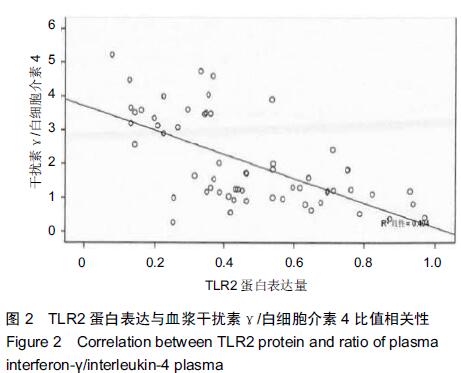
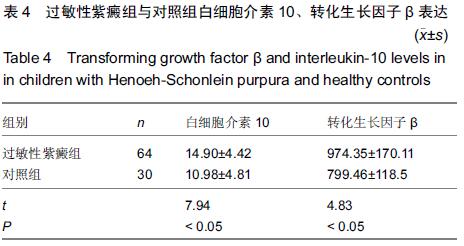
[1] 中华医学会儿科学分会肾脏病学组. 儿童常见肾脏疾病诊治循证指南(二):紫癜性肾炎的诊治循证指南(试行)[J].中华儿科杂志, 2009,47(12): 911-913.
[2] 杨军,李成荣,祖莹,等.调节性T细胞在儿童过敏性紫癜发病机制中的作用初探[J].中华儿科杂志,2006,44(6):411-414.
[3] 董胜英,张秋业,刘伟,等.过敏性紫癜患儿急性期血浆转化生长因子-β1和血管内皮生长因子检测及其临床意义[J].中国实用儿科杂志,2004,19(11): 666-668.
[4] Yang YH, Wang SJ, Chuang YH, et al. The level of IgA antibodies to human umbilical vein endothelial cells can be enhanced by TNF-alpha treatment in children with Henoch- Schönlein purpura. Clin Exp Immunol. 2002;130(2): 352-357.
[5] Yang YH, Lai HJ, Huang CM, et al. Sera from children with active Henoch-Schönlein purpura can enhance the production of interleukin 8 by human umbilical venous endothelial cells. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004;63(11):1511-1513.
[6] 陈永兴. 过敏性紫癜病儿外周血树突状细胞共刺激分子表达及与Th1/Th2平衡的相关性研究[D].青岛: 青岛大学, 2007.
[7] Li M, Zhou Y, Feng G, et al. The critical role of Toll-like receptor signaling pathways in the induction and progression of autoimmune diseases. Curr Mol Med. 2009;9(3):365-374.
[8] Iwahashi M, Yamamura M, Aita T, et al. Expression of Toll-like receptor 2 on CD16+ blood monocytes and synovial tissue macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004; 50(5):1457-1467.
[9] 陶于洪,罗秋红. Toll样受体与肾脏疾病研究进展[J]实用儿科临床杂志,2012,27(17):1362-1365.
[10] 林珊,刘建梅,贾俊亚,等.Toll样受体4在糖尿病肾病患者肾小管中的表达及意义[J].临床荟萃,2010,25(8): 680-682.
[11] Pawar RD, Castrezana-Lopez L, Allam R, et al. Bacterial lipopeptide triggers massive albuminuria in murine lupus nephritis by activating Toll-like receptor 2 at the glomerular filtration barrier. Immunology. 2009;128(1 Suppl):e206-221.
[12] 庄琼冬,翁惠兰,汤银惠.饮食干预对过敏性紫癜患儿康复的影响[J].河北医学,2009,15(8):955-957.
[13] 戴慎,薛建国,岳沛平.中医病证诊疗标准与方剂选用[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2003:113.
[14] 黄琼远,王瑷萍.桃红解毒化瘀汤治疗过敏性紫癜临床疗效观察[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2010,19(21):2616-2617.
[15] Coppo R, Camilla R, Amore A, et al. Toll-like receptor 4 expression is increased in circulating mononuclear cells of patients with immunoglobulin A nephropathy. Clin Exp Immunol. 2010;159(1):73-81.
[16] 李媛媛,李成荣,王国兵,等. Toll样受体信号途径异常活化在过敏性紫癜免疫发病机制中的作用初探[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2010, 14(8):538-542.
[17] Weighardt H, Holzmann B. Role of Toll-like receptor responses for sepsis pathogenesis. Immunobiology. 2007;212(9-10):715-722.
[18] Janssens S, Burns K, Vercammen E, et al. MyD88S, a splice variant of MyD88, differentially modulates NF-kappaB- and AP-1-dependent gene expression. FEBS Lett. 2003; 548(1-3): 103-107.
[19] Eisenbarth SC, Piggott DA, Huleatt JW, et al. Lipopolysaccharide-enhanced, toll-like receptor 4-dependent T helper cell type 2 responses to inhaled antigen. J Exp Med. 2002;196(12):1645-1651.
[20] 付劲蓉,李成荣,周玉峰,等.粘附分子在川崎病血管炎性损伤中的作用机制探讨[J].中华儿科杂志,2002,40(2):108-109.
[21] 王国兵,李成荣,祖莹,等.Toll样受体信号途径活化在川崎病免疫发病机制中的作用[J].中华儿科杂志,2006,44(5): 333-336.
[22] 程娜,常红,张秋业,等.幼年特发性关节炎49例临床分析[J].青岛大学医学院学报,2013,49(1): 73-75.
[23] 陈洪敏.链球菌感染与过敏性紫癜及肾损害的关系[J].江苏医药,2011,37(8): 978-979.
[24] 马莲美,贾秀红,王宝宏,等.过敏性紫癜并支原体感染患儿细胞免疫功能的研究[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2011,5(11):3179- 3184.
[25] 仝桃玲.过敏性紫癜复发与幽门螺杆菌感染的关系[J].医药论坛杂志,2011,32(7):85-86.
[26] 陈小红,何芳,柳青,等.肾型过敏性紫癜患者血清IL-5、IL-10、CD+4CD+25调节性T细胞测定及意义[J].疑难病杂志,2013, 12(2): 140-141.
[27] 常红,张秋业,程娜,等. 过敏性紫癜患儿外周血单个核细胞 TLR2、TLR4表达及其与 Th1和 Th2型免疫应答相关性观察[J].中华微生物学和免疫学杂志,2013,33(11):839-844.
[28] Ozen S, Ruperto N, Dillon MJ, et al. EULAR/PReS endorsed consensus criteria for the classification of childhood vasculitides. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65(7):936-941.
[29] 孙丽萍,孙春荣,崔小岱,等.自身免疫性疾病患儿CD4+CD25+调节性T细胞的变化[J].实用儿科临床杂志,2009,24(9):664-665.
[30] Tamaki Y, Takakubo Y, Hirayama T, et al. Expression of Toll-like receptors and their signaling pathways in rheumatoid synovitis. J Rheumatol. 2011;38(5):810-820.
[31] Abdollahi-Roodsaz S, Joosten LA, Koenders MI, et al. Stimulation of TLR2 and TLR4 differentially skews the balance of T cells in a mouse model of arthritis. J Clin Invest. 2008;118(1):205-216.
[32] Spachidou MP, Bourazopoulou E, Maratheftis CI, et al. Expression of functional Toll-like receptors by salivary gland epithelial cells: increased mRNA expression in cells derived from patients with primary Sjögren's syndrome. Clin Exp Immunol. 2007;147(3):497-503.
[33] Kawakami A, Nakashima K, Tamai M, et al. Toll-like receptor in salivary glands from patients with Sjögren's syndrome: functional analysis by human salivary gland cell line. J Rheumatol. 2007;34(5):1019-1026.
[34] 赵梅青,赵洪国.敏性紫癜病人血清TGF-β1和HGF水平的变化[J].齐鲁医学杂志,2011,26(6):513-514.
[35] 唐雪梅.过敏性紫癜病因及免疫发病机制[J].实用儿科临床杂志, 2012,27(21):1634-1636.
[36] 吴容,王强,董巍. 过敏性紫癜患儿血浆IL-2、IFN-γ、IL-4与TGF-β1的变化及其意义[J].实用医院临床杂志,2014,11(1): 144-146.
[37] 姜晶,陆彪.过敏性紫癜患儿急性期血清IL-10、IL-13、IL-15水平的变化及意义[J].宁夏医科大学学报,2012,34(3): 225-228.
[38] 王兰英,张慧玉,岳爱红. 过敏性紫癜患儿血、尿TGF-β1检测及临床意义[J].现代预防医学,2010,37(7):1257-1259.
[39] Ishida H. Henoch-Schönlein purpura accompanied with myeloperoxidase-antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (MPO-ANCA) associated vasculitis with elevated serum interleukin-10. Nihon Naika Gakkai Zasshi. 2005;94(8): 1615-1617.
[40] Morgan ME, Koelink PJ, Zheng B,et al. Toll-like receptor 6 stimulation promotes T-helper 1 and 17 responses in gastrointestinal-associated lymphoid tissue and modulates murine experimental colitis. Mucosal Immunol. 2014; 7(5): 1266-1277.