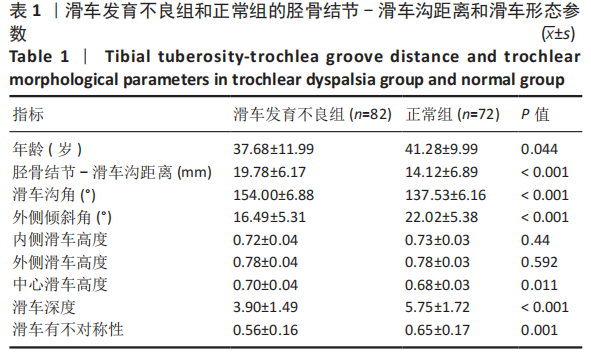
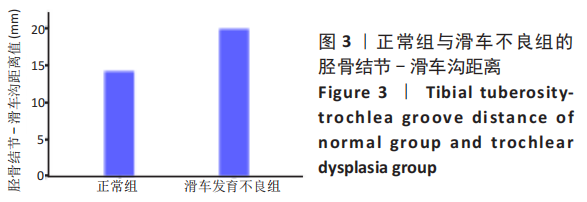
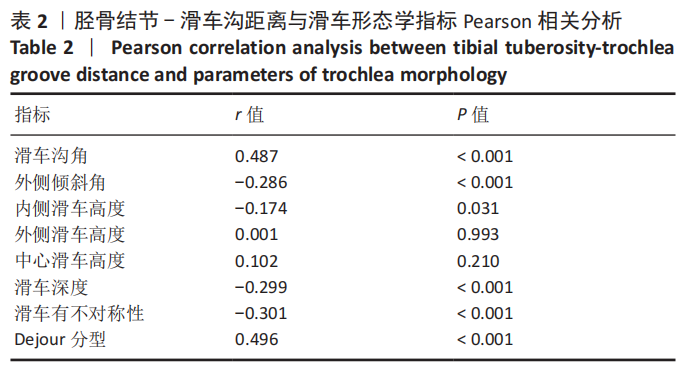
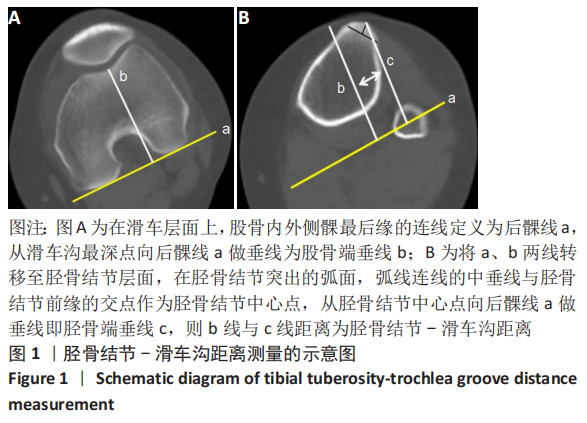
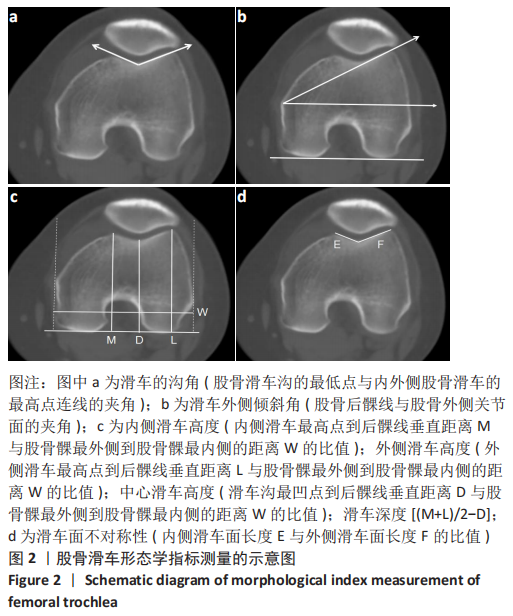
[1] IRGER M, ACHTNICH A, IMHOFF AB, et al. Diagnosis and therapy of chronic patellofemoral instability. Orthopade. 2020;49(1):73-84.
[2] FROSCH S, BALCAREK P, WALDE TA, et al. The treatment of patellar dislocation: a systematic review. Z Orthop Unfall. 2011;149(6):630-645.
[3] WEBER AE, NATHANI A, DINES JS, et al. An Algorithmic Approach to the Management of Recurrent Lateral Patellar Dislocation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016;98(5):417-427.
[4] STEENSEN RN, BENTLEY JC, TRINH TQ, et al. The prevalence and combined prevalences of anatomic factors associated with recurrent patellar dislocation: a magnetic resonance imaging study. Am J Sports Med. 2015;43(4):921-927.
[5] SUNDARARAJAN SR, RAJ M, RAMAKANTH R, et al. Prediction of recurrence based on the patellofemoral morphological profile and demographic factors in first-time and recurrent dislocators. Int Orthop. 2020;44(11):2305-2314.
[6] HUNTINGTON LS, WEBSTER KE, DEVITT BM, et al. Factors Associated With an Increased Risk of Recurrence After a First-Time Patellar Dislocation: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Am J Sports Med. 2020;48(10):2552-2562.
[7] SANDERS TL, PAREEK A, HEWETT TE, et al. High rate of recurrent patellar dislocation in skeletally immature patients: a long-term population-based study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26(4):1037-1043.
[8] VAN HAVER A, DE ROO K, DE BEULE M, et al. The effect of trochlear dysplasia on patellofemoral biomechanics: a cadaveric study with simulated trochlear deformities. Am J Sports Med. 2015;43(6):1354-1361.
[9] REZVANIFAR SC, FLESHER BL, JONES KC, et al. Lateral patellar maltracking due to trochlear dysplasia: A computational study. Knee. 2019;26(6):1234-1242.
[10] DEJOUR H, WALCH G, NOVE-JOSSERAND L, et al. Factors of patellar instability: an anatomic radiographic study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 1994;2(1):19-26.
[11] LEWALLEN L, MCINTOSH A, DAHM D. First-Time Patellofemoral Dislocation: Risk Factors for Recurrent Instability. J Knee Surg. 2015;28(4):303-309.
[12] GARRON E, JOUVE JL, TARDIEU C, et al. Anatomic study of the anterior patellar groove in the fetal period. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 2003;89(5): 407-412.
[13] GLARD Y, JOUVE JL, GARRON E, et al. Anatomic study of femoral patellar groove in fetus. J Pediatr Orthop. 2005;25(3):305-308.
[14] LU J, WANG C, LI F, et al. Changes in Cartilage and Subchondral Bone of Femoral Trochlear Groove After Patellectomy in Growing Rabbits. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(2): 653-660.
[15] HURI G, ATAY OA, ERGEN B, et al. Development of femoral trochlear groove in growing rabbit after patellar instability. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(2):232-238.
[16] KAYMAZ B, ATAY OA, ERGEN FB, et al. Development of the femoral trochlear groove in rabbits with patellar malposition. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(8):1841-1848.
[17] ØYE CR, FOSS OA, HOLEN KJ. Breech presentation is a risk factor for dysplasia of the femoral trochlea. Acta Orthop. 2016;87(1):17-21.
[18] FERLIC PW, RUNER A, DAMMERER D, et al. Patella Height Correlates With Trochlear Dysplasia: A Computed Tomography Image Analysis. Arthroscopy. 2018; 34(6):1921-1928.
[19] 徐鑫. 高位髌骨与股骨滑车发育不良的相关性分析[D]. 济南:山东大学,2019.
[20] STEPHEN JM, LUMPAOPONG P, DODDS AL, et al. The effect of tibial tuberosity medialization and lateralization on patellofemoral joint kinematics, contact mechanics, and stability. Am J Sports Med. 2015;43(1):186-194.
[21] 纪刚. 胫骨结节转移术对髌骨关节接触压力影响的生物力学研究[D]. 石家庄:河北医科大学,2013.
[22] CARRILLON Y, ABIDI H, DEJOUR D, et al. Patellar instability: assessment on MR images by measuring the lateral trochlear inclination-initial experience. Radiology. 2000;216(2):582-585.
[23] PAIVA M, BLØND L, HÖLMICH P, et al. Quality assessment of radiological measurements of trochlear dysplasia; a literature review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26(3):746-755.
[24] BIEDERT RM, BACHMANN M. Anterior-posterior trochlear measurements of normal and dysplastic trochlea by axial magnetic resonance imaging. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2009;17(10):1225-1230.
[25] PFIRRMANN CW, ZANETTI M, ROMERO J, et al. Femoral trochlear dysplasia: MR findings. Radiology. 2000;216(3):858-864.
[26] IMHOFF FB, FUNKE V, MUENCH LN, et al. The complexity of bony malalignment in patellofemoral disorders: femoral and tibial torsion, trochlear dysplasia, TT-TG distance, and frontal mechanical axis correlate with each other. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28(3):897-904.
[27] BRATTSTROEM H. Shape of the intercondylar groove normally and in recurrent dislocation of patella. A clinical and x-ray-anatomical investigation. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl. 1964;68:SUPPL 68:1-148.
[28] ØYE CR, FOSS OA, HOLEN KJ. Minor change in the sulcus angle during the first six years of life: a prospective study of the femoral trochlea development in dysplastic and normal knees. J Child Orthop. 2018;12(3):245-250.
[29] WANG S, JI G, YANG X, et al. Femoral trochlear groove development after patellar subluxation and early reduction in growing rabbits. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(1):247-253.
[30] LIEBENSTEINER MC, RESSLER J, SEITLINGER G, et al. High Femoral Anteversion Is Related to Femoral Trochlea Dysplasia. Arthroscopy. 2016;32(11):2295-2299.
[31] 付琨朋. 复发性髌骨脱位伴股骨滑车发育不良的儿童患者在手术纠正髌骨位置后滑车形态的变化[D]. 石家庄:河北医科大学,2018.
[32] 陈辉,王群,燕双喜,等.外侧支持带松解联合髌骨韧带重建修复复发性髌骨脱位[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(29):4747-4751.
[33] 任逸众,韩长旭,贾岩波,等.自体腘绳肌腱重建内侧髌股韧带治疗复发性髌骨脱位:中期随访评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(42):6822-6826.
[34] RAJDEV NR, PARIKH SN. Femoral trochlea does not remodel after patellar stabilization in children older than 10 years of age. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2019; 28(2):139-143.
|