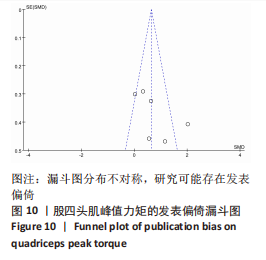
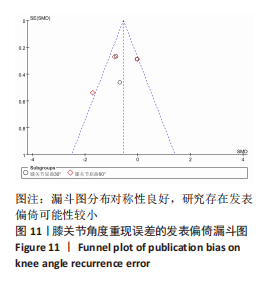
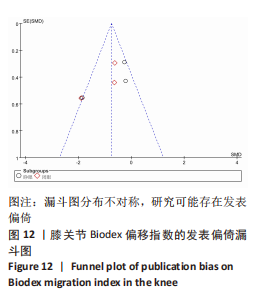
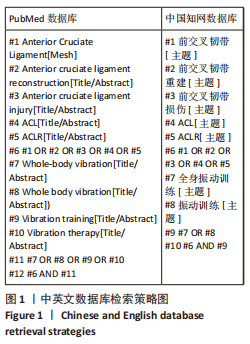
[1] JONES HSR, MOORE IS, KING E, et al. Movement strategy correspondence across jumping and cutting tasks after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2022;32(3):612-621.
[2] 季程程,杨鹏飞,张信波,等.神经肌肉训练在前交叉韧带重建后康复中的应用进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2020, 26(8):917-922.
[3] RIVERA-BROWN AM, FRONTERA WR, FONTáNEZ R, et al. Evidence for isokinetic and functional testing in return to sport decisions following ACL surgery. Pm r. 2022; 14(5):678-690.
[4] LV ZT, ZHANG JM, PANG ZY, et al. The efficacy of platelet rich plasma on anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Platelets. 2022;33(2):229-241.
[5] PASCHOS NK, HOWELL SM. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: principles of treatment. EFORT Open Rev. 2016;1(11): 398-408.
[6] KIAPOUR AM, MURRAY MM. Basic science of anterior cruciate ligament injury and repair. Bone Joint Res. 2014; 3(2):20-31.
[7] PISTONE EM, LAUDANI L, CAMILLIERI G, et al. Effects of early whole-body vibration treatment on knee neuromuscular function and postural control after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a randomized controlled trial. J Rehabil Med. 2016;48(10):880-886.
[8] 成琳,汪皓男,王丽娜,等.血流限制训练在前交叉韧带重建后康复中的应用研究进展[J].中国运动医学杂志,2021,40(8): 663-670.
[9] PALMIERI-SMITH RM, LEPLEY LK. Quadriceps strength asymmetry after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction alters knee joint biomechanics and functional performance at time of return to activity. Am J Sports Med. 2015;43(7):1662-1669.
[10] ARDERN CL, TAYLOR NF, FELLER JA, et al. Fifty-five per cent return to competitive sport following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis including aspects of physical functioning and contextual factors. Br J Sports Med. 2014;48(21):1543-1552.
[11] WIGGINS AJ, GRANDHI RK, SCHNEIDER DK, et al. Risk of secondary injury in younger athletes after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Sports Med. 2016;44(7): 1861-1876.
[12] ALAM MM, KHAN AA, FAROOQ MJW. Effect of whole-body vibration on neuromuscular performance: a literature review. Work. 2018;59(4):571-583.
[13] BECK BR. Vibration therapy to prevent bone loss and falls: mechanisms and efficacy. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2015;13(6):381-389.
[14] KRAUSE A, LEE K, KöNIG D, et al. Six weeks of whole-body vibration improves fine motor accuracy, functional mobility and quality of life in people with multiple sclerosis. PLoS One. 2022;17(7): e0270698.
[15] VERSCHUEREN SM, ROELANTS M, DELECLUSE C, et al. Effect of 6-month whole body vibration training on hip density, muscle strength, and postural control in postmenopausal women: a randomized controlled pilot study. J Bone Miner Res. 2004;19(3):352-359.
[16] ROELANTS M, DELECLUSE C, VERSCHUEREN SM. Whole-body-vibration training increases knee-extension strength and speed of movement in older women. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2004;52(6):901-908.
[17] 张丽,瓮长水,赵占波.全身振动训练对老年人下肢肌肉力量及功能干预效果的Meta分析[J].中国康复理论与实践,2015, 21(10):1222-1228.
[18] GIOMBINI A, MACALUSO A, LAUDANI L, et al. Acute effect of whole-body vibration at optimal frequency on muscle power output of the lower limbs in older women. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2013;92(9):797-804.
[19] PAMUKOFF DN, MONTGOMERY MM, CHOE KH, et al. Effect of whole-body vibration on sagittal plane running mechanics in individuals with anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a randomized crossover trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2018;99(5):973-980.
[20] DA COSTA KSA, BORGES DT, DE BRITO MACEDO L, et al. Whole-body vibration on performance of quadriceps after ACL reconstruction: a blinded randomized controlled trial. J Sport Rehabil. 2019;28(1): 52-58.
[21] QIU J, ONG MT, LEONG HT, et al. Effects of whole-body vibration therapy on quadriceps function in patients with anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a systematic review. Sports Health. 2022;14(2):216-226.
[22] SEIXAS A, SAñUDO B, Sá-CAPUTO D, et al. Whole-body vibration for individuals with reconstructed anterior cruciate ligament: a systematic review. Biomed Res Int. 2020; 1(5):7362069.
[23] 屈云,何俐,刘鸣.Cochrane系统评价的基本方法[J].中国临床康复,2003,7(4): 532-533,536.
[24] JADAD AR, MOORE RA, CARROLL D, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials. 1996;17(1):1-12.
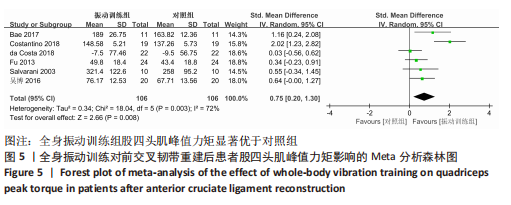
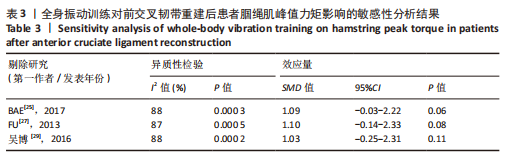
[25] BAE CH, LEE JH, KIM JC, et al. Effects of resistance exercise using vibration stimulation on knee muscle strength and balance after anterior cruciate ligament Reconstruction. Korea Sci. 2017;23(2):17-25.
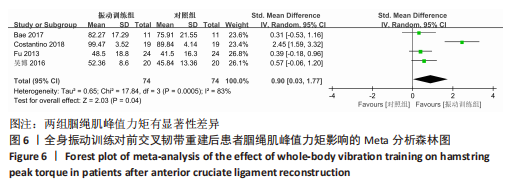
[26] COSTANTINO C, BERTULETTI S, ROMITI D. Efficacy of whole-body vibration board training on strength in athletes after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a randomized controlled study. Clin J Sport Med. 2018;28(4):339-349.
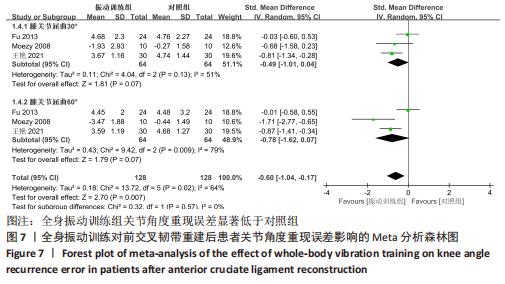
[27] FU CL, YUNG SH, LAW KY, et al. The effect of early whole-body vibration therapy on neuromuscular control after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(4):804-814.
[28] SALVARANI A, AGOSTI M, ZANRE A, et al. Mechanical vibration in the rehabilitation of patients with reconstructed anterior cruciate ligament. Eur Medicophysica. 2003;39(1):19-25.
[29] 吴博,张雷,庞文君,等.全身振动训练对前交叉韧带损伤重建后患者下肢运动控制的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志,2016, 31(4):421-425.
[30] MOEZY A, OLYAEI G, HADIAN M, et al. A comparative study of whole body vibration training and conventional training on knee proprioception and postural stability after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Br J Sports Med. 2008;42(5):373-378.
[31] 王艳,吴珊红,戚彪,等.振动疗法结合常规康复训练对前交叉韧带重建后膝关节本体感觉及动态稳定性的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志,2021,36(7):858-862.
[32] BERSCHIN G, SOMMER B, BEHRENS A, et al. Whole body vibration exercise protocol versus a standard exercise protocol after ACL reconstruction: a clinical randomized controlled trial with short term follow-up. J Sports Sci Med. 2014;13(3):580-589.
[33] 张莉,许建文,黄浪,等.全身振动结合运动训练对前交叉韧带重建后患者早期康复的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2021,43(2):158-161.
[34] PIETROSIMONE B, BLACKBURN JT, HARKEY MS, et al. Clinical strategies for addressing muscle weakness following knee injury. Clin Sports Med. 2015;34(2):285-300.
[35] PAMUKOFF DN, PIETROSIMONE B, LEWEK MD, et al. Whole-body and local muscle vibration immediately improve quadriceps function in individuals with anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2016;97(7):1121-1129.
[36] GOETSCHIUS J, HERTEL J, SALIBA S, et al. The effects of patellar tendon vibration on quadriceps strength in anterior cruciate ligament reconstructed knees. Phys Ther Sport. 2019;40(11):71-77.
[37] LEPLEY LK. Deficits in quadriceps strength and patient-oriented outcomes at return to activity after ACL reconstruction: a review of the current literature. sports health. 2015;7(3):231-238.
[38] LUC-HARKEY BA, FRANZ JR, LOSINA E, et al. Association between kinesiophobia and walking gait characteristics in physically active individuals with anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Gait Posture. 2018;64(7):220-225.
[39] PAMUKOFF DN, PIETROSIMONE B, LEWEK MD, et al. Immediate effect of vibratory stimuli on quadriceps function in healthy adults. Muscle Nerve. 2016;54(3):469-478.
[40] ZECH A, HüBSCHER M, VOGT L, et al. Neuromuscular training for rehabilitation of sports injuries: a systematic review. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2009;41(10):1831-1841.
[41] FAXON JL, SANNI AA, MCCULLY KK. Hamstrings and quadriceps muscles function in subjects with prior ACL reconstruction surgery. J Funct Morphol Kinesiol. 2018;3(4):56-65.
[42] KROGSGAARD MR, DYHRE-POULSEN P, FISCHER-RASMUSSEN T. Cruciate ligament reflexes. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2002; 12(3):177-182.
[43] 王玲,陈鹏,王广兰,等.肌内效贴对慢性踝关节不稳的影响:系统综述和Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(14): 2283-2290.
[44] HAN GY, PARK SA, KIM JH, et al. Effects of vibration on the proteome expression of anterior cruciate ligament cells. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2011;236(7):783-789.
[45] POLLOCK RD, WOLEDGE RC, MARTIN FC, et al. Effects of whole body vibration on motor unit recruitment and threshold. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2012;112(3):388-395.
[46] BRUNETTI O, FILIPPI GM, LORENZINI M, et al. Improvement of posture stability by vibratory stimulation following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2006; 14(11):1180-1187.
[47] BOGAERTS A, VERSCHUEREN S, DELECLUSE C, et al. Effects of whole body vibration training on postural control in older individuals: a 1 year randomized controlled trial. Gait Posture. 2007;26(2):309-316.
[48] 方成华,邹晓峰.不同频率振动训练对速滑运动员下肢爆发力的影响[J].沈阳体育学院学报,2013,32(5):125-127.
[49] MARTíNEZ-PARDO E, ROMERO-ARENAS S, ALCARAZ PE. Effects of different amplitudes (high vs. low) of whole-body vibration training in active adults. J Strength Cond Res. 2013;27(7):1798-1806.
[50] CHOI DS, LEE HJ, SHIN YI, et al. Modulation of cortical activity by high-frequency whole-body vibration exercise: an fNIRS study. J Sport Rehabil. 2019;28(7):665-670.
[51] PERCHTHALER D, HORSTMANN T, GRAU S. Variations in neuromuscular activity of thigh muscles during whole-body vibration in consideration of different biomechanical variables. J Sports Sci Med. 2013;12(3):439-446.
[52] GIOMBINI A, MENOTTI F, LAUDANI L, et al. Effect of whole body vibration frequency on neuromuscular activity in ACL-deficient and healthy males. 2015; 32(3):243-247.
[53] KROL P, PIECHA M, SLOMKA K, et al. The effect of whole-body vibration frequency and amplitude on the myoelectric activity of vastus medialis and vastus lateralis. J Sports Sci Med. 2011;10(1):169-174.
[54] POLLOCK RD, WOLEDGE RC, MILLS KR, et al. Muscle activity and acceleration during whole body vibration: effect of frequency and amplitude. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2010;25(8):840-846.
[55] STEWART JA, COCHRANE DJ, MORTON RH. Differential effects of whole body vibration durations on knee extensor strength. J Sci Med Sport. 2009;12(1):50-53.
[56] 张帆,王长生,袁艳,等.不同屈膝角度与g值全身振动刺激对下肢肌肉影响的研究[J].北京体育大学学报,2014, 37(11):86-91, 99.
[57] RITZMANN R, GOLLHOFER A, KRAMER A. The influence of vibration type, frequency, body position and additional load on the neuromuscular activity during whole body vibration. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2013;113(1):1-11.
[58] ROSENKRANZ K, ROTHWELL JC. The effect of sensory input and attention on the sensorimotor organization of the hand area of the human motor cortex. J Physiol. 2004;561(1):307-320.
|