中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (19): 3040-3051.doi: 10.12307/2023.635
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇
外泌体miRNA参与脊柱关节退行性疾病修复的机制
赵 延1,夏秋秋1,向少杰1,毛启名1,孔维军2,杜 迁2,廖文波2,辛志军1
- 1遵义医科大学附属医院骨科,贵州省遵义市 563000;2遵义医科大学第二附属医院骨科,贵州省遵义市 563000
Exosomal miRNA in the repair mechanism of degenerative diseases of the spine and joints
Zhao Yan1, Xia Qiuqiu1, Xiang Shaojie1, Mao Qiming1, Kong Weijun2, Du Qian2, Liao Wenbo2, Xin Zhijun1
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
摘要:
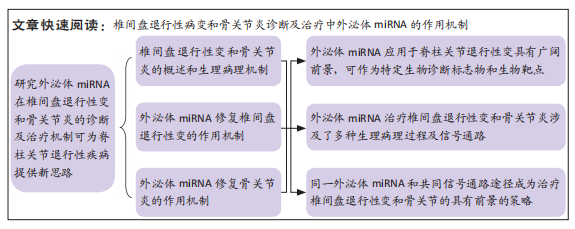
文题释义:
外泌体:是细胞通过出芽方式分泌的具有双层磷脂膜结构的纳米级(直径40-120 nm)囊性小泡,包含母细胞的细胞因子、蛋白、脂类、mRNA、miRNA(microRNA)及非编码RNA等信息分子,其渗透性与稳定性良好,能够远程或局部与靶细胞融合。miRNA:是一类由19-25个核苷酸组成的非编码单链RNA,通过降解靶基因mRNA或阻遏mRNA的蛋白翻译对靶基因在细胞中差异性表达,进而调控下游通路的激活以获得效能。
背景:脊柱关节退行性病变主要包括椎间盘退行性病变和骨关节炎,近年来利用外泌体miRNA通过促进细胞的自噬和增殖、迁移等治疗脊柱关节退行性病变已成为具有前景的新兴治疗手段。
目的:综述外泌体miRNA在椎间盘退行性病变和骨关节炎的疾病发展、诊断及治疗机制的研究进展。
方法:第一作者以“Intervertebral disc degeneration,Osteoarthritis,Exosomes,miRNA,Autophagy,Extracellular matrix,Apoptosis,Cell proliferation,Pyroptosis,Biomarkers,Mechanistic pathways”为检索词检索PubMed数据库,最终纳入133篇英文文献进行归纳总结。
结果与结论:①外泌体miRNA治疗脊柱关节退行性疾病的主要作用机制是通过促进自噬和细胞的迁移和增殖,抑制细胞外基质降解、细胞凋亡、细胞焦亡及炎症反应等多个方面发挥对脊柱关节退行性疾病的治疗作用,并且同一外泌体miRNA能够参与同一疾病的不同生理病理过程;②Wnt/β-catenin途径、mTOR、NLRP3、核转录因子κB及MAPK等信号通路在外泌体治疗脊柱关节退行性病变中发挥重要作用,其中MAKP信号通路是外泌体miRNA治疗改善椎间盘退行性病变和骨关节炎疾病进程中共同存在的信号通路,对于寻找椎间盘退行性病变、骨关节炎疾病及其他脊柱关节退行性疾病的共同靶点具有重要启示意义;③同一miRNA家族可参与不同的退行性病变的修复,对于探索或合成新型外泌体miRNA来治疗其他脊柱关节退行性疾病具有重要的借鉴意义,但未来需进一步明确外泌体miRNA对脊柱关节退行性疾病的安全性和不良反应。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4763-6634 (赵延);https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4714-6691 (辛志军)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: