中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (19): 2958-2962.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3533
• 造血干细胞 hematopoietic stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
自体外周血造血干细胞动员采集的影响因素
陈 晓,郭 智,陈丽娜,刘玄勇,张弋慧智,李旭绵,王月乔,韦丽娅,谢 晶,蔺 莉
- 国家癌症中心/国家肿瘤临床医学研究中心/中国医学科学院北京协和医学院肿瘤医院深圳医院血液肿瘤科,广东省深圳市 518116
Factors affecting the mobilization and collection of autologous peripheral blood hematopoietic stem cells
Chen Xiao, Guo Zhi, Chen Lina, Liu Xuanyong, Zhang Yihuizhi, Li Xumian, Wang Yueqiao, Wei Liya, Xie Jing, Lin Li
- Department of Hematology & Oncology, National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Cancer for Cancer/Cancer Hospital & Shenzhen Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Shenzhen 518116, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:

文题释义:
造血干细胞:是血液系统中一类具有自我更新和定向分化能力的细胞群,用于临床移植的造血干细胞来源有外周血、骨髓和脐血,其中外周血造血干细胞的采集最为方便。移植后造血功能的重建主要取决于输入造血干细胞的数量和质量。因此,分析影响造血干细胞采集的各种因素,提高临床造血干细胞采集的成功率,在造血干细胞移植中有重要意义,检测标本中造血干细胞表面特异性表达的CD34分子,可有效计数造血干细胞。
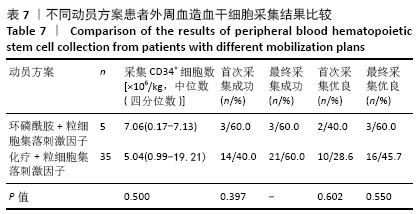
自体外周血造血干细胞采集:外周血干细胞动员大多采用大剂量化疗,继之以粒细胞集落刺激因子动员的方案,动员后通过监测血常规指标,有条件的机构通过监测外周血CD34+细胞数,决定干细胞采集的时间。采集次数根据采得的CD34+细胞数而定,目前采集成功的标准为CD34+细胞数≥2×106/kg。
背景:自体外周血造血干细胞移植因患者年龄范围宽、移植后并发症少、费用低,临床应用日益广泛。移植后造血功能的重建主要取决于输入造血干细胞的数量和质量。文章从临床实际出发,分析影响外周血造血干细胞采集的各种因素,并计算出适宜采集的血常规标准,对提高临床外周血造血干细胞采集成功率进而提高自体移植成功率有重要意义。
目的:分析血液肿瘤患者自体外周血造血干细胞动员采集过程中相关因素对CD34+细胞数的影响。
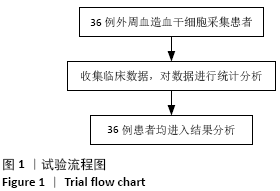
方法:回顾性分析中国医学科学院肿瘤医院深圳医院2018年6月至2020年6月共36例患者自体外周血造血干细胞动员采集过程中各种因素对所采集的CD34+细胞数的影响,主要包括年龄、性别、体表面积、疾病种类、采集当天各类细胞水平、采集前化疗次数、采集前疾病状态、初诊时有无骨髓受累等因素。
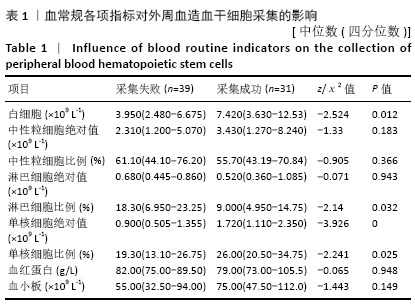
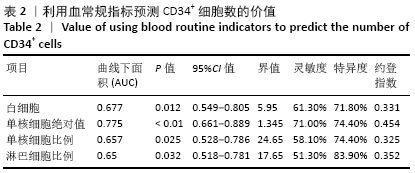
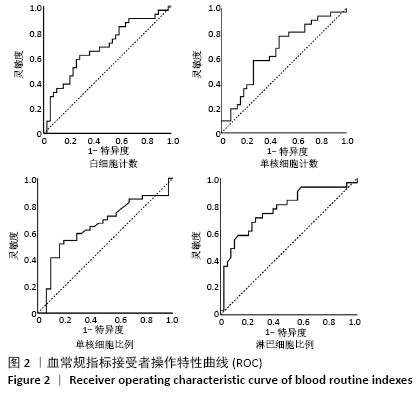
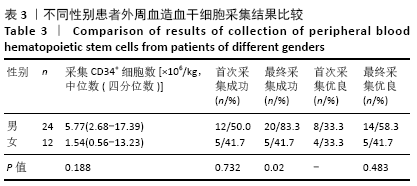
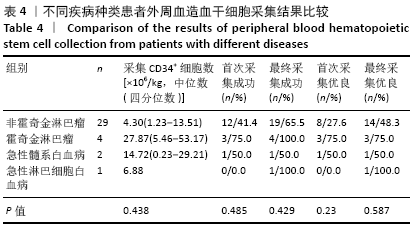
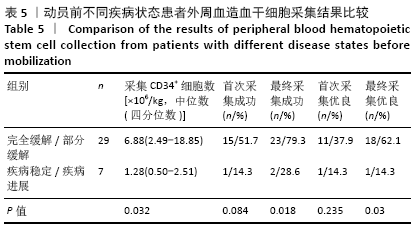
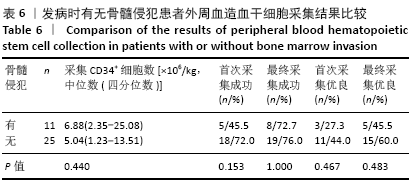
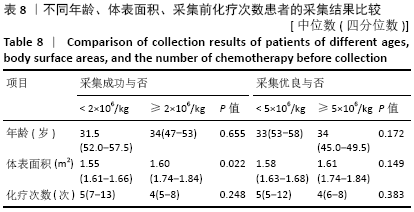
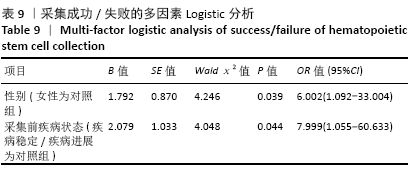
结果与结论:①CD34+细胞数与采集当天白细胞数、单核细胞绝对值、单核细胞比例、淋巴细胞比例有关,差异有显著性意义(均P < 0.05);对上述4个指标进一步分析,发现采集当天单核细胞绝对值对CD34+细胞数的预测价值最高,其次为淋巴细胞比例、白细胞数、单核细胞比例;②单因素分析发现,年龄、疾病种类、动员方案、采集前化疗次数、发病时有无骨髓侵犯对最终采集成功率无影响,差异均无显著性意义(均P > 0.05),而性别、动员前疾病状态、体表面积与最终采集成功率有关,差异均有显著性意义(均P < 0.05);③结果表明,动员后通过监测血常规来决定外周血造血干细胞采集的时间,其中主要监测白细胞数、单核细胞绝对值、单核细胞比例、淋巴细胞比例,预测价值最高的为单核细胞绝对值,其界值为1.345×109 L-1。男性、采集前疾病状态为完全缓解或部分缓解、体表面积偏大时,最终采集的成功率高。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: