 mRNA水平;采用Western blot检测FoxO1和DNMT1蛋白表达水平;采用巢式降落式特异性PCR(nMS-PCR)测验FoxO1 的DNA甲基化水平。
结果与结论:①与对照组相比,同型半胱氨酸组足细胞中Bax和caspase12表达明显增高,Bcl-2表达明显降低;②FoxO1的mRNA和蛋白表达水平明显降低(P < 0.01);③与对照组相比,同型半胱氨酸组FoxO1 DNA甲基化水平明显升高(P < 0.01),同型半胱氨酸组足细胞中DNMT1蛋白表达明显增高(P < 0.01);④结果表明:FoxO1 DNA高甲基化在同型半胱氨酸致足细胞凋亡中作用显著,而DNMT1参与同型半胱氨酸诱导的足细胞凋亡过程。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0938-1378(刘昆)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: