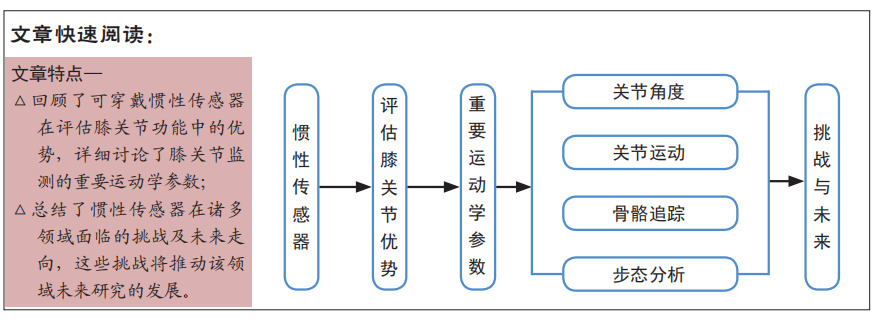
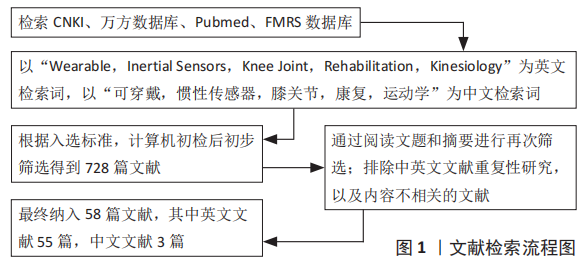
[1] RG A, QLA B. Emotion-relevant activity recognition based on smart cushion using multi-sensor fusion. Information Fusion. 2019;48:1-10.
[2] FORTINO G, GALZARANO S, GRAVINA R, et al. A framework for collaborative computing and multi-sensor data fusion in body sensor networks. Information Fusion. 2015;22:50-70.
[3] CMA B, WL A, JC A, et al. Adaptive sliding window based activity recognition for assisted livings. Information Fusion. 2020;53:55-65.
[4] NCA B, HZ A, SQ A, et al. A sensor-to-segment calibration method for motion capture system based on low cost MIMU - ScienceDirect. Measurement. 2019;131:490-500.
[5] TOGNETTI A, LORUSSI F, CARBONARO N, et al. Wearable Goniometer and Accelerometer Sensory Fusion for Knee Joint Angle Measurement in Daily Life. Sensors (Basel). 2015;15(11):28435-28455.
[6] HA M, HAN D. The relationship between knee joint angle and knee flexor and extensor muscle strength. J Phys Ther Sci. 2017;29(4): 662-664.
[7] FAISAL AI, MAJUMDER S, MONDAL T, et al. Monitoring Methods of Human Body Joints: State-of-the-Art and Research Challenges. Sensors (Basel). 2019;19(11):2629.
[8] VALEVICIUS AM, JUN PY, HEBERT JS, et al. Use of Optical Motion Capture for the Analysis of Normative Upper Body Kinematics during Functional Upper Limb Tasks: A Systematic Review. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2018:1-15.
[9] MOROMIZATO K, KIMURA R, FUKASE H, et al. Whole-body patterns of the range of joint motion in young adults: masculine type and feminine type. J Physiol Anthropol. 2016;35(1):23.
[10] ZHANG H, NIU W, ZHANG S. Extremely Stretchable, Stable, and Durable Strain Sensors Based on Double-Network Organogels. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(38):32640-32648.
[11] JEONG SM, KANG Y, LIM T, et al. Hydrophobic Microfiber Strain Sensor Operating Stably in Sweat and Water Environment. Advanced Materials Interfaces. 2018;5(24). doi: 10.1002/admi.201801376
[12] PARK S, AHN S, SUN J, et al. Highly Bendable and Rotational Textile Structure with Prestrained Conductive Sewing Pattern for Human Joint Monitoring. Adv Funct Mater. 2019;29(10). doi: 10.1002/adfm.201808369
[13] MONTAZERIAN H, DALILI A, MILANI AS, et al. Piezoresistive sensing in chopped carbon fiber embedded PDMS yarns. Composites Part B Engineering . 2020. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.01.090
[14] MILANESE S, GORDON S, BUETTNER P, et al. Reliability and concurrent validity of knee angle measurement: smart phone app versus universal goniometer used by experienced and novice clinicians. Man Ther. 2014; 19(6):569-74.
[15] JENNY JY, BUREGGAH A, DIESINGER Y. Measurement of the knee flexion angle with smartphone applications: Which technology is better? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(9):2874-2877.
[16] VOHRALIK SL, BOWEN AR, BURNS J, et al. Reliability and validity of a smartphone app to measure joint range. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2015;94(4):325-330.
[17] JOHNSON LB, SUMNER S, DUONG T, et al. Validity and reliability of smartphone magnetometer-based goniometer evaluation of shoulder abduction – A pilot study. Man Ther. 2015;20(6):777-782.
[18] CASTAEDA JJ, RUIZ-OLAYA AF, LARA-HERRERA CN, et al. Knee Joint Angle Monitoring System Based on Inertial Measurement Units for Human Gait Analysis. 2017. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-4086-3_173
[19] VARGAS-VALENCIA LS, ELIAS A, ROCON E, et al. An IMU-to-Body Alignment Method Applied to Human Gait Analysis. Sensors (Basel). 2016;16(12):2090.
[20] BONNET V, JOUKOV V, KULIC D, et al. Monitoring of Hip and Knee Joint Angles Using a Single Inertial Measurement Unit During Lower Limb Rehabilitation. IEEE Sens J. 2016;16(6):1557-1564.
[21] ARGENT R, DRUMMOND S, REMUS A, et al. Evaluating the use of machine learning in the assessment of joint angle using a single inertial sensor. J Rehabil Assist Technol Eng. 2019;6:2055668319868544.
[22] CORDILLET S, BIDEAU N, BIDEAU B, et al. Estimation of 3D Knee Joint Angles during Cycling Using Inertial Sensors: Accuracy of a Novel Sensor-to-Segment Calibration Procedure Based on Pedaling Motion. Sensors (Basel). 2019;19(11):2474.
[23] OUBRE B, DANEAULT JF, BOYER K, et al. A Simple Low-Cost Wearable Sensor for Long-Term Ambulatory Monitoring of Knee Joint Kinematics. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2020;67(12):3483-3490.
[24] STRAATEN R, WESSELING M, JONKERS I, et al. Discriminant validity of 3D joint kinematics and centre of mass displacement measured by inertial sensor technology during the unipodal stance task. PLoS ONE. 2020;15(5):e0232513.
[25] CHIANG CY, CHEN KH, LIU KC, et al. Data Collection and Analysis Using Wearable Sensors for Monitoring Knee Range of Motion after Total Knee Arthroplasty. Sensors (Basel). 2017;17(2):418.
[26] TOTARO M, POLIERO T, MONDINI A, et al. Soft Smart Garments for Lower Limb Joint Position Analysis. Sensors (Basel). 2017;17(10):2314.
[27] WANG Z, LIU G, TIAN G. Human skeleton tracking using information weighted consensus filter in distributed camera networks//Chinese Automation Congress (CAC). 2018.
[28] STETTER B, RINGHOF S, KRAFFT FC, et al. Estimation of Knee Joint Forces in Sport Movements Using Wearable Sensors and Machine Learning. Sensors (Basel). 2019;19(17):3690.
[29] SIGWARD SM, CHAN MSM, LIN PE, et al. Characterizing knee loading asymmetry in individuals following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using inertial sensors. Gait Posture. 2016;49:114-119.
[30] ISLAM MU, MAHMUD H, ASHRAF FB, et al. Yoga posture recognition by detecting human joint points in real time using microsoft kinect//2017 IEEE Region 10 Humanitarian Technology Conference (R10-HTC). IEEE, 2017.
[31] AHMADI A, DESTELLE F, UNZUETA L, et al. 3D Human Gait Reconstruction and Monitoring Using Body-Worn Inertial Sensors and Kinematic Modeling. IEEE Sens J. 2016;16(24):8823-8831.
[32] SAUL KR, HU X, GOEHLER CM, et al. Benchmarking of dynamic simulation predictions in two software platforms using an upper limb musculoskeletal model. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2015;18(13):1445-1458.
[33] JALAL A, KAMAL S, KIM D. A Depth Video-based Human Detection and Activity Recognition using Multi-features and Embedded Hidden Markov Models for Health Care Monitoring Systems. International Journal of Interactive Multimedia and Artificial Intelligence. 2017; 4(4):54.
[34] WAN Z, JAILANI R, OMAR AR, et al. Development of MATLAB Kinect Skeletal Tracking System (MKSTS) for gait analysis// 2016 IEEE Symposium on Computer Applications & Industrial Electronics (ISCAIE). IEEE, 2016.
[35] STØVE MP, PALSSON TS, HIRATA RP. Smartphone-based accelerometry is a valid tool for measuring dynamic changes in knee extension range of motion. Knee. 2018;25(1):66-72.
[36] Bae J, Tomizuka M. A tele-monitoring system for gait rehabilitation with an inertial measurement unit and a shoe-type ground reaction force sensor. Mechatronics. 2013;23( 6):646-651.
[37] MAJUMDER S, AGHAYI E, NOFERESTI M, et al. Smart Homes for Elderly Healthcare—Recent Advances and Research Challenges. Sensors (Basel). 2017;17(11):2496.
[38] QIU S, WANG H, LI J, et al. Towards Wearable-Inertial-Sensor-Based Gait Posture Evaluation for Subjects with Unbalanced Gaits. Sensors (Basel). 2020;20(4):1193.
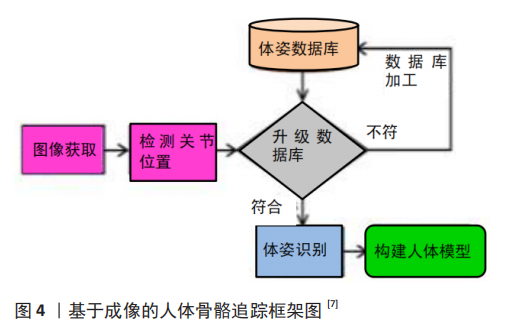
[39] 欧攀,吴帅,周锴.基于深度传感器骨骼追踪的快速人体测量方法[J].激光与光电子学进展,2017,54(12):229-236.
[40] AZIZ O, PARK EJ, MORI G, et al. Distinguishing the causes of falls in humans using an array of wearable tri-axial accelerometers. Gait Posture. 2014;39(1):506-512.
[41] VAN SCHOOTEN KS, PIJNAPPELS M, LORD SR, et al. Quality of Daily-Life Gait: Novel Outcome for Trials that Focus on Balance, Mobility, and Falls. Sensors (Basel). 2019;19(20):4388.
[42] SENSINGER JW, INTAWACHIRARAT N, GARD SA. Contribution of prosthetic knee and ankle mechanisms to swing-phase foot clearance. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2013;21(1):74-80.
[43] QIU S, LIU L, ZHAO H, et al. MEMS Inertial Sensors Based Gait Analysis for Rehabilitation Assessment via Multi-Sensor Fusion. Micromachines (Basel). 2018;9(9):442.
[44] LEAL-JUNIOR AG, FRIZERA A, AVELLAR LM, et al. Polymer Optical Fiber for In-Shoe Monitoring of Ground Reaction Forces During the Gait. IEEE Sens J. 2018:1-1.
[45] VILLENEUVE E, HARWIN W, HOLDERBAUM W, et al. Reconstruction of Angular Kinematics From Wrist-Worn Inertial Sensor Data for Smart Home Healthcare. IEEE Access. 2016;PP(99):1-1.
[46] SCHICKETMUELLER A, ROSE G, HOFMANN M. Feasibility of a Sensor-Based Gait Event Detection Algorithm for Triggering Functional Electrical Stimulation during Robot-Assisted Gait Training. Sensors (Basel). 2019;19(21):4804.
[47] QIU S, LONG L, ZHAO H, et al. MEMS Inertial Sensors Based Gait Analysis for Rehabilitation Assessment via Multi-Sensor Fusion. Micromachines (Basel). 2018;9(9):442.
[48] DONATH L, FAUDE O, LICHTENSTEIN E, et al. Validity and reliability of a portable gait analysis system for measuring spatiotemporal gait characteristics: comparison to an instrumented treadmill. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2016;13:6.
[49] GOMEZ BERNAL A, BECERRO-DE-BENGOA-VALLEJO R, LOSA-IGLESIAS ME. Reliability of the OptoGait portable photoelectric cell system for the quantification of spatial-temporal parameters of gait in young adults. Gait Posture. 2016;50:196-200.
[50] YEO SS, PARK GY. Accuracy Verification of Spatio-Temporal and Kinematic Parameters for Gait Using Inertial Measurement Unit System. Sensors (Basel). 2020;20(5):1343.
[51] KAYAALP ME, AGRES AN, REICHMANN J, et al. Validation of a Novel Device for the Knee Monitoring of Orthopaedic Patients. Sensors (Basel). 2019;19(23):5193.
[52] DE VROEY H, STAES F, WEYGERS I, et al. The implementation of inertial sensors for the assessment of temporal parameters of gait in the knee arthroplasty population. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2018;54:22-27.
[53] 李玳,于宏,梁子轩,等.前交叉韧带断裂三维不对称度步态分析初探[J].中国康复理论与实践,2018,24(8): 956-962.
[54] 袁心一,王家莉,仇一青,等.帕金森病冻结步态的实时监测系统[J].北京生物医学工程,2019,38(2):182-189.
[55] IBRAHIM AA, KÜDERLE A, GAßNER H, et al. Inertial sensor-based gait parameters reflect patient-reported fatigue in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2020;17(1):165.
[56] WEYGERS I, KOK M, KONINGS M, et al. Inertial Sensor-Based Lower Limb Joint Kinematics: A Methodological Systematic Review. Sensors (Basel). 2020;20(3):673.
[57] O’REILLY M, CAULFIELD B, WARD T, et al. Wearable Inertial Sensor Systems for Lower Limb Exercise Detection and Evaluation: A Systematic Review. Sports Med. 2018;48(5):1221-1246.
[58] GIGGINS O, SWEENEY KT, CAULFIELD B. The use of inertial sensors for the classification of rehabilitation exercises. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2014;2014:2965-2968. |