2.1 LncRNA对骨髓间充质干细胞的调控 骨髓间充质干细胞是一种多能干细胞,具有自我更新能力和多向分化潜能。在特定的微环境中诱导,骨髓间充质干细胞可以分化为多种细胞类型,如成骨细胞、脂肪细胞、软骨细胞、神经元、肌细胞等。
2.1.1 LncRNA促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化 LncRNA H19是一种致癌基因,在多种癌症中过度表达,近年来发现了其在骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化中的作用。LncRNA H19的表达在成骨分化第7天开始增加,第14-28天一直维持在较高水平,表明其在成骨分化的早期阶段起着至关重要的作用[5]。随后在诱导成骨细胞分化过程中,LncRNA H19显著上调。在体内和体外实验,LncRNA H19的过表达显著刺激成骨细胞分化,而LncRNA-H19基因敲除则抑制了这些作用[6]。此外,发现绝经后骨质疏松症患者血清和去卵巢(OVX)小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞中LncRNA H19表达降低,LncRNA H19过表达促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化,进一步的研究发现LncRNA H19通过WNT/β-catenin信号通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化[7]。机械拉伸可促进人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化,且增加LncRNA H19的表达,而沉默LncRNA H19抑制机械拉伸诱导的成骨分化,表明LncRNA H19还可以介导机械张力诱导骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化[8]。
LncRNA MALAT1是一个8.5 kb的LncRNA,位于11号染色体,最初在早期非小细胞肺癌研究中发现[9],最近发现了其在骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化中的作用。GAO等[10]的研究中LncRNA MALAT1基因敲除后,骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化明显降低;过表达LncRNA MALAT1基因,骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化明显升高。此外,地塞米松呈剂量依赖性抑制骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,导致成骨标志物如碱性磷酸酶活性下降,Runt相关转录因子2(RUNX2)和碱性磷酸酶表达降低。LncRNA MALAT1的过表达可改善地塞米松诱导的骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化抑制作用[11]。这些都表明LncRNA MALAT1是间充质干细胞成骨分化的正调控因子。但是,
LncRNA MALAT1对骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的调控表现出了矛盾性。一项研究证实LncRNA MALAT1可以通过激活MAPK信号通路来抑制骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,从而促进骨质疏松的进展[12]。
此外,多项研究发现LncRNA可以通过与miRNA相互作用,促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化。如LncRNA
KCNQ1OT1通过海绵化miRNA-214、LncRNA MSC-AS1通过海绵化miRNA-140-5p均可以上调骨形态发生蛋白2的表达、促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化来减轻骨质疏松[13-14];LncRNA GAS5作为miRNA-135A-5p的竞争性内源RNA上调叉形头转录因子O1(forkhead transcription factor O1,FOXO1)的表达,促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化[15];LncRNA XIXT通过靶控miRNA-30A-5p上调RUNX2的表达,从而诱导骨髓间充质干细胞成骨,减轻骨质疏松[16]。骨形态发生蛋白2[17]、FOXO1及RUNX2不仅是骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨或脂肪细胞分化的重要调节因子[18-19],还是成骨细胞和/或破骨细胞等的调节因子。
2.1.2 LncRNA抑制骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化 在骨质疏松症小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞和血清中观察到LncRNA ORLNC1表达上调。LncRNA ORLNC1过表达可显著降低骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨能力;LncRNA ORLNC1基因敲除后促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化[20],表明LncRNA ORLNC1是骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的负调控因子。
SHEN等[21]发现去卵巢(OVX)模型小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞中过表达LncRNA HOTAIR抑制成骨细胞分化,且下调了WNT/β-catenin信号通路相关蛋白(β-catenin、cyclind和c-myc)的表达,而WNT通路拮抗剂DKK1逆转了这一作用。LncRNA HOTAIR基因敲除后可诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化,成骨细胞标志物基因碱性磷酸酶和RUNX2的mRNA水平显著升高。证明LncRNA HOTAIR可以通过抑制WNT/β-catenin
信号通路,抑制大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化。
2.1.3 LncRNA调节骨髓间充质干细胞成脂分化 LncRNA LOXL1-AS1通过调节miRNA-196A-5p/HMGA2轴抑制绝经后骨质疏松症患者骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化、促进成脂分化[22]。
具体表现是在诱导骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化过程中,LncRNA LOXL1-AS1的表达呈逐渐下降趋势。过表达LncRNA LOXL1-AS1后,抑制了骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,但促进了成脂分化。进一步研究发现LncRNA LOXL1-AS1为
miRNA-196A-5P的海绵基因,HMGA2(一种表观遗传因子,促进骨髓间充质干细胞成脂分化[23])为miRNA-196A-5P的靶基因。提示LncRNA LOXL1-AS1通过海绵化miRNA-196A-5p上调HMGA2的表达,对骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化和成脂分化起到相反的调节作用。
关于LncRNA H19,一部分的实验将目光集中于骨髓间充质干细胞的成脂分化上。在诱导骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化过程中LncRNA H19的表达明显降低,第11天下降了80%。在体外LncRNA H19过表达抑制脂肪细胞分化;LncRNA H19基因敲除促进脂肪细胞分化[7],表明LncRNA H19可以负调控骨髓间充质干细胞的成脂分化。在糖皮质激素诱导的骨髓间充质干细胞成脂和成骨分化过程中,LncRNA TCON-00041960的表达下调。此外,上调LncRNA TCON-00041960基因的表达水平,促进了成骨基因RUNX2、OSTERIX(OSX,又称SP7,是一种新的含锌指的成骨细胞特异性转录因子,对成骨细胞增殖、成骨细胞分化和骨形成具有重要作用。遗传学研究表明:OSX在成骨细胞分化信号通路中作为RUNX-2的下游基因[24])和骨钙素,而脂肪细胞特异性标志物的表达减少。提示LncRNA TCON-00041960可以促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化和抑制成脂分化[25]。
2.1.4 LncRNA调节骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨细胞分化 除了成骨和成脂分化外,关于LncRNA调控骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨分化的研究也很多。由于SOX9是软骨形成过程中最重要的转录因子之一,许多研究都集中在SOX9的表达上。如在人骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨细胞诱导分化过程,LncRNA UCA1的过度表达提高了软骨形成标志物Ⅱ型胶原、SOX9的水平,下调了miRNA-145-5p和miRNA-124-3p的表达;而miRNA-145-5p和miRNA-124-3p过表达下调了软骨形成标志物Ⅱ型胶原、SOX9的表达水平,表明LncRNA UCA1可以通过下调miRNA-145-5p和miRNA-124-3p促进骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨细胞分化[26]。
也有实验将目光放在了另一种促进软骨基因表达的转录因子——SCRG1上。过度表达LncRNA ADAMTS9-AS2促进骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨细胞分化。进一步发现LncRNA ADAMTS9-AS2可以海绵miR-942-5p来调节SCRG1的表达[27]。提示LncRNA ADAMTS9-AS2作为竞争性内源RNA在软骨细胞分化过程中起重要作用。
2.1.5 LncRNA调节骨髓间充质干细胞向神经细胞分化 在应用多种神经诱导因子诱导骨髓间充质干细胞分化为神经样细胞过程中,骨髓间充质干细胞获得了神经元样的形态,
LncRNA H19和miRNA-675表达水平的下调伴随着胰岛素样生长因子1的上调,而胰岛素样生长因子1是miRNA-675参与神经细胞形成的既定靶点[28]。目前的研究结果提示LncRNA H19可能在骨髓间充质干细胞的神经分化中起着关键作用。
2.2 LncRNA对成骨细胞的调控 成骨细胞不仅通过合成多种骨基质蛋白在骨形成中起关键作用,而且通过可溶性因子和同源相互作用诱导破骨细胞发育,导致骨吸收[29]。一系列研究表明,不同的LncRNA参与了成骨细胞增殖和功能的调节。
2.2.1 LncRNA促进成骨细胞的增殖和分化 MULATI等[30]提供了LncRNA CNDE通过WNT/β-catenin信号通路促进成骨细胞的增殖证据。SUN等[31]发现小鼠成骨细胞特异性过表达LncRNA OB1基因后,改善了卵巢切除引起的小鼠骨丢失,骨形成率增加和骨量增加;且LncRNA OB1还可显著促进成骨细胞的体外分化。在机制上,LncRNA OB1抑制其启动子上的组蛋白H3在27位赖氨酸(H3K27me3)甲基化,上调OSX在小鼠和人成骨细胞中的表达。表明LncRNA OB1是成骨细胞增殖和矿化的正调节因子。
长时间的机械卸载(如长时间太空飞行和长时间卧床)会导致人类失用性骨质疏松症[32]。越来越多的证据表明LncRNA通过调节成骨细胞的代谢来缓解人类失用性骨质疏松症。研究发现向后肢模拟骨骼卸载模型(HLU)小鼠补充LncRNA OGRU可以部分缓解卸载引起的骨丢失,证明了LncRNA与失用性骨质疏松症的相关性[33]。另一个研究发现发现模拟微重力条件下与成骨细胞分化相关的LncRNA ODSM在体外可以抑制成骨细胞凋亡,促进成骨细胞矿化。在微重力卸载条件下,LncRNA ODSM表达水平的增加部分减少了MC3T3-E1细胞的凋亡,促进了细胞的分化。在后肢去负荷的小鼠补充LncRNA ODSM可导致骨组织中凋亡细胞数量的减少和成骨细胞活性的增加。并且在成骨细胞中靶向过表达LncRNA ODSM在微观结构和生物力学水平上部分逆转了机械卸载引起的骨丢失。这些发现提示LncRNA在失用性骨质疏松症骨量减少治疗中具有潜在的价值[34]。
2.2.2 LncRNA抑制成骨细胞的增殖和分化 ZHANG等[35]证实了LncRNA UCA1可抑制成骨细胞的增殖和分化。细胞实验表明,LncRNA UCA1敲除后可明显促进成骨细胞系MC3T3-E1的增殖和分化,分化相关基因RUNX2、骨保护素和骨桥蛋白的mRNA水平下降;过表达LncRNA UCA1则作用相反。
在另一项研究中,绝经后骨质疏松症小鼠LncRNA ANCR表达增加,细胞内钙离子浓度升高。沉默LncRNA ANCR后,可显著增加成骨细胞增殖、碱性磷酸酶活性、钙沉积,减少细胞凋亡;同时,沉默LncRNA ANCR还促进了羟基磷灰石-磷酸三钙处理的小鼠的类骨形成;当下调LncRNA ANCR的表达后,提高了RUNX2和OSX的表达水平。这些表明LncRNA ANCR可抑制绝经后骨质疏松症成骨细胞的成骨[36]。
2.3 LncRNA对破骨细胞的调控 破骨细胞来源于造血干细胞或巨大的多核细胞的单核/巨噬细胞前体细胞,它们负责骨吸收[37]。多项研究验证了LncRNA在破骨细胞功能和骨吸收中的调控作用。
2.3.1 LncRNA促进破骨细胞增殖、分化 LncRNA LINC00311过表达诱导破骨细胞增殖和抑制凋亡,LncRNA LINC00311敲除后细胞凋亡率升高[38]。LncRNA NEAT1是促进破骨细胞增殖的一个潜在的、独立的、有影响的因子。LncRNA NEAT1基因的敲除减弱了破骨细胞的形成,而过表达LncRNA NEAT1则加速了破骨细胞的形成;同时,体内实验发现LncRNA NEAT1与miRNA-7竞争性结合,促进破骨细胞的生成,并减少了小鼠的骨量[39]。
LIU等[40]发现上调LncRNA LNC-AK077216的水平会促进破骨细胞分化、骨吸收和NFATC1(破骨细胞分化的主要调节者,调节一些破骨细胞特异性基因,如组织蛋白酶K、降钙素受体和破骨细胞相关受体,从而促进破骨细胞增殖、分化[41])的表达;此外,发现LncRNA LNC-AK077216和NFATC1在去卵巢小鼠骨髓和脾脏组织中表达均上调。提示LncRNA LNC-AK077216可调节NFATC1的表达,促进破骨细胞的形成和功能,为破骨细胞的分化提供了新的机制。
2.3.2 LncRNA促进破骨细胞凋亡 众所周知,核因子κB受体活化因子配体是一种明确的破骨细胞分化调节因子,也是激活骨重建调控的关键细胞因子。在破坏性骨代谢紊乱中,核因子κB受体活化因子配体的高表达被认为是一个有害因素[42]。
LncRNA BMNCR可以抑制核因子κB受体活化因子配体诱导的破骨细胞增殖、分化,减缓骨质疏松的进展。在骨质疏松症小鼠骨髓和脾脏中发现LncRNA BMNCR低表达;在核因子κB受体活化因子配体诱导的体外破骨细胞分化过程中,LncRNA BMNCR的表达逐渐下调,在72 h达到最低水平;相反的是,LncRNA BMNCR过表达减少了破骨细胞的数量,抑制了骨吸收能力,下调了破骨细胞相关基因(ATP6VOD2、ACP5和CTR)的表达水平[43]。
2.4 LncRNA对软骨细胞的调控 大量的LncRNAs通过调节miRNA及其下游途径和蛋白的表达,在体外或体内模型中被证实可以诱导软骨细胞凋亡和促进骨关节炎的发展,如基质金属蛋白酶、去整合素金属蛋白酶(a disintegrin and
metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs,ADAMTS)、Ⅱ型胶原和聚集蛋白聚糖(aggrecan,ACAN),基质金属蛋白酶和ADAMTS是已知的主要软骨降解酶,Ⅱ型胶原和ACAN是软骨细胞中重要的细胞外基质蛋白。
在骨关节炎的发病过程中,LncRNA GAS5的过表达促进软骨细胞凋亡,减少软骨细胞自噬,且抑制了miRNA-21的表达。此外,在小鼠模型中miRNA-21的过表达导致LncRNA GAS5和基质金属蛋白酶2,3,9,13和ADAMTS-4的表达水平降低,而Ⅱ型胶原和ACAN的表达水平增加[44]。提示LncRNA GAS5可以通过海绵miRNA-21,促进软骨细胞凋亡。LncRNA MALAT1基因敲除可抑制软骨细胞增殖,促进细胞凋亡。同时,LncRNA MALAT1基因敲除增加了白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞基质金属蛋白酶13、ADAMTS-5的表达,降低了Ⅱ型胶原和ACAN的表达[45]。LncRNA HOTAIR可直接与miRNA-17-5p结合,促进细胞外基质降解和软骨细胞凋亡。此外,还发现LncRNA HOTAIR的过表达和下调分别显著增加和降低了ADAMTS-5的表达[46]。LncRNA HOTAIR可能成为抑制人骨关节炎软骨中ADAMTS-5的一个新的治疗靶点。
2.5 其他 成骨细胞中Ⅰ型胶原a1与a2的正常比例(2∶1)维持正常的骨微结构。Ⅰ型胶原a1与a2比例的改变会导致胶原蛋白同源三聚体的形成和骨骼微结构的恶化。体外细胞实验表明,LncRNA AWPPH基因敲除导致成骨细胞a1表达上调,a2表达下调,使比值高于2∶1;反之,LncRNA AWPPH过表达导致成骨细胞a1表达下调,a2表达上调,使比值低于2∶1。在骨质疏松患者中LncRNA AWPPH表达水平下调,并改变了成骨细胞Ⅰ型胶原a1和a2的比例,改变了骨骼微结构[47]。
2.6 LncRNA调控的信号通路 常见的LncRNA调节的信号通路有WNT、TGF-β/BMPs、NOTCH及PI3K/AKT信号通路,其他的信号通路如成纤维细胞生长因子、Hedgehogs(HH)等也有报道。信号通路之间往往存在串扰,共同参与对骨细胞代谢的调控。
2.6.1 WNT信号通路 WNT家族由许多分泌的糖蛋白组成。作为几乎所有生物进化过程中高度保守的信号通路,WNT信号参与了许多重要的生物学过程,如发育、细胞增殖和细胞分化。根据β-catenin是否参与,WNT信号可以分为经典(β-catenin依赖的)和非经典的(β-catenin不依赖的)途径。在骨细胞的代谢过程中,经典的途径被更多地研究。在经典途径中,WNT蛋白与属于Frizzled(FZD)家族的7-跨膜区特异性受体结合,这种结合是由低密度脂蛋白相关蛋白5和6(LRP-5/6)介导的。然后,该信号被转导并与胞浆内的磷蛋白DSH结合,抑制胞浆内β-catenin降解。在这些条件下,β-catenin在细胞质中积累并移位到细胞核,在那里它与转录因子TCF和LEF结合,激活靶基因的转录[48]。
越来越多的证据表明,LncRNA可以通过WNT信号通路来调控骨相关细胞的分化。例如LncRNA LINC-ROR作为miRNA-138和miRNA-14的竞争性内源RNA,抑制共同靶标ZEB2,最终激活WNT/β-catenin信号通路,促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化[49]。
2.6.2 TGF-β/BMPs信号通路 转化生长因子β和骨形态发生蛋白作用于四聚体受体复合体,分别向典型的Smad依赖的信号通路(即转化生长因子β/骨形态发生蛋白配体、受体和Smad)和非典型的Smad不依赖的信号通路(即MAPK)传导信号,调节成骨细胞分化、骨骼发育、骨形成及骨稳态。此外,转化生长因子β/骨形态发生蛋白信号通路与几种重要的细胞因子信号通路(如骨髓间充质干细胞、NOTCH)之间也存在串扰,以协调成骨、骨骼发育和骨稳态[50]。
(1)典型Smad依赖的信号通路:LncRNA MSC-AS1通过海绵microRNA-140e5p,上调骨形态发生蛋白2和Smad1/5/8水平促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化[15]。在体外沉默LncRNA KCNQ1OT1通过直接调控miRNA-214抑制骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化。LncRNA KCNQ1OT1基因敲除显著下调骨形态发生蛋白2、p-Smad1/5/8的蛋白水平。miRNA-214抑制剂可逆转沉默LncRNA KCNQ1OT1诱导的骨形态发生蛋白2、pSmad1/5/8蛋白水平[14]。表明LncRNA KCNQ1OT1可能通过海绵作用调节骨形态发生蛋白2的表达及其下游的Smad信号通路抑制骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化。
(2)非典型Smad不依赖的信号通路(MAPK)信号通路:沉默LncRNA MALAT1基因后,促进了骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化,上调了MAPK信号通路相关蛋白细胞外信号调节激酶1/2(ERK1/2)和P38的表达水平。在另一项研究中,体外诱导骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化,蛋白磷酸化酪氨酸磷酸化蛋白激酶(P-P38)表达水平升高,LncRNA SNHG1表达下调。LncRNA SNHG1过表达破坏了p-p38的蛋白稳定性,促进了P-P38的泛素化,抑制了P38的活性。这些结果表明LncRNA MALAT1、LncRNA SNHG1通过p38MAPK信号通路,从而调控骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化[51]。
2.6.3 NOTCH信号通路 NOTCH受体在内质网中产生,并运输到质膜。受体与细胞上的跨膜配体的相互作用,一系列的裂解暴露出NOTCH胞内域(NICD),NICD移位到细胞核,在细胞核它诱导NOTCH靶基因的转录。在成骨细胞系的细胞中,NOTCH激活抑制细胞分化,并由于骨形成障碍而导致松质骨骨量减少。在破骨细胞系的细胞中,NOTCH1抑制破骨细胞生成和骨吸收,而NOTCH2促进破骨细胞生成和骨吸收[52]。
LncRNA H19通过聚集与NOTCH配体相关的miRNAs,如miRNA-107、miRNA-27b和miRNA-106b,介导骨形态发生蛋白9诱导间骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化[53]。在骨质疏松症大鼠破骨细胞过表达LncRNA LINC00311,促进了破骨细胞增殖、分化;且上调了NOTCH2的表达水平,降低NOTCH1的表达水平。提示LncRNA LINC00311可能通过NOTCH信号通路促进骨质疏松大鼠破骨细胞增殖分化。
2.6.4 PI3K/AKT信号通路 磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(PI3K)-蛋白激酶B(AKT)通路在细胞代谢过程中普遍存在。PI3K激活后在质膜上产生第二信使三磷酸肌醇(PIP3),PIP3与细胞内含有pH结构域的信号蛋白AKT和3-磷酸肌醇依赖性蛋白激酶1
(3-phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1,PDK1)结合,促使PDK1磷酸化AKT蛋白使其活化,活化的AKT通过磷酸化作用激活或抑制其下游靶蛋白,进而调节骨细胞的增殖、分化及凋亡等[54]。
一项实验发现了LncRNA AK023948通过PI3K/AKT信号通路实现对雌激素缺乏性骨质疏松大鼠破骨细胞代谢的调控。绝经后骨质疏松大鼠的骨组织中PI3K、AKT和PDK1水平显著降低。在大鼠成骨细胞中,LncRNA AK023948基因的过度表达上调了AKT的磷酸化水平,敲除LncRNA AK023948基因导致细胞中AKT磷酸化水平下调,成骨细胞的增殖率下降[55]。
2.7 LncRNA调控的主要机制
2.7.1 LncRNA与miRNA的相互作用 编码RNA和非编码RNA之间通过竞争miRNA结合位点来相互调节广泛的串扰网络已经被确定。基于这个网络,提出了竞争性内源RNA假说。某些LncRNA的碱基对通过充当海绵或诱饵有效地消耗miRNA。
此外,一些LncRNA作为miRNA的前体来调节基因表达[56]。
近年来,越来越多的实验研究了LncRNA通过miRNA的相互作用来调控骨相关细胞。如LncRNA FOXD2-AS1通过作为miRNA-206的海绵调节CCND1的表达来调节骨关节炎软骨细胞的增殖[57];LncRNA TUG1通过海绵miRNA-195上调基质金属蛋白酶13的表达水平,促进了软骨细胞外基质降解[58]。
2.7.2 LncRNA通过与转录因子结合进行调控 核因子κB 家族蛋白是近年来研究较多的核转录因子,核因子κB家族蛋白与细胞的增殖、凋亡等息息相关。P65、p50及IκBα蛋白是常见的核因子κB家族蛋白成员[59]。LncRNA MIR31HG基因的敲除不仅能显著促进人脂肪干细胞的成骨分化,而且能显著缓解炎症对脂肪干细胞成骨的抑制作用。从机制上讲,LncRNA MIR31HG直接与IκBα结合,并参与其磷酸化和核因子κB的活化。沉默IκBα可消除MIR31HG与核因子κB:IκB复合物的亲和力[60]。
SOX2转录因子是SOX基因家庭成员,跟细胞分化紧密关联,属诱导干细胞的核心转录因子,也属于保持干细胞特征的关键基因,可以调节血细胞形成和骨组织发育等[61]。LncRNA MEG3位于骨形态发生蛋白4基因附近,将转录因子SOX2从骨形态发生蛋白4启动子中分离出来并与之结合,增加骨形态发生蛋白4基因的表达,从而促进多发性骨髓瘤患者骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[62]。LncRNA MEG3与SOX2结合调控骨形态发生蛋白4的机制见图2。

2.7.3 表观遗传修饰
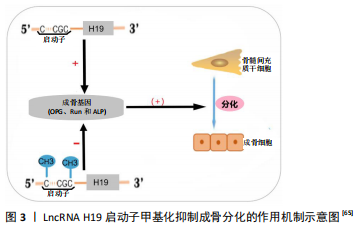
(1)甲基化修饰:近年来,几项研究报道了LncRNA介导甲基化修饰参与了骨髓间充质干细胞分化和成骨细胞分化等过程。如LncRNA PLNC1通过DNA甲基化介导骨髓间充质干细胞成脂分化[64]。在失用性骨质疏松中,HLU小鼠LncRNA H19启动子高度甲基化,DNMT1表达水平提高,LncRNA H19的表达水平下降。在体外,UMR-106细胞过表达DNMT1导致H19启动子甲基化,H19低表达,从而抑制了成骨基因(骨保护素、Runx2和碱性磷酸酶)的表达水平[65]。LncRNA H19启动子甲基化抑制成骨分化的作用机制见图3。
组蛋白甲基转移酶Zeste同源蛋白2增强子(EZH2)在干细胞中高表达,并参与其向不同细胞系的分化。EZH2可以在靶基因启动子中催化H3K27me3甲基化达到抑制基因表达的目的[66]。最近的研究表明,一些LncRNA与EZH2相互作用,调节基因表达。LncRNA ANCR 3'端的305-nt区域可以与EZH2结合,通过催化Runx2基因启动子中的H3K27me3的甲基化来抑制RUNX2的表达,从而抑制成骨细胞分化。
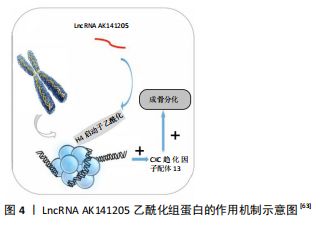
(2)乙酰化修饰:一些LncRNA通过乙酰化组蛋白调节骨髓间充质干细胞的分化。LncRNA HIF1α-AS1通过促进组蛋白乙酰化增加HOXD10的表达,从而促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[67]。上调LncRNA AK141205可诱导间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化。从机制上讲,LncRNA AK141205通过乙酰化组蛋白H4的启动子,上调CXC趋化因子配体13(CXCL13)的表达水平从而促进了成骨细胞分化[68]。LncRNA AK141205乙酰化组蛋白的作用机制见图4。