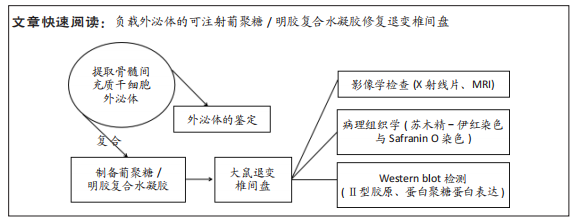
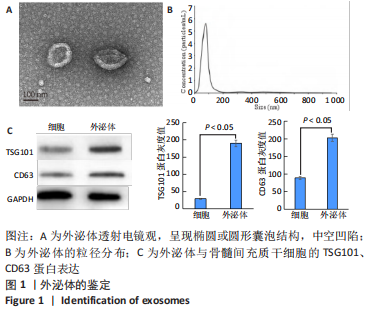
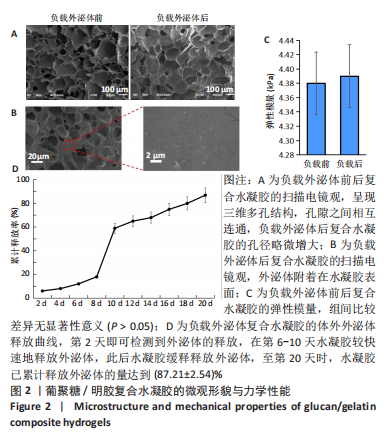
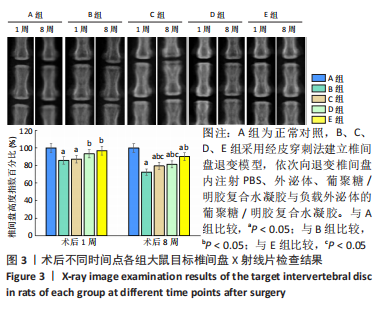
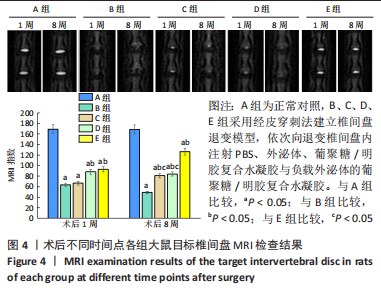
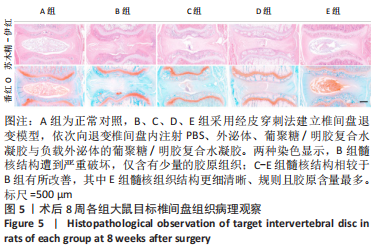
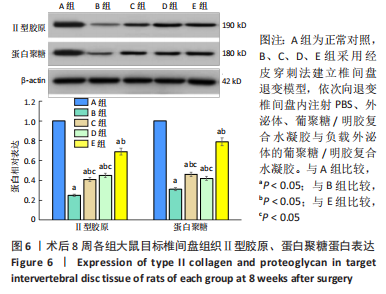
[1] WANG Y, CHE M, XIN J, et al. The role of IL-1β and TNF-α in intervertebral disc degeneration. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131:110660.
[2] KIRNAZ S, CAPADONA C, WONG T, et al. Fundamentals of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. World Neurosurg. 2022;157:264-273.
[3] CHAO-YANG G, PENG C, HAI-HONG Z. Roles of NLRP3 inflammasome in intervertebral disc degeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021;29(6):793-801.
[4] KOS N, GRADISNIK L, VELNAR T. A Brief Review of the Degenerative Intervertebral Disc Disease. Med Arch. 2019;73(6):421-424.
[5] XU P, GUAN J, CHEN Y, et al. Stiffness of photocrosslinkable gelatin hydrogel influences nucleus pulposus cell propertiesin vitro. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(2):880-891.
[6] CHEN W, CHEN H, ZHENG D, et al. Gene-Hydrogel Microenvironment Regulates Extracellular Matrix Metabolism Balance in Nucleus Pulposus. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019;7(1):1902099.
[7] LI M, LI R, YANG S, et al. Exosomes Derived from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Prevent Acidic pH-Induced Damage in Human Nucleus Pulposus Cells. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:e922928.
[8] HE L, HE T, XING J, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes protect cartilage damage and relieve knee osteoarthritis pain in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):276.
[9] 甘翼搏,李培,周强,等.不同浓度的葡聚糖/明胶复合水凝胶支架性能表征及其对体外构建组织工程髓核的影响[J].第三军医大学学报,2015,37(8):707-712
[10] LUO L, JIAN X, SUN H, et al. Cartilage endplate stem cells inhibit intervertebral disc degeneration by releasing exosomes to nucleus pulposus cells to activate Akt/autophagy. Stem Cells. 2021;39(4):467-481.
[11] WANG Y, WU Y, DENG M, et al. Establishment of a Rabbit Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Model by Percutaneous Posterolateral Puncturing of Lumbar Discs Under Local Anesthesia. World Neurosurg. 2021;154: e830-e837.
[12] BAI JY, ZHANG YZ, FAN Q, et al. Reactive Oxygen Species-Scavenging Scaffold with Rapamycin for Treatment of Intervertebral Disk Degeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020; 9(3):e1901186.
[13] BOUHSINA N, DECANTE C, HARDEL JB, et al. Correlation between magnetic resonance, X-ray imaging alterations and histological changes in an ovine model of age-related disc degeneration. Eur Cell Mater. 2021;42:166-178.
[14] ZHOU J, WU Y, ZHANG X, et al. Enzyme Catalyzed Hydrogel as Versatile Bioadhesive for Tissue Wound Hemostasis, Bonding, and Continuous Repair. Biomacromolecules. 2021; 22(4):1346-1356.
[15] ZHANG W, BAO B, JIANG F, et al. Promoting Oral Mucosal Wound Healing with a Hydrogel Adhesive Based on a Phototriggered S-Nitrosylation Coupling Reaction. Adv Mater. 2021; 33(48):e2105667.
[16] ZHANG FX, LIU P, DING W, et al. Injectable Mussel-Inspired highly adhesive hydrogel with exosomes for endogenous cell recruitment and cartilage defect regeneration. Biomaterials. 2021;278:121169.
[17] LIN J, WANG Z, HUANG J, et al. Microenvironment-Protected Exosome-Hydrogel for Facilitating Endometrial Regeneration, Fertility Restoration, and Live Birth of Offspring. Small. 2021;17(11):e2007235.
[18] HU J, LU Y, CAI L, et al. Functional compressive mechanics and tissue biocompatibility of an injectable SF/PU hydrogel for nucleus pulposus replacement. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):2347.
[19] CHRISTIANI T, MYS K, DYER K, et al. Using embedded alginate microparticles to tune the properties of in situ forming poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-graft-chondroitin sulfate bioadhesive hydrogels for replacement and repair of the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disc. JOR Spine. 2021;4(3):e1161.
[20] YU L, SUN ZJ, TAN QC, et al. Thermosensitive injectable decellularized nucleus pulposus hydrogel as an ideal biomaterial for nucleus pulposus regeneration. J Biomater Appl. 2020; 35(2):182-192.
[21] ZHU Y, TAN J, ZHU H, et al. Development of kartogenin-conjugated chitosan-hyaluronic acid hydrogel for nucleus pulposus regeneration. Biomater Sci. 2017;5(4):784-791.
[22] GENG X, MO X, FAN L, et al. Hierarchically designed injectable hydrogel from oxidized dextran, amino gelatin and 4-arm poly(ethylene glycol)-acrylate for tissue engineering application. J Mater Chem. 2012;22(48):25130-25139.
[23] UNAL S, ARSLAN S, KARADEMIR YILMAZ B, et al.Glioblastoma cell adhesion properties through bacterial cellulose nanocrystals in polycaprolactone/gelatin electrospun nanofibers. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;233:115820.
[24] CAZZANELLI P, WUERTZ-KOZAK K. MicroRNAs in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration, Apoptosis, Inflammation, and Mechanobiology. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(10):3601.
[25] ZHANG Y, HAN S, KONG M, et al. Single-cell RNA-seq analysis identifies unique chondrocyte subsets and reveals involvement of ferroptosis in human intervertebral disc degeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021;29(9):1324-1334.
[26] SHIM EK, LEE JS, KIM DE, et al. Autogenous Mesenchymal Stem Cells from the Vertebral Body Enhance Intervertebral Disc Regeneration via Paracrine Interaction: An in Vitro Pilot Study. Cell Transplant. 2016;25(10):1819-1832.
[27] Bhujel B, Shin HE, Choi DJ, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes and Intervertebral Disc Regeneration: Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(13):7306.
[28] FOO JB, LOOI QH, CHONG PP, et al. Comparing the therapeutic potential of stem cells and their secretory products in regenerative medicine. Stem Cells Int. 2021;2021:2616807.
[29] ONO M, KOSAKA N, TOMINAGA N, et al. Exosomes from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells contain a micro RNA that promotes dormancy in metastatic breast cancer cells. Science signaling. 2014;7(332):ra63.
[30] LIAO Z, LUO R, LI G, et al. Exosomes from mesenchymal stem cells modulate endoplasmic reticulum stress to protect against nucleus pulposus cell death and ameliorate intervertebral disc degeneration in vivo. Theranostics. 2019;9(14):4084-4100.
[31] HU Y, TAO R, WANG L, et al. Exosomes Derived from Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Compression-Induced Nucleus Pulposus Cell Apoptosis by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:2310025.
[32] XIAO Q, ZHAO Z, TENG Y, et al. BMSC-Derived Exosomes Alleviate Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Modulating AKT/mTOR-Mediated Autophagy of Nucleus Pulposus Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2022;2022:9896444.
[33] ZHU L, SHI Y, LIU L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes ameliorate nucleus pulposus cells apoptosis via delivering miR-142-3p: therapeutic potential for intervertebral disc degenerative diseases. Cell Cycle. 2020;19(14):1727-1739.
[34] QIAN J, WANG X, SU G, et al. Platelet-rich plasma-derived exosomes attenuate intervertebral disc degeneration by promoting NLRP3 autophagic degradation in macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;110:108962. |