中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (7): 1078-1083.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1001
• 组织构建细胞学实验 cytology experiments in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
生物信息分析细粒棘球绦虫EgA31蛋白T细胞及B细胞的优势抗原表位
赵 骁1,张峰波2,王红英1,闫 芳3,安梦婷1,李玉娇1,庞楠楠4,丁剑冰1
- (1新疆医科大学基础医学院,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830011;新疆医科大学第一附属医院,2检验科,3呼吸科,4血液科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830054)
Dominant T cell and B cell epitopes in EgA31 protein of Echinococcus granulosus by bioinformatics
Zhao Xiao1, Zhang Fengbo2, Wang Hongying1, Yan Fang3, An Mengting1, Li Yujiao1, Pang Nannan4, Ding Jianbing1
- (1Basic Medical College of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Clinical Laboratory, 3Department of Respiratory Medicine, 4Department of Hematology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
细粒棘球绦虫:细粒棘球绦虫,又称包生绦虫,属带科、棘球属生物,1716年由Pallas发现。成虫寄生于犬科食肉动物,幼虫(棘球蚴)寄生于人和多种食草类家畜及其他动物,引起棘球蚴病或称包虫病。棘球蚴病分布地域广泛,随着世界畜牧业的发展而不断扩散,是一种严重危害人类健康和畜牧业产业生产的人兽共患病。
抗原表位:抗原表位,又称抗原决定簇或抗原决定基,指抗原分子中决定抗原特异性的特殊化学基团。抗原通过抗原表位与相应的T和B淋巴细胞表面的抗原受体结合,从而激活T或B淋巴细胞,引起免疫应答,抗原也借表位与相应抗体或致敏淋巴细胞发生特异性结合而发挥免疫效应。抗原表位的性质、数目和空间构型决定抗原的特异性。
文题释义:
细粒棘球绦虫:细粒棘球绦虫,又称包生绦虫,属带科、棘球属生物,1716年由Pallas发现。成虫寄生于犬科食肉动物,幼虫(棘球蚴)寄生于人和多种食草类家畜及其他动物,引起棘球蚴病或称包虫病。棘球蚴病分布地域广泛,随着世界畜牧业的发展而不断扩散,是一种严重危害人类健康和畜牧业产业生产的人兽共患病。
抗原表位:抗原表位,又称抗原决定簇或抗原决定基,指抗原分子中决定抗原特异性的特殊化学基团。抗原通过抗原表位与相应的T和B淋巴细胞表面的抗原受体结合,从而激活T或B淋巴细胞,引起免疫应答,抗原也借表位与相应抗体或致敏淋巴细胞发生特异性结合而发挥免疫效应。抗原表位的性质、数目和空间构型决定抗原的特异性。
.jpg) 文题释义:
细粒棘球绦虫:细粒棘球绦虫,又称包生绦虫,属带科、棘球属生物,1716年由Pallas发现。成虫寄生于犬科食肉动物,幼虫(棘球蚴)寄生于人和多种食草类家畜及其他动物,引起棘球蚴病或称包虫病。棘球蚴病分布地域广泛,随着世界畜牧业的发展而不断扩散,是一种严重危害人类健康和畜牧业产业生产的人兽共患病。
抗原表位:抗原表位,又称抗原决定簇或抗原决定基,指抗原分子中决定抗原特异性的特殊化学基团。抗原通过抗原表位与相应的T和B淋巴细胞表面的抗原受体结合,从而激活T或B淋巴细胞,引起免疫应答,抗原也借表位与相应抗体或致敏淋巴细胞发生特异性结合而发挥免疫效应。抗原表位的性质、数目和空间构型决定抗原的特异性。
文题释义:
细粒棘球绦虫:细粒棘球绦虫,又称包生绦虫,属带科、棘球属生物,1716年由Pallas发现。成虫寄生于犬科食肉动物,幼虫(棘球蚴)寄生于人和多种食草类家畜及其他动物,引起棘球蚴病或称包虫病。棘球蚴病分布地域广泛,随着世界畜牧业的发展而不断扩散,是一种严重危害人类健康和畜牧业产业生产的人兽共患病。
抗原表位:抗原表位,又称抗原决定簇或抗原决定基,指抗原分子中决定抗原特异性的特殊化学基团。抗原通过抗原表位与相应的T和B淋巴细胞表面的抗原受体结合,从而激活T或B淋巴细胞,引起免疫应答,抗原也借表位与相应抗体或致敏淋巴细胞发生特异性结合而发挥免疫效应。抗原表位的性质、数目和空间构型决定抗原的特异性。摘要
背景:EgA31蛋白是参与成虫吸盘肌收缩的一类蛋白,是细粒棘球蚴绦虫保护性免疫中重要的候选疫苗分子。
目的:应用生物信息学方法对细粒棘球绦虫EgA31蛋白进行分析,预测其可能的T细胞及B细胞优势抗原表位。
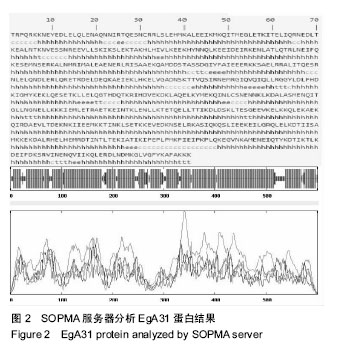
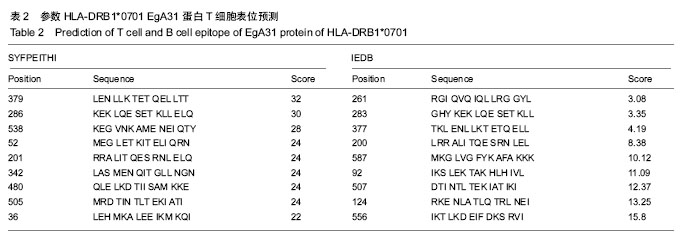
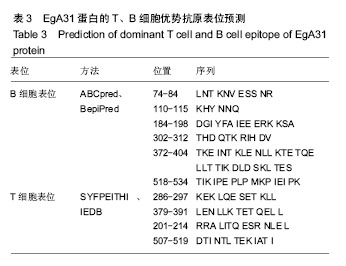
方法:从GenBank中获取EgA31蛋白的氨基酸序列(GenBank登记号为AAC21558.1),利用ProtParam在线程序分析EgA31蛋白的分子质量、理论等电点、氨基酸组成、原子组成、消光系数、不稳定系数和总平均疏水性,DNAstar Protein模块、SOPMA在线服务器分析蛋白二级结构,Phyre的同源建模服务器预测其蛋白质三级结构,最后通过ABCpred、BepiPred、SYFPEITHI、IDBE等软件联合预测细粒棘球绦虫EGA31蛋白的T细胞及B 细胞的优势抗原表位。
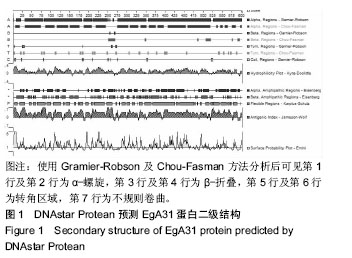
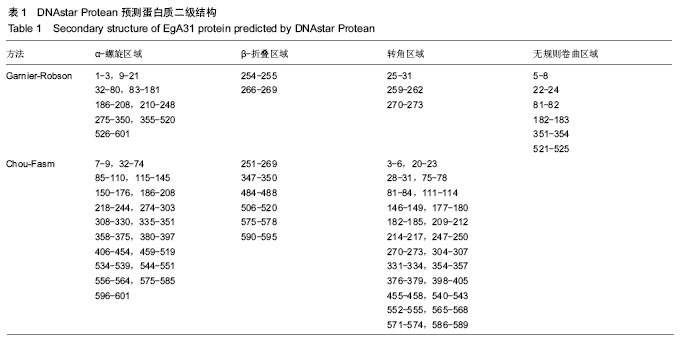
结果与结论:①EgA31蛋白由601个氨基酸组成,其中含有112个强碱性氨基酸,121个强酸性氨基酸,归类为不稳定且亲水性蛋白;②在线分析发现,EgA31蛋白的二级结构中α-螺旋约占82.36%,延长链约占4.16%,β-转角约占3.16%,无规则卷曲约占10.32%;③通过ABCpred、BepiPred、SYFPEITHI、IDBE等软件联合分析后预测了4段优势T细胞抗原、6段优势B细胞抗原以及1段T-B细胞联合表位;④生物学信息方法能较为全面地预测细粒棘球绦虫EgA31蛋白的优势T细胞及B细胞抗原表位,为进一步研制疫苗和检测试剂奠定了基础。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-4265-9458(赵骁)
中图分类号:

.jpg) 文题释义:
细粒棘球绦虫:细粒棘球绦虫,又称包生绦虫,属带科、棘球属生物,1716年由Pallas发现。成虫寄生于犬科食肉动物,幼虫(棘球蚴)寄生于人和多种食草类家畜及其他动物,引起棘球蚴病或称包虫病。棘球蚴病分布地域广泛,随着世界畜牧业的发展而不断扩散,是一种严重危害人类健康和畜牧业产业生产的人兽共患病。
抗原表位:抗原表位,又称抗原决定簇或抗原决定基,指抗原分子中决定抗原特异性的特殊化学基团。抗原通过抗原表位与相应的T和B淋巴细胞表面的抗原受体结合,从而激活T或B淋巴细胞,引起免疫应答,抗原也借表位与相应抗体或致敏淋巴细胞发生特异性结合而发挥免疫效应。抗原表位的性质、数目和空间构型决定抗原的特异性。
文题释义:
细粒棘球绦虫:细粒棘球绦虫,又称包生绦虫,属带科、棘球属生物,1716年由Pallas发现。成虫寄生于犬科食肉动物,幼虫(棘球蚴)寄生于人和多种食草类家畜及其他动物,引起棘球蚴病或称包虫病。棘球蚴病分布地域广泛,随着世界畜牧业的发展而不断扩散,是一种严重危害人类健康和畜牧业产业生产的人兽共患病。
抗原表位:抗原表位,又称抗原决定簇或抗原决定基,指抗原分子中决定抗原特异性的特殊化学基团。抗原通过抗原表位与相应的T和B淋巴细胞表面的抗原受体结合,从而激活T或B淋巴细胞,引起免疫应答,抗原也借表位与相应抗体或致敏淋巴细胞发生特异性结合而发挥免疫效应。抗原表位的性质、数目和空间构型决定抗原的特异性。