中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (33): 5343-5348.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2852
• 骨科植入物 orthopedic implant • 上一篇 下一篇
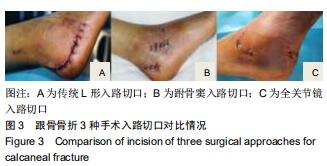
全关节镜辅助下空心螺钉内固定治疗Sanders Ⅱ、Ⅲ型跟骨骨折
沈国栋,邹运璇,张宏宁,李 雪,杨康勇,赖志斌,朱永展
佛山市中医院骨八科,广东省佛山市 528000
Total arthroscopy-assisted reduction and internal fixation with cannulated screws for Sanders II and III calcaneal fractures
Shen Guodong, Zou Yunxuan, Zhang Hongning, Li Xue, Yang Kangyong, Lai Zhibin, Zhu Yongzhan
Eighth Department of Orthopedics, Foshan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fushan 528000, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
跟骨骨折Sanders分型:Sanders分型基于冠状面CT扫描,在冠状面上选择跟骨后距关节面最宽处,向外向内将其分为3分A、B、C,分别代表骨折线位置,这样就有4部分骨折、3部分关节面骨折、2部分载距突骨折,Ⅱ型为二部分骨折,Ⅲ型为三部分骨折。
背景:近年来关节镜技术被广泛应用于跟骨骨折治疗中,但多用于治疗SandersⅠ、Ⅱ型骨折,或作为复杂的跟骨骨折的辅助复位、关节内损伤探查清理的辅助手段。
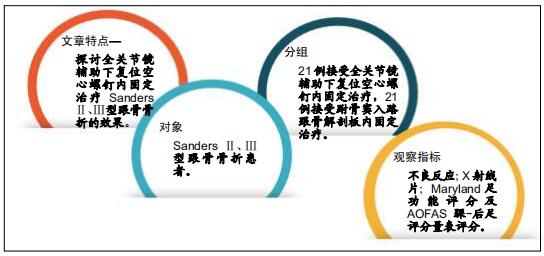
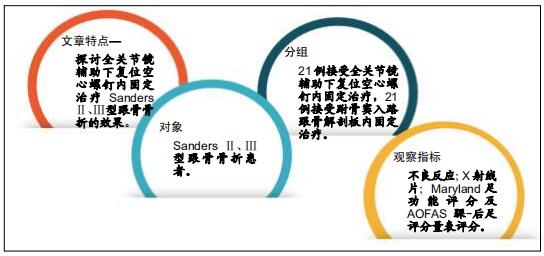
目的:探讨全关节镜辅助下复位空心螺钉内固定治疗Sanders Ⅱ、Ⅲ型跟骨骨折的效果。
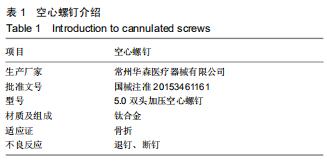
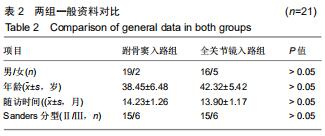
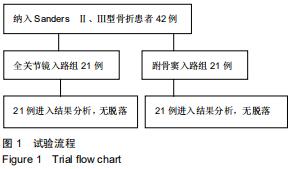
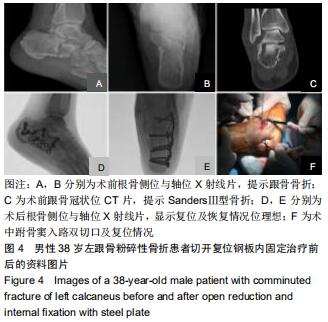
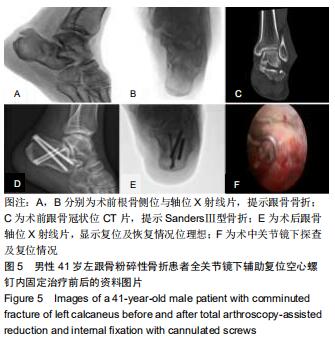
方法:选择2016年12月至2018年11月佛山市中医院收治的42例(42足)Sanders Ⅱ、Ⅲ型跟骨骨折患者,按照手术方案分2组,全关节镜入路组(n=21)接受全关节镜辅助下复位空心螺钉内固定治疗,跗骨窦入路组(n=21)接受跗骨窦入路跟骨解剖板内固定治疗。术后随访12个月,记录不良反应发生情况;复查X射线片,检测Böhler角及Gissane角;评估Maryland足功能评分及AOFAS踝-后足评分量表评分。试验已通过佛山市中医院伦理委员会批准。
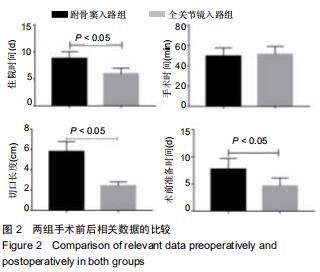
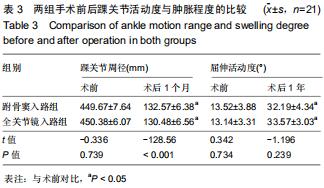
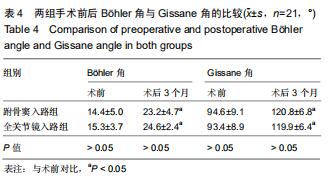
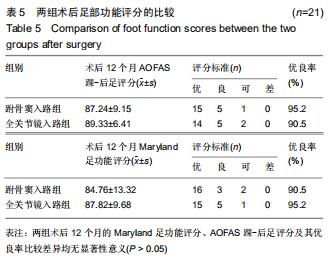
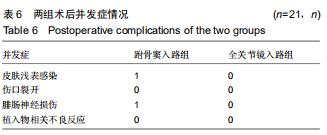
结果与结论:①跗骨窦入路组术前准备时间、平均住院时间长于全关节镜入路组(P < 0.05);全关节镜入路组无胫后血管、胫神经及腓肠神经损伤,无切口软组织感染;跗骨窦入路组发生皮肤浅表感染3足、腓肠神经损伤1足,无切口软组织深部感染及坏死;②术后12个月时,两组Böhler角及Gissane角均较术前明显改善(P < 0.05),两组间比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05);③两组术后的踝关节周径均较术前明显减少(P < 0.05),踝关节屈伸活动度均较术前明显增加(P < 0.05);全关节镜入路组术后1个月的踝关节周径小于跗骨窦入路组(P < 0.05),两组间术后1年的踝关节屈伸活动度比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);④术后12个月时,两组Maryland足功能评分及AOFAS踝-后足评分比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05);⑤结果表明与跗骨窦入路跟骨解剖板内固定相比,全关节镜辅助下复位空心螺钉内固定治疗Sanders Ⅱ、Ⅲ型跟骨骨折有利于促进患者足部功能恢复,减少术后并发症的发生。
ORCID: 0000-0002-5253-6891(沈国栋)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: