[1] CHENG C, WENTWORTH K, SHOBACK DM. New Frontiers in Osteoporosis Therapy. Annu Rev Med. 2020;71:277-288.
[2] SATHYAPALAN T, AYE M, RIGBY AS, et al. Soy Reduces Bone Turnover Markers in Women During Early Menopause: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Bone Miner Res. 2017;32(1):157-164.
[3] LEVIN VA, JIANG X, KAGAN R. Estrogen therapy for osteoporosis in the modern era. Osteoporos Int. 2018;29(5):1049-1055.
[4] JACKSON RD, MYSIW WJ. Insights into the epidemiology of postmenopausal osteoporosis: the Women’s Health Initiative. Semin Reprod Med. 2014;32(6):454-462.
[5] REGINSTER JY, BURLET N. Osteoporosis: a still increasing prevalence. Bone. 2006;38(2 Suppl 1): S4-9.
[6] CRANDALL CJ, NEWBERRY SJ, DIAMANT A, et al. Comparative effectiveness of pharmacologic treatments to prevent fractures: an updated systematic review. Ann Intern Med. 2014;161(10): 711-723.
[7] KOTHAWALA P, BADAMGARAV E, RYU S, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of real-world adherence to drug therapy for osteoporosis. Mayo Clin Proc. 2007;82(12):1493-1501.
[8] SHEA B, BONAIUTI D, IOVINE R, et al. Cochrane Review on exercise for preventing and treating osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Eura Medicophys. 2004;40(3):199-209.
[9] PALOMBARO KM, BLACK JD, BUCHBINDER R, et al. Effectiveness of exercise for managing osteoporosis in women postmenopause. Phys Ther. 2013;93(8):1021-1025.
[10] LE Q, QU Y, TAO Y, et al. Effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on hand function recovery and excitability of the motor cortex after stroke: a meta-analysis. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2014;93(5):422-430.
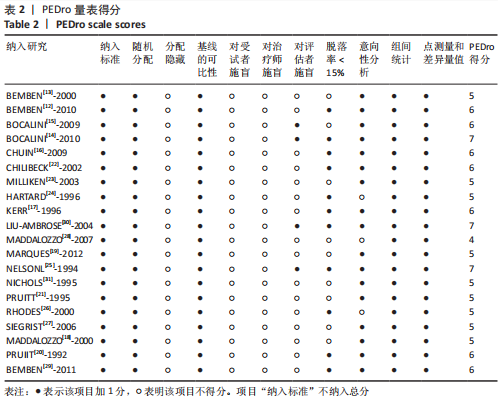
[11] MAHER CG, SHERRINGTON C, HERBERT RD, et al. Reliability of the PEDro scale for rating quality of randomized controlled trials. Phys Ther. 2003; 83(8):713-721.
[12] BEMBEN DA, PALMER IJ, BEMBEN MG, et al. Effects of combined whole-body vibration and resistance training on muscular strength and bone metabolism in postmenopausal women. Bone. 2010;47(3):650-656.
[13] BEMBEN DA, FETTERS NL, BEMBEN MG, et al. Musculoskeletal responses to high- and low-intensity resistance training in early postmenopausal women. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2000;32(11):1949-1957.
[14] BOCALINI DS, SERRA AJ, DOS SANTOS L. Moderate resistive training maintains bone mineral density and improves functional fitness in postmenopausal women. J Aging Res. 2010;2010:760818.
[15] BOCALINI DS, SERRA AJ, DOS SANTOS L, et al. Strength training preserves the bone mineral density of postmenopausal women without hormone replacement therapy. J Aging Health. 2009;21(3):519-527.
[16] CHUIN A, LABONTé M, TESSIER D, et al. Effect of antioxidants combined to resistance training on BMD in elderly women: a pilot study. Osteoporos Int. 2009;20(7):1253-1258.
[17] KERR D, MORTON A, DICK I, et al. Exercise effects on bone mass in postmenopausal women are site-specific and load-dependent. J Bone Miner Res. 1996;1(2):218-225.
[18] MADDALOZZO GF, SNOW CM. High intensity resistance training: effects on bone in older men and women. Calcif Tissue Int. 2000;66(6):399-404.
[19] MARQUES EA, MOTA J, CARVALHO J. Exercise effects on bone mineral density in older adults: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Age (Dordr). 2012;34(6):1493-1515.
[20] PRUITT LA, JACKSON RD, BARTELS RL, et al. Weight-training effects on bone mineral density in early postmenopausal women. J Bone Miner Res. 1992;7(2):179-185.
[21] PRUITT LA, TAAFFE DR, MARCUS R. Effects of a one-year high-intensity versus low-intensity resistance training program on bone mineral density in older women. J Bone Miner Res. 1995; 10(11):1788-1795.
[22] CHILIBECK PD, DAVISON KS, WHITING SJ, et al. The effect of strength training combined with bisphosphonate (etidronate) therapy on bone mineral, lean tissue, and fat mass in postmenopausal women. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2002;80(10):941-950.
[23] MILLIKEN LA, GOING SB, HOUTKOOPER LB, et al. Effects of exercise training on bone remodeling, insulin-like growth factors, and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women with and without hormone replacement therapy. Calcif Tissue Int. 2003;72(4):478-484.
[24] HARTARD M, HABER P, ILIEVA D, et al. Systematic strength training as a model of therapeutic intervention. A controlled trial in postmenopausal women with osteopenia. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 1996;75(1):21-28.
[25] NELSON ME, FIATARONE MA, MORGANTI CM, et al. Effects of high-intensity strength training on multiple risk factors for osteoporotic fractures. A randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 1994;272(24):1909-1914.
[26] RHODES EC, MARTIN AD, TAUNTON JE, et al. Effects of one year of resistance training on the relation between muscular strength and bone density in elderly women. Br J Sports Med. 2000; 34(1):18-22.
[27] SIEGRIST CL, JESCHKE D. Strength training using conventional or vibration machines and spinal gymnastics in the prevention of osteoporosis in post-menopausal women. Dtsch Z Sportmed. 2006;57:182-188.
[28] MADDALOZZO GF, WIDRICK JJ, CARDINAL BJ, et al. The effects of hormone replacement therapy and resistance training on spine bone mineral density in early postmenopausal women. Bone. 2007;40(5):1244-1251.
[29] BEMBEN DA, BEMBEN MG. Dose-response effect of 40 weeks of resistance training on bone mineral density in older adults. Osteoporos Int. 2011;22(1):179-186.
[30] LIU-AMBROSE TY, KHAN KM, ENG JJ, et al. Both resistance and agility training increase cortical bone density in 75- to 85-year-old women with low bone mass: a 6-month randomized controlled trial. J Clin Densitom. 2004;7(4):390-398.
[31] NICHOLS KP, PETERSON KK. Bone mineral density responses to high-intensity strength training in active older women. Aging Phys. 1995;5(3):26-38.
[32] BOROń D, KAMIńSKI A, KOTRYCH D, et al. Polymorphism of vitamin D3 receptor and its relation to mineral bone density in perimenopausal women. Osteoporos Int. 2015; 26(3):1045-1052.
[33] DROR AD, VIRK K, LEE K, et al. Resistance Training Threshold for Elevating Bone Mineral Density in Growing Female Rats. Int J Sports Med. 2018; 39(5):382-389.
[34] STUNES AK, ERBEN RG, SCHüLER C, et al. Skeletal effects of plyometric exercise and metformin in ovariectomized rats. Bone. 2020;132:115193.
[35] 赵忠海,闫彤,李洪秋,等.抗阻训练干预绝经后骨质疏松患者骨密度的系统综述和Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(30):4914-4920.
[36] KISTLER-FISCHBACHER M, WEEKS BK, BECK BR. The effect of exercise intensity on bone in postmenopausal women (part 1): A systematic review. Bone. 2021;143:115696.
[37] 阚世锋,陈文华,余波,等.不同运动强度对骨密度影响的研究进展[A].中国康复医学会运动疗法分会第十一届全国康复学术大会,2011.
[38] 张林.不同强度运动对骨质疏松大鼠骨生物力学性能的影响[J].体育科学,2000,20(5):72-76.
[39] PEARCE G, BASS S, YOUNG N, et al. Does weight-bearing exercise protect against the effects of exercise-induced oligomenorrhea on bone density? Osteoporos Int. 1996;6(6):448-452.
[40] VERSCHUEREN SM, ROELANTS M, DELECLUSE C, et al. Effect of 6-month whole body vibration training on hip density, muscle strength, and postural control in postmenopausal women: a randomized controlled pilot study. J Bone Miner Res. 2004;19(3):352-359.
[41] STEVEN J, BRYAN SJ, GIULIANO C, et al. Progressive Resistance Training for Concomitant Increases in Muscle Strength and Bone Mineral Density in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2022;52(8):1939-1960.
[42] 杨则宜.运动营养生物化学研究进展[J].中国运动医学杂志,2004,23(2):158-165+199.
[43] BORBA-PINHEIRO CJ, DANTAS EH, VALE RG, et al. Resistance training programs on bone related variables and functional independence of postmenopausal women in pharmacological treatment: A randomized controlled trial. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2016;65:36-44.
[44] FUCHS RK, BAUER JJ, SNOW CM. Jumping improves hip and lumbar spine bone mass in prepubescent children: a randomized controlled trial. J Bone Miner Res. 2001;16(1):148-156.
[45] 丁明晖,黄东锋,李燕,等.运动对骨密度的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2006,12(1):80-81+88.
|