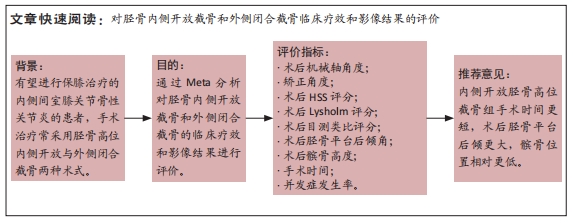
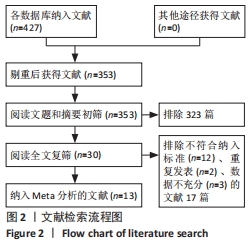
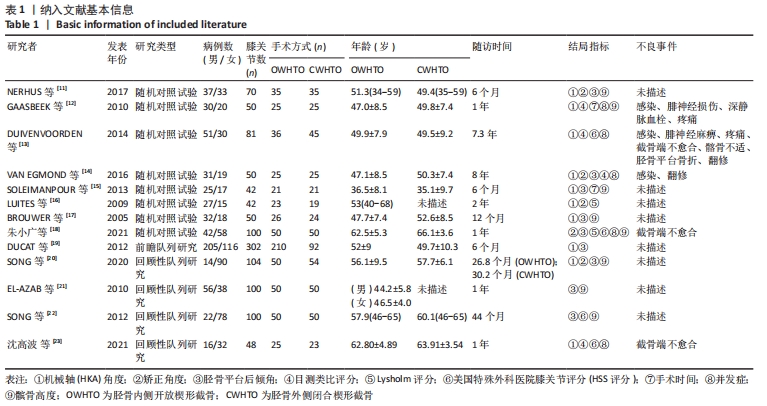
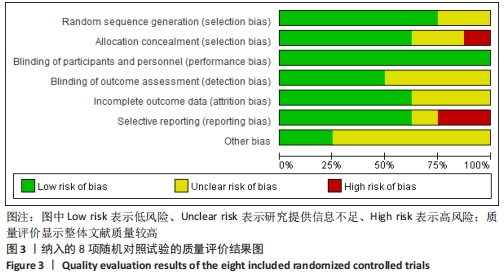
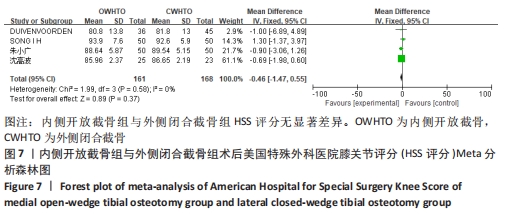
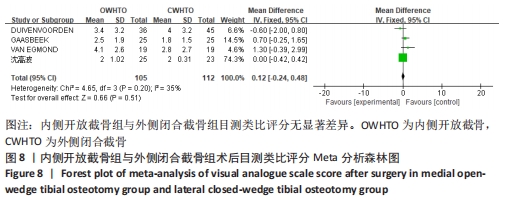
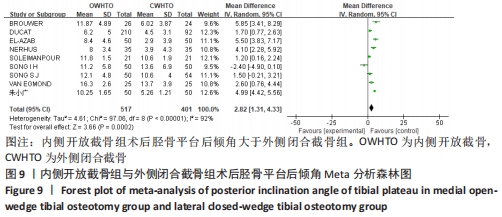
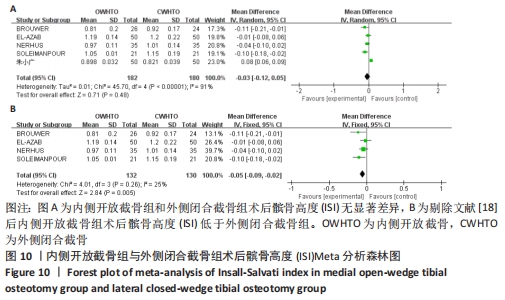
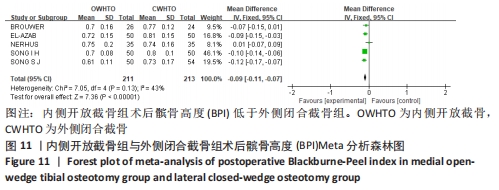
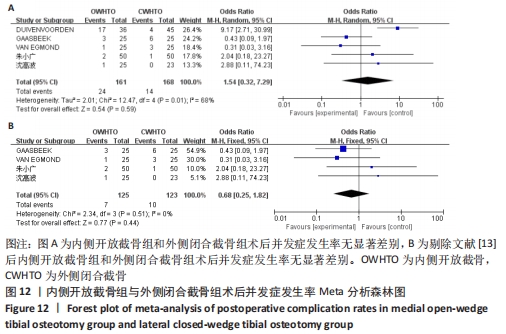
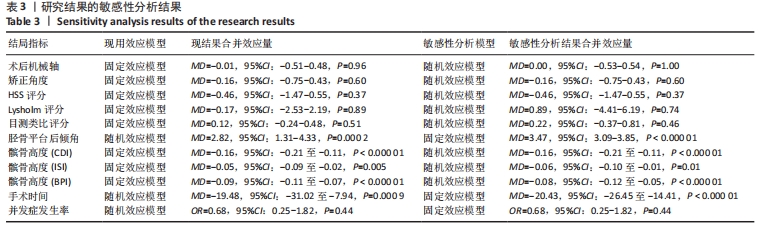
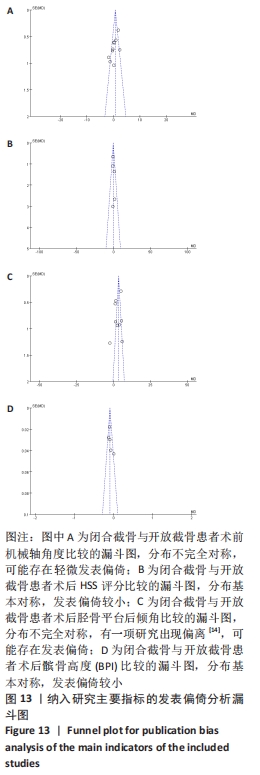
[1] 中国医院协会临床新技术应用专业委员会,中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组,中国医师协会骨科医师分会骨关节炎学组.中国膝关节周围截骨下肢力线矫正术治疗膝关节骨关节炎临床指南[J].中华骨科杂志, 2021,41(23):1655-1672.
[2] ENGH GA, AMMEEN D. Is an intact anterior cruciate ligament needed in order to have a well-functioning unicondylar knee replacement? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004; (428):170-173.
[3] KIM JH, KIM HJ, LEE DH. Survival of opening versus closing wedge high tibial osteotomy: a meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):7296.
[4] KUNZE KN, BELETSKY A, HANNON CP, et al. Return to work and sport after proximal tibial osteotomy and the effects of opening versus closing wedge techniques on adverse outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Sports Med. 2020;48(9):2295-2304.
[5] 黄野.坚持膝关节骨关节炎的阶梯化治疗[J].实用骨科杂志,2020,26(12):1057-1058.
[6] 黄野,柳剑,王兴山,等.胫骨高位截骨术适应证解析[J].中华外科杂志,2020,58(6): 420-424.
[7] BERRUTO M, MAIONE A, TRADATI D, et al. Closing-wedge high tibial osteotomy, a reliable procedure for osteoarthritic varus knee. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28(12):3955-3961.
[8] 王兴山,柳剑,顾建明,等.改良闭合楔形胫骨高位截骨术治疗膝内翻畸形的疗效观察[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2016, 10(5):474-480.
[9] 李静,李幼平.不断完善与发展的Cochrane系统评价[J].中国循证医学杂志,2008,8(9): 742-743.
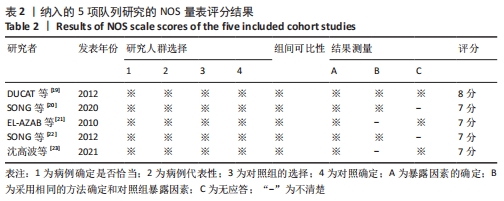
[10] CLAUDIO L, BRENDON S, MARCO S, et al. Assessing the quality of studies in meta-analyses: advantages and limitations of the Newcastle Ottawa Scale. World J Meta Anal. 2017;5(4):80-84.
[11] NERHUS TK, EKELAND A, SOLBERG G, et al. Radiological outcomes in a randomized trial comparing opening wedge and closing wedge techniques of high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(3):910-917.
[12] GAASBEEK RD, NICOLAAS L, RIJNBERG WJ, et al. Correction accuracy and collateral laxity in open versus closed wedge high tibial osteotomy. A one-year randomised controlled study. Int Orthop. 2010;34(2):201-207.
[13] DUIVENVOORDEN T, BROUWER RW, BAAN A, et al. Comparison of closing-wedge and opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy for medial compartment osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomized controlled trial with a six-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014; 96(17):1425-1432.
[14] VAN EGMOND N, VAN GRINSVEN S, VAN LOON CJ, et al. Better clinical results after closed- compared to open-wedge high tibial osteotomy in patients with medial knee osteoarthritis and varus leg alignment. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016; 24(1):34-41.
[15] SOLEIMANPOUR J, ELMI A, JAFARI MA, et al. Comparison of genu varum treating results using open and closed wedge high tibial osteotomy. Pak J Biol Sci. 2013;16(14):686-691.
[16] LUITES JW, BRINKMAN JM, WYMENGA AB, et al.
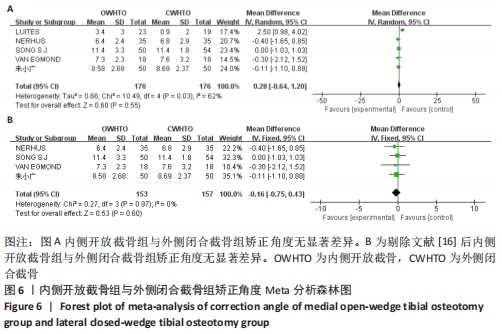
Fixation stability of opening- versus closing-wedge high tibial osteotomy: a randomised clinical trial using radiostereometry. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009;91(11):1459-1465.
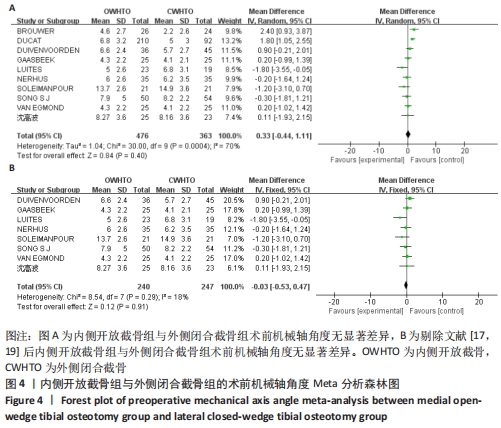
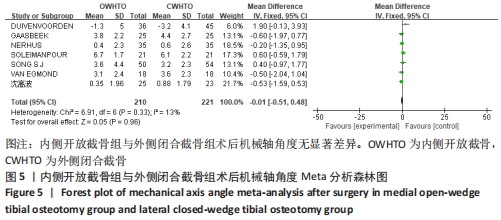
[17] BROUWER RW, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA SM, VAN KOEVERINGE AJ, et al. Patellar height and the inclination of the tibial plateau after high tibial osteotomy. The open versus the closed-wedge technique. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(9):1227-1232.
[18] 朱小广,彭庆州,王大鹏.开放与闭合胫骨高位截骨治疗膝骨性关节炎临床对比研究[J].中华老年医学杂志,2021,40(4):491-495.
[19] DUCAT A, SARIALI E, LEBEL B, et al. Posterior tibial slope changes after opening- and closing-wedge high tibial osteotomy: a comparative prospective multicenter study. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012;98(1):68-74.
[20] SONG SJ, YOON KH, PARK CH. Patellofemoral cartilage degeneration after closed- and open-wedge high tibial osteotomy with large alignment correction. Am J Sports Med. 2020; 48(11):2718-2725.
[21] EL-AZAB H, GLABGLY P, PAUL J, et al. Patellar height and posterior tibial slope after open- and closed-wedge high tibial osteotomy: a radiological study on 100 patients. Am J Sports Med. 2010;38(2):323-329.
[22] SONG IH, SONG EK, SEO HY, et al. Patellofemoral alignment and anterior knee pain after closing- and opening-wedge valgus high tibial osteotomy. Arthroscopy. 2012; 28(8):1087-1093.
[23] 沈高波,崔龙慷,方源,等.内侧开放与外侧闭合胫骨高位截骨治疗内侧间室膝骨性关节炎的早期疗效对比[J].实用医学杂志, 2021,37(8):1031-1036.
[24] BROUWER RW, HUIZINGA MR, DUIVENVOORDEN T, et al. Osteotomy for treating knee osteoarthritis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(12):D4019.
[25] SCHROTER S, ATESCHRANG A, LOWE W, et al. Early full weight-bearing versus 6-week partial weight-bearing after open wedge high tibial osteotomy leads to earlier improvement of the clinical results: a prospective, randomised evaluation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(1):325-332.
[26] ZIQI Z, YUFENG M, LEI Z, et al. Therapeutic effects comparison and revision case analysis of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty and open wedge high tibial osteotomy in treating medial knee osteoarthritis in patients under 60 years: a 2-6-year follow-up study[J]. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(6):1635-1643.
[27] 郭保逢,秦泗河,黄野.膝关节骨关节炎的保膝治疗进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2018,32(10):1292-1296.
[28] JONES GG, JAERE M, CLARKE S, et al. 3D printing and high tibial osteotomy. EFORT Open Rev. 2018;3(5):254-259.
[29] NOYES FR, GOEBEL SX, WEST J. Opening wedge tibial osteotomy: the 3-triangle method to correct axial alignment and tibial slope. Am J Sports Med. 2005;33(3):378-387.
[30] KIM GB, KIM KI, SONG SJ, et al. Increased posterior tibial slope after medial open-wedge high tibial osteotomy may result in degenerative changes in anterior cruciate ligament. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(9):1922-1928.
[31] AMIS AA. Biomechanics of high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(1):197-205.
[32] SCHUSTER P, GESSLEIN M, SCHLUMBERGER M, et al. Ten-year results of medial open-wedge high tibial osteotomy and chondral resurfacing in severe medial osteoarthritis and varus malalignment. Am J Sports Med. 2018;46(6):1362-1370.
[33] BITO H, TAKEUCHI R, KUMAGAI K, et al. Opening wedge high tibial osteotomy affects both the lateral patellar tilt and patellar height. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18(7):955-960.
[34] ELMALI N, ESENKAYA I, CAN M, et al. Monoplanar versus biplanar medial open-wedge proximal tibial osteotomy for varus gonarthrosis: a comparison of clinical and radiological outcomes. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(12):2689-2695.
[35] NUTE DW, BOTTONI CR. Editorial commentary: uniplane high tibial osteotomy just below the metaphyseal flare is preferable to biplane opening wedge high tibial osteotomy distal to the tuberosity: a cut below our expectations. Arthroscopy. 2021;37(8):2579-2581.
[36] KIM JS, LEE JI, CHOI HG, et al. Retro-tubercle biplanar opening wedge high tibial osteotomy is favorable for the patellofemoral joint but not for the osteotomized tubercle itself compared with supra-tubercle osteotomy. Arthroscopy. 2021;37(8):2567-2578.
[37] IACONO V, DE FRANCO C, AULETTA N, et al. New plates with polyaxial locking system and PSI technique in medial open wedge high tibial osteotomy: preliminary results. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2020;34(3 Suppl 2):111-113.
|