中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (36): 5870-5874.doi: 10.12307/2023.709
• 骨科植入物相关临床实践 Clinical practice of orthopedic implant • 上一篇 下一篇
血清戊糖素水平和骨小梁分数影响2型糖尿病患者椎体骨折的严重程度
钱 光,余月明,董有海,洪 洋,王明海
- 复旦大学附属上海市第五人民医院骨科,上海市 200240
Serum pentosidine level and trabecular bone score affect the severity of vertebral fractures in type 2 diabetes patients
Qian Guang, Yu Yueming, Dong Youhai, Hong Yang, Wang Minghai
- Department of Orthopedics, Shanghai Fifth People’s Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai 200240, China
摘要:
文题释义:
骨小梁分数:是一个通过评估脊柱双能X射线骨密度图像中的灰阶变化,间接评估骨小梁微结构的临床工具,该技术已被广泛应用于评估原发性和继发性骨质疏松,如糖皮质激素性骨质疏松、糖尿病、甲状旁腺功能亢进症等患者的骨质量。血清戊糖素:被认为是骨骼中糖基化终末产物的一个有用标志物,戊糖素水平与骨强度呈负相关。
背景:研究显示,2型糖尿病患者可以在骨密度正常范围甚至较高的情况下发生骨折,因此,在2型糖尿病患者中骨质量比骨密度预测骨折风险的作用更大。
目的:评估血清戊糖素水平和骨小梁分数与2型糖尿病患者椎体骨折压缩程度的相关性。
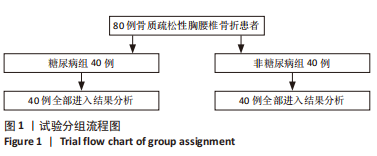
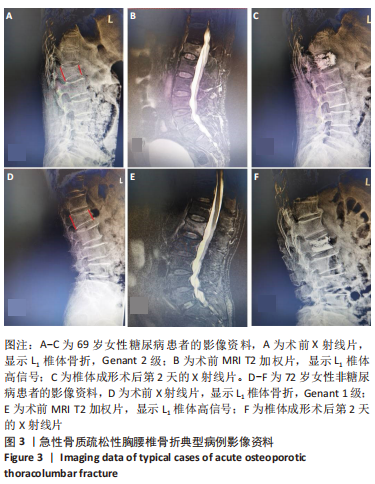
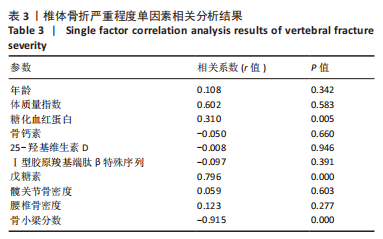
方法:选择2021年1月至 2022年 6月复旦大学附属上海市第五人民医院收治的骨质疏松性胸腰椎骨折患者80例,包括40例2型糖尿病患者和40例非糖尿病患者。收集所有患者的一般信息,包括性别、年龄、体质量指数、骨代谢生化指标等;采用双能X射线吸收仪检测患者骨密度,根据测量获得的图像使用TBS Insight®软件计算脊柱骨小梁分数;采用高效液相色谱法测定患者血清中戊糖素水平;使用Genant半定量分型对所有患者脊柱骨折压缩程度进行分级,分析各种变量因素与椎体骨折压缩程度的相关性。
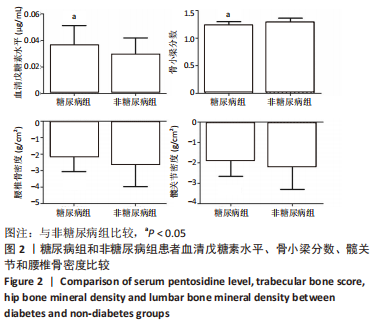
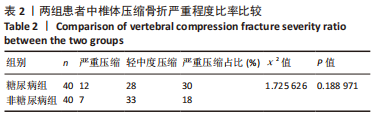
结果与结论:①糖尿病组患者的血清戊糖素水平高于非糖尿病组(P < 0.05),骨小梁分数值低于非糖尿病组(P < 0.05),两组腰椎骨密度、髋关节骨密度、严重骨折压缩占比比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05);②Spearman单因素相关分析结果显示,椎体骨折严重程度与糖化血红蛋白、血清戊糖素水平存在显著的正相关关系(r=0.310,0.796,P=0.005,0.000),椎体骨折严重程度与骨小梁分数之间存在显著的负相关关系(r=-0.915,P=0.000);③结果显示,骨小梁分数和血清戊糖素水平可作为一种评价骨质量的方法,两者与骨质疏松性椎体骨折严重程度显著相关。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7052-4262 (钱光)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: