[1] CHEN X, WANG Z, DUAN N, et al. Osteoblast-osteoclast interactions. Connect Tissue Res. 2018;59(2):99-107.
[2] BORASCHI D, ITALIANI P, WEIL S, et al. The family of the interleukin-1 receptors. Immunol Rev. 2018;281(1):197-232.
[3] WESCHE H, KORHERR C, KRACHT M, et al. The interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein (IL-1RAcP) is essential for IL-1-induced activation of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK) and stress-activated protein kinases (SAP kinases). J Biol Chem. 1997;272(12):7727-7731.
[4] WANG Q, DELCORDE J, TANG T, et al. Regulation of IL-1 signaling through control of focal adhesion assembly. FASEB J. 2018;32(6):3119-3132.
[5] AKATSU T, TAKAHASHI N, UDAGAWA N, et al. Role of prostaglandins in interleukin-1-induced bone resorption in mice in vitro. J Bone Miner Res. 1991;6(2):183-189.
[6] CAO Y, JANSEN ID, SPRANGERS S, et al. IL-1β differently stimulates proliferation and multinucleation of distinct mouse bone marrow osteoclast precursor subsets. J Leukoc Biol. 2016;100(3):513-523.
[7] AMARASEKARA DS, YUN H, KIM S, et al. Regulation of Osteoclast Differentiation by Cytokine Networks. Immune Netw. 2018;18(1):e8.
[8] LEE WC, GUNTUR AR, LONG F, et al. Energy Metabolism of the Osteoblast: Implications for Osteoporosis. Endocr Rev. 2017;38(3):255-266.
[9] LANGE J, SAPOZHNIKOVA A, LU C, et al. Action of IL-1beta during fracture healing. J Orthop Res. 2010;28(6):778-784.
[10] OLMEDO ML, LANDRY PS, SADASIVAN KK, et al. Regulation of osteoblast levels during bone healing. J Orthop Trauma. 1999;13(5):356-362.
[11] SI J, WANG C, ZHANG D, et al. Osteopontin in Bone Metabolism and Bone Diseases. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:e919159.
[12] FORSPRECHER J, WANG Z, GOLDBERG HA, et al. Transglutaminase-mediated oligomerization promotes osteoblast adhesive properties of osteopontin and bone sialoprotein. Cell Adh Migr. 2011;5(1):65-72.
[13] NALDINI A, LEALI D, PUCCI A, et al. Cutting edge: IL-1beta mediates the proangiogenic activity of osteopontin-activated human monocytes. J Immunol. 2006;177(7):4267-4270.
[14] ATTUR MG, DAVE MN, STUCHIN S, et al. Osteopontin: an intrinsic inhibitor of inflammation in cartilage. Arthritis Rheum, 2001;44(3):578-584.
[15] SHIMODAIRA T, MATSUDA K, UCHIBORI T, et al. Upregulation of osteopontin expression via the interaction of macrophages and fibroblasts under IL-1b stimulation. Cytokine. 2018;110:63-69.
[16] WANG J, HUANG J, ZHU M, et al. Osteopontin potentiates PM-induced IL-1α and IL-1β production via the ERK/JNK signaling pathway. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2019;171:467-474.
[17] REDDI AH. Bone and cartilage differentiation. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994;4(5):737-744.
[18] FUKUI N, ZHU Y, MALONEY WJ, et al. Stimulation of BMP-2 expression by pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1 and TNF-alpha in normal and osteoarthritic chondrocytes. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A Suppl 3: 59-66.
[19] SKODA AM, SIMOVIC D, KARIN V, et al. The role of the Hedgehog signaling pathway in cancer: a comprehensive review. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2018;18(1):8-20.
[20] SILVESTRI L, NAI A, DULJA A, et al. Hepcidin and the BMP-SMAD pathway: an unexpected liaison. Vitam Horm. 2019;110:71-99.
[21] LI L, DONG Q, WANG Y, et al. Hedgehog signaling is involved in the BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol Med. 2015;35(6):1641-1650.
[22] HU Z, CHEN B, ZHAO Q. Hedgehog signaling regulates osteoblast differentiation in zebrafish larvae through modulation of autophagy. Biol Open. 2019;8(5):bio040840.
[23] AKHTAR N, MAKKI MS, HAQQI TM. MicroRNA-602 and microRNA-608 regulate sonic hedgehog expression via target sites in the coding region in human chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67(2):423-434.
[24] LERNER UH, OHLSSON C. The WNT system: background and its role in bone. J Intern Med. 2015;277(6):630-649.
[25] YOSHIDA Y, YAMASAKI S, OI K, et al. IL-1β Enhances Wnt Signal by Inhibiting DKK1. Inflammation. 2018;41(5):1945-1954.
[26] KOMORI T. Molecular Mechanism of Runx2-Dependent Bone Development. Mol Cells. 2020;43(2):168-175.
[27] KOMORI T. Regulation of Proliferation, Differentiation and Functions of Osteoblasts by Runx2. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(7):1694.
[28] DING J, GHALI O, LENCEL P, et al. TNF-alpha and IL-1beta inhibit RUNX2 and collagen expression but increase alkaline phosphatase activity and mineralization in human mesenchymal stem cells. Life Sci. 2009; 84(15-16):499-504.
[29] HUANG RL, YUAN Y, TU J, et al. Opposing TNF-α/IL-1β- and BMP-2-activated MAPK signaling pathways converge on Runx2 to regulate BMP-2-induced osteoblastic differentiation. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5(4): e1187.
[30] LIU X, LI X, HUA B, et al. WNT16 is upregulated early in mouse TMJ osteoarthritis and protects fibrochondrocytes against IL-1β induced inflammatory response by regulation of RUNX2/MMP13 cascade. Bone. 2021;143:115793.
[31] ONO T, NAKASHIMA T. Recent advances in osteoclast biology. Histochem Cell Biol. 2018;149(4):325-341.
[32] SUDA T, TAKAHASHI N, UDAGAWA N, et al. Modulation of osteoclast differentiation and function by the new members of the tumor necrosis factor receptor and ligand families. Endocr Rev. 1999;20(3):345-357.
[33] UDAGAWA N, KOIDE M, NAKAMURA M, et al. Osteoclast differentiation by RANKL and OPG signaling pathways. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021; 39(1):19-26.
[34] MUN SH, PARK PSU, PARK-MIN KH. The M-CSF receptor in osteoclasts and beyond. Exp Mol Med. 2020;52(8):1239-1254.
[35] GYŐRI DS, MÓCSAI A. Osteoclast signal transduction during bone metastasis formation. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:507.
[36] PARK-MIN KH. Metabolic reprogramming in osteoclasts. Semin Immunopathol. 2019;41(5):565-572.
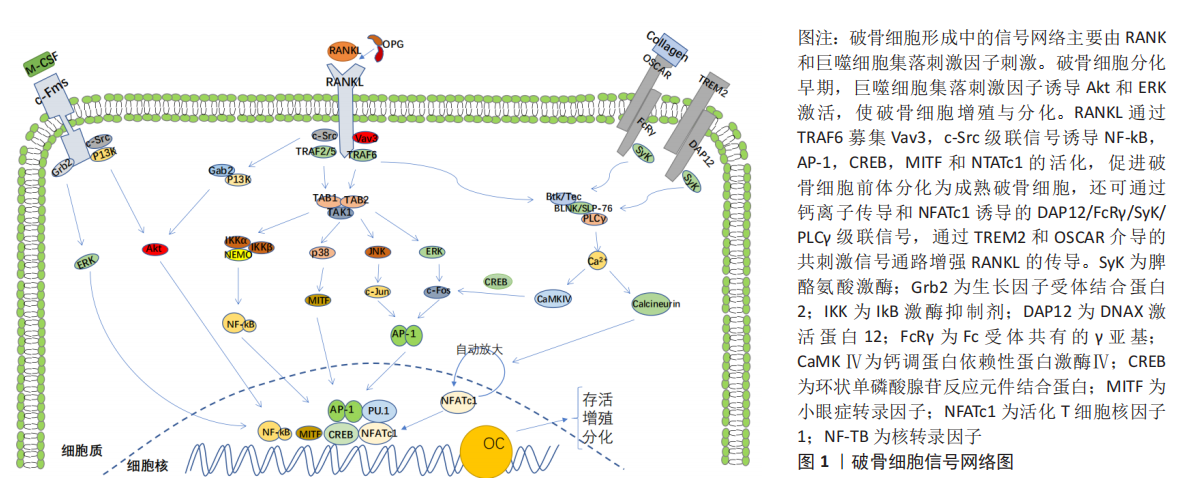
[37] PARK JH, LEE NK, LEE SY. Current understanding of RANK signaling in osteoclast differentiation and maturation. Mol Cells. 2017;40(10):706-713.
[38] TAKAYANAGI H, KIM S, KOGA T, et al. Induction and activation of the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2) integrate RANKL signaling in terminal differentiation of osteoclasts. Dev Cell. 2002;3(6):889-901.
[39] KIM J.H, JIN HM, KIM K, et al. The mechanism of osteoclast differentiation induced by IL-1. J Immunol. 2009;183(3):1862-1870.
[40] ZHOU, J, SONG J, PING F, et al. Enhancement of the p38 MAPK and PKA signaling pathways is associated with the pro-melanogenic activity of Interleukin 33 in primary melanocytes. J Dermatol Sci. 2014;73(2):110-116.
[41] NAKAGAWA N, KINOSAKI M, YAMAGUCHI K, et al. RANK is the essential signaling receptor for osteoclast differentiation factor in osteoclastogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;253(2):395-400.
[42] MA QL, FANG L, JIANG N, et al. Bone mesenchymal stem cell secretion of sRANKL/OPG/M-CSF in response to macrophage-mediated inflammatory response influences osteogenesis on nanostructured Ti surfaces. Biomaterials. 2018;154:234-247.
[43] TREBEC-REYNOLDS DP, VORONOV I, HEERSCHE JN, et al. IL-1alpha and IL-1beta have different effects on formation and activity of large osteoclasts. J Cell Biochem. 2010;109(5):975-982.
[44] MENG M, CHEN Y, CHEN X, et al. IL-1α Regulates Osteogenesis and Osteoclastic Activity of Dental Follicle Cells Through JNK and p38 MAPK Pathways. Stem Cells Dev. 2020;29(24):1552-1566.
[45] PUTNAM NE, FULBRIGHT LE, CURRY JM, et al. MyD88 and IL-1R signaling drive antibacterial immunity and osteoclast-driven bone loss during Staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis. PLoS Pathog. 2019; 15(4):e1007744.
[46] TANABE N, MAENO M, SUZUKI N, et al. IL-1 alpha stimulates the formation of osteoclast-like cells by increasing M-CSF and PGE2 production and decreasing OPG production by osteoblasts. Life Sci. 2005;77(6):615-626.
[47] INFANTE M, FABI A, COGNETTI F, et al. RANKL/RANK/OPG system beyond bone remodeling: involvement in breast cancer and clinical perspectives. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38(1):12.
[48] WILLIAMS LM, GILMORE TD. Looking Down on NF-κB. Mol Cell Biol. 2020;40(15):e00104-e00120.
[49] XING L, CARLSON L, STORY B, et al. Expression of either NF-kappaB p50 or p52 in osteoclast precursors is required for IL-1-induced bone resorption. J Bone Miner Res. 2003;18(2):260-269.
[50] JIMI E, NAKAMURA I, IKEBE T, et al. Activation of NF-kappaB is involved in the survival of osteoclasts promoted by interleukin-1. J Biol Chem. 1998;273(15):8799-8805.
[51] HWANG YH, KIM T, KIM R, et al. The Natural product 6-gingerol inhibits inflammation-associated osteoclast differentiation via reduction of prostaglandin E₂ levels. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(7):2068.
[52] MALTY RH, HUDMON A, FEHRENBACHER JC, et al. Long-term exposure to PGE2 causes homologous desensitization of receptor-mediated activation of protein kinase A. J Neuroinflammation. 2016;13(1):181.
[53] MIYAMOTO T. The dendritic cell-specific transmembrane protein DC-STAMP is essential for osteoclast fusion and osteoclast bone-resorbing activity. Mod Rheumatol. 2006;16(6):341-342.
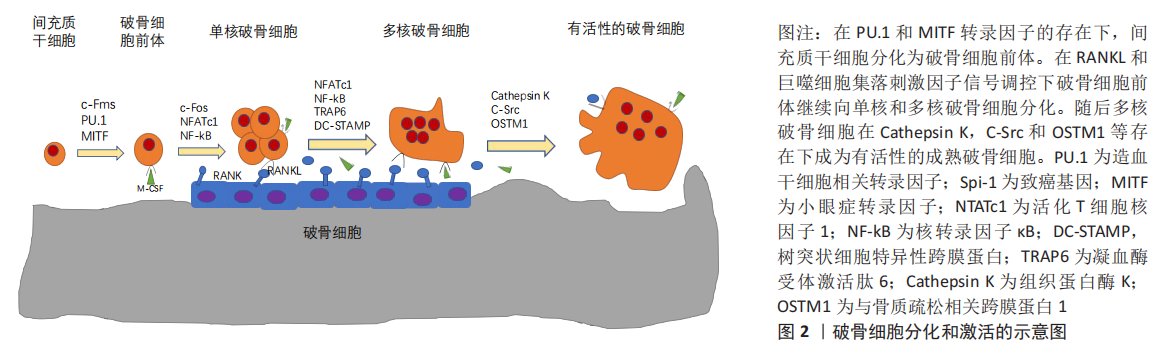
[54] KODAMA J, KAITO T. Osteoclast multinucleation: review of current literature. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(16):5685.
[55] DOU C, DING N, LUO F, et al. Graphene-based microRNA transfection blocks preosteoclast fusion to increase bone formation and vascularization. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2018;5(2):1700578.
[56] JIMI E, NAKAMURA I, DUONG LT, et al. Interleukin 1 induces multinucleation and bone-resorbing activity of osteoclasts in the absence of osteoblasts/stromal cells. Exp Cell Res. 1999;247(1):84-93.
[57] HEGEWALD AB, BREITWIESER K, OTTINGER SM, et al. Extracellular miR-574-5p induces osteoclast differentiation via TLR 7/8 in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. 2020;11:585282.
[58] XING Q, DE VOS P, FAAS MM, et al. LPS promotes pre-osteoclast activity by up-regulating CXCR4 via TLR-4. J Dent Res. 2011;90(2):157-62.
[59] KESSELRING R, GLAESNER J, HIERGEIST A, et al. IRAK-M expression in tumor cells supports colorectal cancer progression through reduction of antimicrobial defense and stabilization of STAT3. Cancer Cell. 2016; 29(5):684-696.
[60] GHOSH S, KARIN M. Missing pieces in the NF-kappaB puzzle. Cell. 2002; 109 Suppl:S81-S96.
[61] KYRIAKIS JM, AVRUCH J. Mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation. Physiol Rev. 2001;81(2):807-869.
[62] SCARNEO SA, HUGHES PF, YANG KW, et al. A highly selective inhibitor of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinases 1/4 (IRAK-1/4) delineates the distinct signaling roles of IRAK-1/4 and the TAK1 kinase. J Biol Chem. 2020;295(6):1565-1574.
[63] KOBAYASHI K, HERNANDEZ LD, GALÁN JE, et al. IRAK-M is a negative regulator of Toll-like receptor signaling. Cell. 2002;110(2):191-202.
[64] LI H, CUARTAS E, CUI W, et al. IL-1 receptor-associated kinase M is a central regulator of osteoclast differentiation and activation. J Exp Med. 2005;201(7):1169-1177.
[65] SCHLÜTER T, SCHELMBAUER C, KARRAM K, et al. Regulation of IL-1 signaling by the decoy receptor IL-1R2. J Mol Med (Berl). 2018;96(10): 983-992.
[66] SUNYER T, LEWIS J, COLLIN-OSDOBY P, et al. Estrogen’s bone-protective effects may involve differential IL-1 receptor regulation in human osteoclast-like cells. J Clin Invest. 1999;103(10):1409-1418.
[67] ENDO Y, KUMAMOTO H, NAKAMURA M, et al. Underlying mechanisms and therapeutic strategies for bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (BRONJ). Biol Pharm Bull. 2017;40(6):739-750.
[68] DEEKS ED. Denosumab: a review in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Drugs Aging. 2018;35(2):163-173.
[69] SILVA BC, COSTA AG, CUSANO NE, et al. Catabolic and anabolic actions of parathyroid hormone on the skeleton. J Endocrinol Invest. 2011;34(10):801-810.
[70] MILLER PD, HATTERSLEY G, RIIS BJ, et al. Effect of abaloparatide vs placebo on new vertebral fractures in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2016;316(7):722-733.
[71] WEIN MN, KRONENBERG HM. Regulation of bone remodeling by parathyroid hormone. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2018;8(8):031237.
[72] SKARIA T, BACHLI E, SCHOEDON G. Gene ontology analysis for drug targets of the whole genome transcriptome of human vascular endothelial cells in response to proinflammatory IL-1. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:414.
[73] WANG X, LUO Y, MASCI PP, et al. Influence of interleukin-1 Beta on platelet-poor plasma clot formation: a potential impact on early bone healing. PLoS One. 2016;11(2):e0149775.
[74] KOGA T, NIIKURA T, LEE SY, et al. In vitro hypertrophy and calcification of human fracture haematoma-derived cells in chondrogenic differentiation. Int Orthop. 2013;37(5):961-967. |