中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (16): 2473-2477.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2241
• 组织工程骨及软骨材料 tissue-engineered bone and cartilage materials • 上一篇 下一篇
骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折椎体成形修复效果与骨水泥注入量及弥散程度的关系
吴海波,禹志军,白曼莫
- 三亚市中医院中医骨伤科,海南省三亚市 572000
Correlation of percutaneous vertebroplasty effect on osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture with injection amount and dispersion degree of bone cement
Wu Haibo, Yu Zhijun, Bai Manmo
- Traditional Chinese Medicine Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Sanya Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Sanya 572000, Hainan Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折:指有病理性改变,骨量减低、骨强度降低、骨脆性增加,易发生脆性骨折,是骨质疏松的严重后果,常发于中老年人群,以绝经后女性最为高发,临床表现为腰背部剧烈疼痛、活动受限,严重时脊柱形态发生改变,导致后凸畸形,临床常采用椎体成形治疗。
椎体成形:是向病变椎体内注入骨水泥或人工骨等,以达到强化椎体、缓解疼痛及纠正椎体畸形的目的,是临床常用治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的微创手术,由于其可快速缓解临床症状、疗效确切及术后不良反应少,在中老年骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折治疗中得到广泛应用。
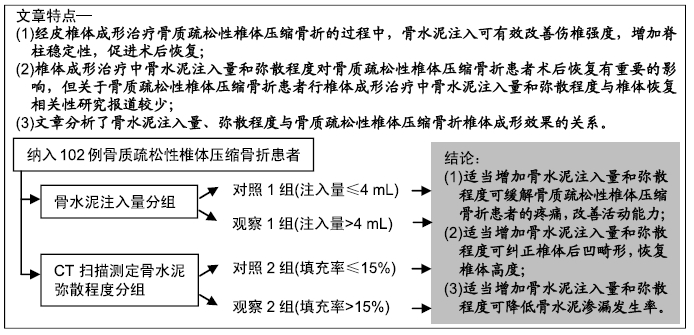
背景:研究显示,椎体成形治疗中骨水泥注入量和弥散程度对骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折患者术后恢复有一定影响,但关于椎体成形治疗中骨水泥注入量和弥散程度与椎体恢复相关性的研究报道较少。
目的:探讨骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折椎体成形后效果与骨水泥注入量及弥散程度的关系。
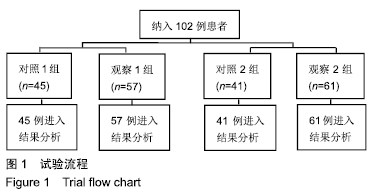
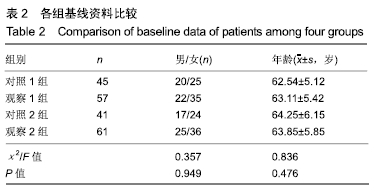
方法:纳入2017年1月至2018年8月三亚市中医院收治的102例(109个椎体)骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折患者,其中男42例,女60例,年龄52-76岁,均进行椎体成形骨水泥注射治疗。根据骨水泥注入量分为观察1组(注入量>4 mL,n=57)和对照1组(注入量≤4 mL,n=45),根据骨水泥弥散程度分为观察2组(填充率>15%,n=61)和对照2组(填充率≤15%,n=41),观察手术前后的目测类比评分、Oswestry功能障碍指数评分、椎体前缘高度、Cobb角变化与骨水泥渗漏发生情况,并分析骨水泥注入量、弥散程度与椎体恢复高度相关性。试验经三亚市中医院伦理委员会批准。
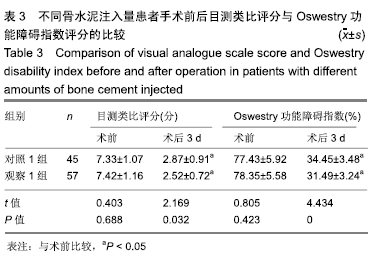
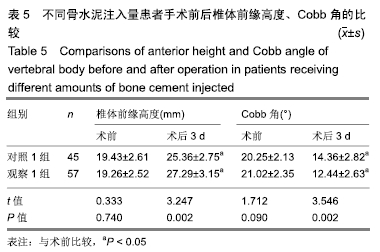
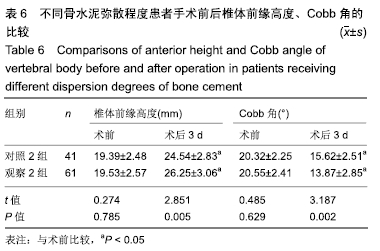
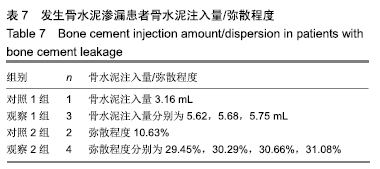
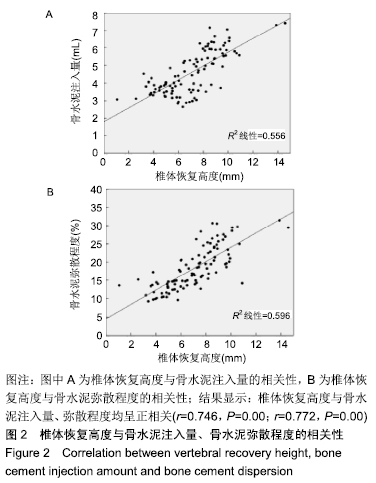
结果与结论:①观察1组、对照1组术后3 d的目测类比评分、Oswestry功能障碍指数评分均较术前明显改善(P < 0.05),并且观察1组的改善情况优于对照1组(P < 0.05);观察2组、对照2组术后3 d的目测类比评分、Oswestry功能障碍指数评分均较术前明显改善(P < 0.05),并且观察2组的改善情况优于对照组2组(P < 0.05);②观察1组、对照1组术后3 d的椎体前缘高度与Cobb角均较术前明显改善(P < 0.05),并且观察1组的改善情况优于对照1组(P < 0.05);观察2组、对照2组术后3 d的椎体前缘高度与Cobb角均较术前明显改善(P < 0.05),并且观察2组的改善情况优于对照组2组(P < 0.05);③观察1组、对照1组骨水泥渗漏率比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),观察2组、对照2组骨水泥渗漏率比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);④椎体恢复高度与骨水泥注入量、弥散程度均呈正相关性(P < 0.05);⑤结果表明,适当增加骨水泥注入量和弥散程度可缓解骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折患者的疼痛,改善活动能力,纠正椎体后凹畸形,较好恢复椎体高度,骨水泥注入量、弥散程度与椎体恢复高度呈正相关。
ORCID: 0000-0001-8214-7150(吴海波)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: