中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (19): 2994-2999.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3537
• 干细胞培养与分化 stem cell culture and differentiation • 上一篇 下一篇
人胎盘间充质干细胞来源外泌体保护氧化应激损伤肺上皮细胞的机制
严秀蕊,陶 金,梁雪云
- 宁夏医科大学总医院人类干细胞研究所,宁夏回族自治区银川市 750004
Mechanism by which exosomes from human fetal placental mesenchymal stem cells protect lung epithelial cells against oxidative stress injury
Yan Xiurui, Tao Jin, Liang Xueyun
- Ningxia Human Stem Cell Institute, the General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
外泌体:是一种机体内大多数细胞分泌的直径在30-150 nm之间的包含了复杂 RNA 和蛋白质的微小膜泡。外泌体的功能取决于其所来源的细胞类型,可参与机体免疫应答、抗原提呈、细胞迁移、细胞分化、肿瘤侵袭等多方面。
氧化应激损伤:机体氧化和抗氧化作用失衡,倾向于氧化,造成机体内许多组织细胞凋亡的过程。
背景:前期研究已证实人胎盘间充质干细胞来源培养上清能够通过抑制细胞凋亡保护氧化损伤的肺上皮细胞。
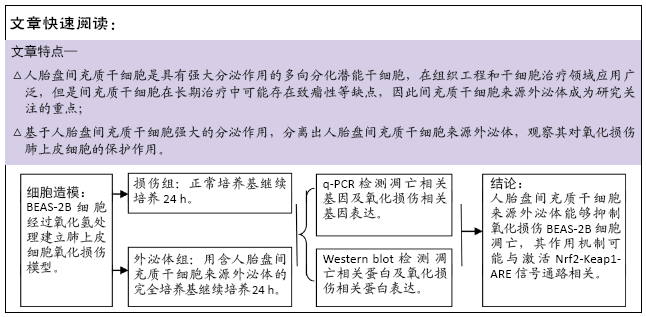
目的:探究人胎盘间充质干细胞来源外泌体对氧化应激损伤肺上皮细胞BEAS-2B的保护作用。
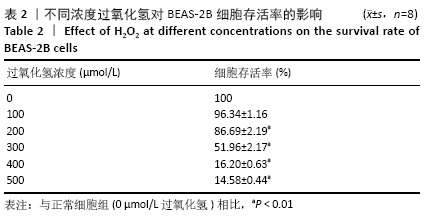
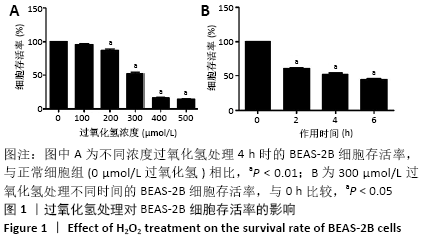
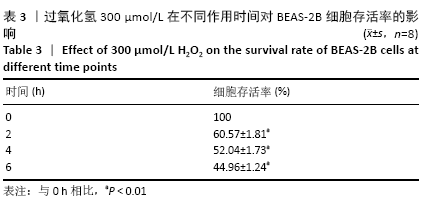
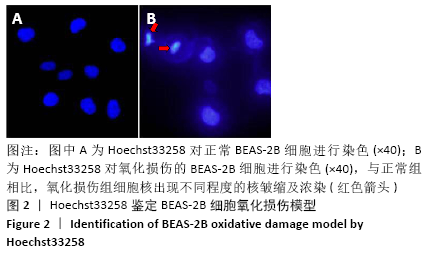
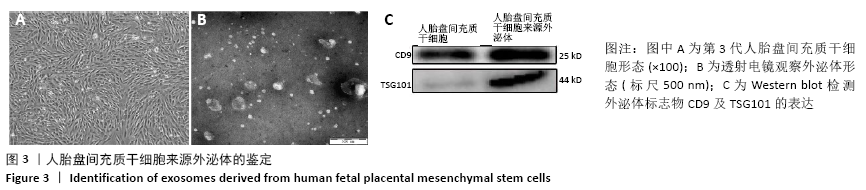
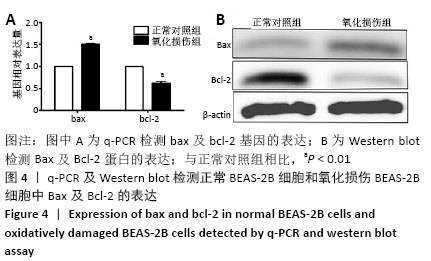
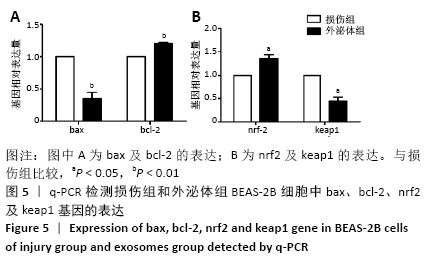
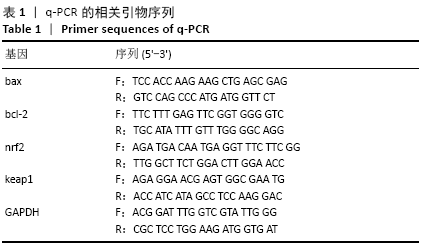
方法:体外培养BEAS-2B细胞,采用含100,200,300,400,500 μmol/L过氧化氢的DME/F-12完全培养基培养细胞4 h,以及用含300 μmol/L过氧化氢的DME/F-12完全培养基分别培养细胞2,4,6 h,CCK-8法测定细胞存活率,以确定过氧化氢氧化损伤模型条件。Hoechst33258染色观察细胞凋亡情况,q-PCR及Western blot检测bax、bcl-2基因和蛋白的表达以确定模型的有效性。收集第3代人胎盘间充质干细胞培养上清,按照外泌体提取试剂盒说明进行外泌体提取,将外泌体作用于氧化损伤的BEAS-2B细胞,q-PCR及Western blot检测bax、bcl-2、nrf2及keap1的表达。
结果与结论:①采用300 μmol/L过氧化氢作用于BEAS-2B细胞4 h,细胞存活率为(51.96±2.17)%,可作为氧化损伤模型的最适条件,且Hoechst33258染色、q-PCR及Western blot证明模型有效;②与损伤组比较,外泌体组bax表达降低而bcl-2表达升高,nrf2表达升高而keap1表达降低,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);③结果提示,人胎盘间充质干细胞来源外泌体能够抑制氧化损伤BEAS-2B细胞凋亡,其作用机制可能与激活Nrf2-Keap1-ARE信号通路相关。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: