| [1] MA L.DNA vaccines: an historical perspective and view to the future.Immunol Reviews.2011,293(1):62-84.[2] Li L,Saade F,Petrovsky N.The future of human DNA vaccines.J Biotechnol.2012;162(2-3):171-182.[3] Ren Y, Wang N, Hu W, et al.Successive site translocating inoculation potentiates DNA/recombinant vaccinia vaccination.Sci Rep.2015;5:18099.[4] Zahm CD,Colluru VT, McNeel DG.DNA vaccines for prostate cancer. Pharmacol Ther.2017.174:27-42.[5] Hannaman D, Dupuy LC, Ellefsen B,et al.A Phase 1 clinical trial of a DNA vaccine for Venezuelan equine encephalitis delivered by intramuscular or intradermal electroporation.Vaccine. 2016;34(31): 3607-3612.[6] Li J,Mo Z,Li G,et al.Generation and evaluation of virulence attenuated mutants of Edwardsiella tarda as vaccine candidates to combat edwardsiellosis in flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Fish Shellfish Immunol.2015;43(1):175-180.[7] Christopher D.Zahm, V. T., Douglas G.McNeel.Technologies for enhanced efficacy of DNA vaccines.Expert Reviews Vaccines. 2012;11:189-209.[8] Barber GN.Innate immune DNA sensing pathways: STING, AIMII and the regulation of interferon production and inflammatory responses.Curr Opin Immunol.2011;23(1):10-20.[9] Desmet CJ, Ishii KJ.Nucleic acid sensing at the interface between innate and adaptive immunity in vaccination.Nat Rev Immunol. 2012;12(7):479-491.[10] Kobiyama K, Jounai N,Aoshi T,et al.Innate Immune Signaling by, and Genetic Adjuvants for DNA Vaccination.Vaccines (Basel). 2013;1(3):278-292.[11] Nie Y,Wang YY.Innate immune responses to DNA viruses.Protein Cell.2013;4(1):1-7.[12] Chen SP, Peng RH, Chiou PP.Modulatory effect of CpG oligodeoxynucleotide on a DNA vaccine against nervous necrosis virus in orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides).Fish Shellfish Immunol.2015;45(2):919-926.[13] Rekoske BT,Smith HA, Olson BM,et al.PD-1 or PD-L1 Blockade Restores Antitumor Efficacy Following SSX2 Epitope-Modified DNA Vaccine Immunization.Cancer Immunol Res.2015;3(8): 946-955.[14] Ishikawa H,Ma Z,Barber GN.STING regulates intracellular DNA-mediated, type I interferon-dependent innate immunity. Nature.2009;461(7265):788-792.[15] Suschak JJ,Wang S,Fitzgerald KA,et al.A cGAS-Independent STING/IRF7 Pathway Mediates the Immunogenicity of DNA Vaccines.J Immunol.2016;196(1):310-316.[16] Shirota H,Petrenko L,Hattori T,et al.Contribution of IRF-3 mediated IFNbeta production to DNA vaccine dependent cellular immune responses.Vaccine.2009;27(15):2144-2149.[17] Ratsimandresy RA, Dorfleutner A,Stehlik C.An Update on PYRIN Domain-Containing Pattern Recognition Receptors: From Immunity to Pathology.Front Immunol.2013;4:440.[18] Fernandes-Alnemri T,Yu JW, Datta P, et al.AIM2 activates the inflammasome and cell death in response to cytoplasmic DNA.Nature.2009;458(7237):509-513.[19] Liu C,Yue R,Yang Y,et al.AIM2 inhibits autophagy and IFN-β production during M. bovis infection.Oncotarget.2016;7(30): 46972-46987.[20] Suschak JJ, Wang S, Fitzgerald KA,et al.Identification of Aim2 as a sensor for DNA vaccines.J Immunol.2015;194(2):630-636.[21] 秦妍,管晓燕,白国辉,等.基因疫苗黏膜免疫及其机制的研究进展[J].贵州医药,2016,40(4):426-428.[22] Walters JN, Ferraro B, Duperret EK,et al.A Novel DNA Vaccine Platform Enhances Neo-antigen-like T Cell Responses against WT1 to Break Tolerance and Induce Anti-tumor Immunity.Mol Ther.2017;25(4):976-988.[23] Smith TR, Schultheis FK, Morrow MP,et al.Development of an intradermal DNA vaccine delivery strategy to achieve single-dose immunity against respiratory syncytial virus.Vaccine.2017;35(21): 2840-2847.[24] Johnson LE, Frye TP,McNeel DG.Immunization with a prostate cancer xenoantigen elicits a xenoantigen epitope-specific T-cell response.Oncoimmunology. 2012;1(9):1546-1556.[25] Lambert L,Kinnear E, McDonald JU,et al.DNA Vaccines Encoding Antigen Targeted to MHC Class II Induce Influenza-Specific CD8(+) T Cell Responses, Enabling Faster Resolution of Influenza Disease.Front Immunol.2016;7:321.[26] UlmerJ, Otten G.Priming of CTL responses by DNA vaccines-direct transfection of antigen presenting cells versus cross-priming.Developmental Biology.2000;104:9-14.[27] 李敏,董竞男,刘建国,等.基因疫苗作用机制和免疫途径的研究现状[J].贵州医药,2013,37(8):748-751.[28] Hon H,Oran A, Brocker T, et al.B Lymphocytes Participate in Cross-Presentation of Antigen following Gene Gun Vaccination.The Journal of Immunology.2005;174(9):5233-5242.[29] Zhao Y,Wei Z,Yang H,et al.Enhance the anti-renca carcinoma effect of a DNA vaccine targeting G250 gene by co-expression with cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated antigen-4(CTLA-4). Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 2017;90:147-152.[30] Ashok M, Rangarajan P.Immunization with DNA Plasmids Coding for Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus Capsid and Envelope Proteins andor Virus-Like Particles Induces Protection and Survival in Challenged Mice.Vaccine.2002;20(12):1563-1570.[31] Iwasaki A,Medzhitov R.Regulation of adaptive immunity by the innate immune system.Science.2010;327(5963):291-295.[32] Bot A,Stan AC,Inaba K,et al.Dendritic cells at a DNA vaccination site express the encoded influenza nucleoprotein and prime MHC class I-restricted cytolytic lymphocytes upon adoptive transfer. International Immunology.2000;12(6):825-832.[33] Farris E,Brown DM,Ramer-Tait AE,et al.Micro- and nanoparticulates for DNA vaccine delivery.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2016;241(9):919-929.[34] Zhang M,Hong Y,Chen W,et al.Polymers for DNA Vaccine Delivery.ACS Biomaterials Sci Eng.2016;3(2):108-125.[35] Fernando GJ, Zhang J, Ng HI,et al.Influenza nucleoprotein DNA vaccination by a skin targeted, dry coated, densely packed microprojection array (Nanopatch) induces potent antibody and CD8(+) T cell responses.J Control Release.2016;237:35-41.[36] Watkins C,Hopkins J,Harkiss G.Reporter gene expression in dendritic cells after gene gun administration of plasmid DNA. Vaccine.2005;23(33):4247-4256.[37] Hu Y,Xu B,Xu J,et al.Microneedle-assisted dendritic cell-targeted nanoparticles for transcutaneous DNA immunization.Polym Chem. 2015;6(3):373-379.[38] Wang J,Zhu R,Gao B,et al.The enhanced immune response of hepatitis B virus DNA vaccine using SiO2@LDH nanoparticles as an adjuvant.Biomaterials.2014;35(1):466-478.[39] Gerloni M,Rizzi M,Castiglioni P,et al.T cell immunity using transgenic B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004; 101(11):3892-3897.[40] Colluru VT, McNee DG.B lymphocytes as direct antigen-presenting cells for anti-tumor DNA vaccines.Oncotarget. 2016;7(42):67901-67918.[41] Garu A, Moku G, Gulla SK, et al.Genetic Immunization With In Vivo Dendritic Cell-targeting Liposomal DNA Vaccine Carrier Induces Long-lasting Antitumor Immune Response.Mol Ther.2016; 24(2):385-397.[42] 刘浩.凋亡基因与DNA疫苗[J].现代免疫学,2004,24(6):520-522.[43] SasakiS, Xin KQ, Okudela K,et al.Immunomodulation by apoptosis-inducing caspases for an influenza DNA vaccine delivered by gene gun.Gene Therapy.2002;9(12):828-831.[44] Kojima Y, Jounai N, Takeshita F,et al.The degree of apoptosis as an immunostimulant for a DNA vaccine against HIV-1 infection. Vaccine.2007;25(3):438-445.[45] 李平忠.DNA疫苗和细胞凋亡[J].国外医学:预防诊断治疗用生物制品分册,2004,27(5):218-220.[46] Wang Y, Yue X, Jin H, et al.A suicidal DNA vaccine expressing the fusion protein of peste des petits ruminants virus induces both humoral and cell-mediated immune responses in mice.J Virol Methods.2015;225:35-40.[47] Zheng L, Hu Y, Hua Q, et al.Protective immune response in mice induced by a suicidal DNA vaccine encoding NTPase-II gene of Toxoplasma gondii.Acta Trop.2017;166:336-342. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
DNA疫苗:是指将编码特异抗原的基因片段构建在含有表达调控元件的DNA质粒中,将其直接递送体内,使外源基因在活体内表达,表达的抗原诱导机体产生特异的细胞免疫和体液免疫应答,达到治疗和预防疾病的目的。
质粒:是一种染色体外稳定遗传因子,大小1-200 kb不等,以双链、闭环的DNA分子和超螺旋状态存在于宿主细胞。主要存在于细菌、放线菌和真菌细胞中,具有自主复制和转录能力,能在子代细胞中保持稳定的拷贝数,并表达所携带的遗传信息。
文题释义:
DNA疫苗:是指将编码特异抗原的基因片段构建在含有表达调控元件的DNA质粒中,将其直接递送体内,使外源基因在活体内表达,表达的抗原诱导机体产生特异的细胞免疫和体液免疫应答,达到治疗和预防疾病的目的。
质粒:是一种染色体外稳定遗传因子,大小1-200 kb不等,以双链、闭环的DNA分子和超螺旋状态存在于宿主细胞。主要存在于细菌、放线菌和真菌细胞中,具有自主复制和转录能力,能在子代细胞中保持稳定的拷贝数,并表达所携带的遗传信息。.jpg) 文题释义:
DNA疫苗:是指将编码特异抗原的基因片段构建在含有表达调控元件的DNA质粒中,将其直接递送体内,使外源基因在活体内表达,表达的抗原诱导机体产生特异的细胞免疫和体液免疫应答,达到治疗和预防疾病的目的。
质粒:是一种染色体外稳定遗传因子,大小1-200 kb不等,以双链、闭环的DNA分子和超螺旋状态存在于宿主细胞。主要存在于细菌、放线菌和真菌细胞中,具有自主复制和转录能力,能在子代细胞中保持稳定的拷贝数,并表达所携带的遗传信息。
文题释义:
DNA疫苗:是指将编码特异抗原的基因片段构建在含有表达调控元件的DNA质粒中,将其直接递送体内,使外源基因在活体内表达,表达的抗原诱导机体产生特异的细胞免疫和体液免疫应答,达到治疗和预防疾病的目的。
质粒:是一种染色体外稳定遗传因子,大小1-200 kb不等,以双链、闭环的DNA分子和超螺旋状态存在于宿主细胞。主要存在于细菌、放线菌和真菌细胞中,具有自主复制和转录能力,能在子代细胞中保持稳定的拷贝数,并表达所携带的遗传信息。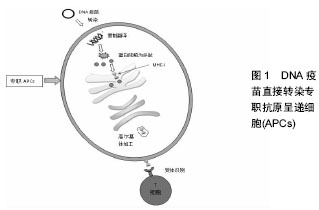

.jpg) 文题释义:
DNA疫苗:是指将编码特异抗原的基因片段构建在含有表达调控元件的DNA质粒中,将其直接递送体内,使外源基因在活体内表达,表达的抗原诱导机体产生特异的细胞免疫和体液免疫应答,达到治疗和预防疾病的目的。
质粒:是一种染色体外稳定遗传因子,大小1-200 kb不等,以双链、闭环的DNA分子和超螺旋状态存在于宿主细胞。主要存在于细菌、放线菌和真菌细胞中,具有自主复制和转录能力,能在子代细胞中保持稳定的拷贝数,并表达所携带的遗传信息。
文题释义:
DNA疫苗:是指将编码特异抗原的基因片段构建在含有表达调控元件的DNA质粒中,将其直接递送体内,使外源基因在活体内表达,表达的抗原诱导机体产生特异的细胞免疫和体液免疫应答,达到治疗和预防疾病的目的。
质粒:是一种染色体外稳定遗传因子,大小1-200 kb不等,以双链、闭环的DNA分子和超螺旋状态存在于宿主细胞。主要存在于细菌、放线菌和真菌细胞中,具有自主复制和转录能力,能在子代细胞中保持稳定的拷贝数,并表达所携带的遗传信息。