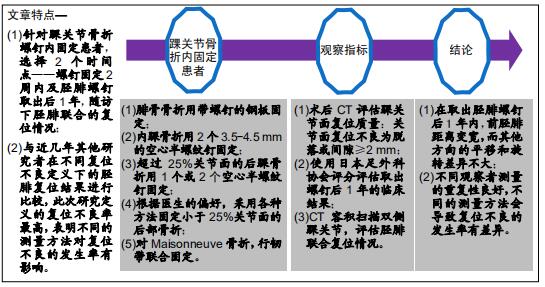
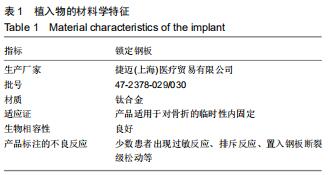
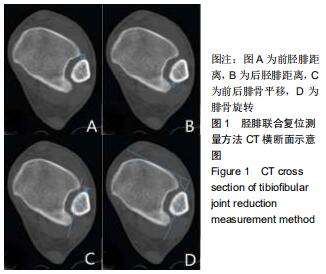
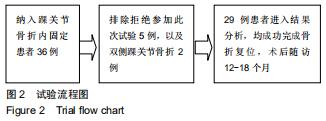
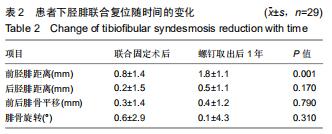
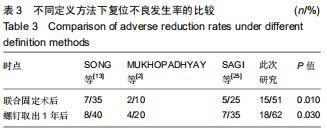
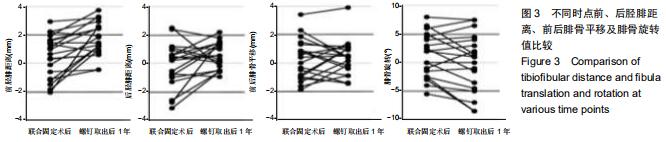
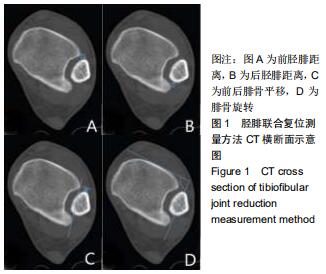
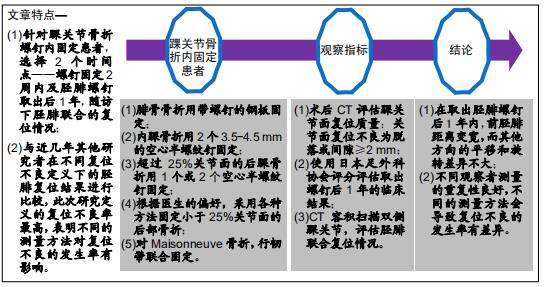
|
[1] DATTANI R, PATNAIK S, KANTAK A,et al. Injuries to the tibiofibular syndesmosis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;(90): 405-410.
[2] MUKHOPADHYAY S, METCALFE A, GUHA AR, et al. Malreduction of syndesmosis-are we considering the anatomical variation? Injury. 2011;(42):1073-1076.
[3] OSTRUM RF, AVERY MC. open reduction internal fixation of a bimalleolar ankle fracture with syndesmotic injury. J Orthop Trauma. 2016;30 Suppl 2:S43-44.
[4] SCHEPERS T. Acute distal tibiofibular syndesmosis injury: a systematic review of suture-button versus syndesmotic screw repair. Int Orthop. 2012;(36):1199-1206.
[5] BEKEROM MP, HOGERVORST M, BOLHUIS HW, et al. Operative aspects of the syndesmotic screw: review of current concepts. Injury. 2008;(39):491-498.
[6] JORDAN TH, TALARICO RH, SCHUBERTH JM. The radiographic fate of the syndesmosis after trans-syndesmotic screw removal in displaced ankle fractures. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2011;(50):407-412.
[7] GENNIS E, KOENIG S, RODERICKS D, et al. The fate of the fixed syndesmosis over time. Foot Ankle Int. 2015;(36):1202-1208.
[8] 吴少科,陈晓驷,陈海聪,等.皮质骨螺钉与Endobutton钢板治疗踝关节骨折合并下胫腓联合损伤的疗效比较[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2018,20(12): 1091-1094.
[9] NAULT ML, HÉBERT-DAVIES J, LAFLAMME GY, et al. CT scan assessment of the syndesmosis: a new reproducible method. J Orthop Trauma. 2013;(27):638-641.
[10] WARNER SJ, FABRICANT PD, GARNER MR, et al. The measurement and clinical importance of syndesmotic reduction after operative fixation of rotational ankle fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;(97): 1935-1944.
[11] GARDNER MJ, DEMETRAKOPOULOS D, BRIGGS SM, et al. Malreduction of the tibiofibular syndesmosis in ankle fractures. Foot Ankle Int. 2006;(27):788-792.
[12] KORTEKANGAS T, SAVOLA O, FLINKKILÄ T, et al. A prospective randomised study comparing TightRope and syndesmotic screw fixation for accuracy and maintenance of syndesmotic reduction assessed with bilateral computed tomography. Injury. 2015;(46): 1119-1126.
[13] SONG DJ, LANZI JT, GROTH AT, et al. The effect of syndesmosis screw removal on the reduction of the distal tibiofibular joint: a prospective radiographic study. Foot Ankle Int. 2014;(35):543-548.
[14] KNOPS SP, KOHN MA, HANSEN EN, et al. Rotational malreduction of the syndesmosis: reliability and accuracy of computed tomography measurement methods. Foot Ankle Int. 2013;(34):1403-1410.
[15] GIFFORD PB, LUTZ M. The tibiofibular line: an anatomical feature to diagnose syndesmosis malposition. Foot Ankle Int. 2014;(35): 1181-1186.
[16] STUFKENS SA, BEKEROM MP, DOORNBERG JN, et al. Evidence-based treatment of maisonneuve fractures. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2011;(50):62-67.
[17] MARSH JL, SLONGO TF, AGEL J, et al. Fracture and dislocation classification compendium-2007: Orthopaedic Trauma Association classification, database and outcomes committee. J Orthop Trauma. 2007;(21):S1-133.
[18] BARG A, PAGENSTERT GI, HÜGLE T, et al. Ankle osteoarthritis: etiology, diagnostics, and classification. Foot Ankle Clin. 2013;(18): 411-426.
[19] BLACK EM, ANTOCI V, LEE JT, et al. Role of preoperative computed tomography scans in operative planning for malleolar ankle fractures. Foot Ankle Int. 2013;(34):697-704.
[20] BEKEROM MP. Diagnosing syndesmotic instability in ankle fractures. World J Orthop. 2011;(2):51-56.
[21] NAQVI GA, CUNNINGHAM P, LYNCH B, et al. Fixation of ankle syndesmotic injuries: comparison of tightrope fixation and syndesmotic screw fixation for accuracy of syndesmotic reduction. Am J Sports Med. 2012;(40):2828-2835.
[22] SCHEPERS T. To retain or remove the syndesmotic screw: a review of literature. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;(131):879-883.
[23] NIKI H, AOKI H, INOKUCHI S, et al. Development and reliability of a standard rating system for outcome measurement of foot and ankle disorders I: development of standard rating system. J Orthop Sci. 2005;(10):457-465.
[24] DAVIDOVITCH RI, WEIL Y, KARIA R, et al. Intraoperative syndesmotic reduction: three-dimensional versus standard fluoroscopic imaging. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;(95):1838-1843.
[25] SAGI HC, SHAH AR, SANDERS RW. The functional consequence of syndesmotic joint malreduction at a minimum 2-year follow-up. J Orthop Trauma. 2012;26(7):439-443.
[26] 李岳伟,张茗慧,李小荣,等.弹性固定及坚强固定治疗踝关节旋前-外旋型骨折合并下胫腓联合分离的疗效比较[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2017, 31(7):820-824.
[27] VAN ZUUREN WJ, SCHEPERS T, BEUMER A, et al. Acute syndesmotic instability in ankle fractures: a review. Foot Ankle Surg. 2017;23(3):135-141.
|