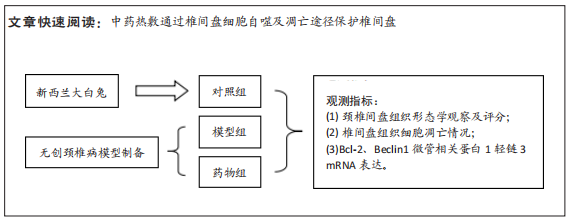
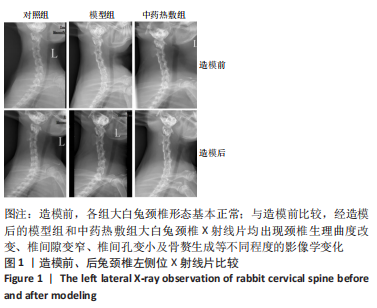
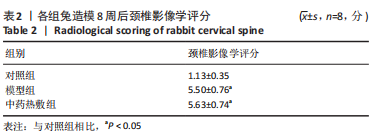
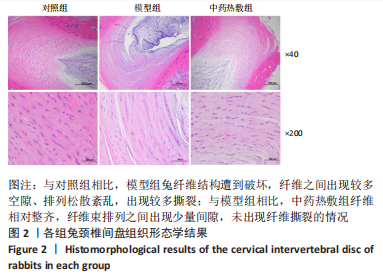
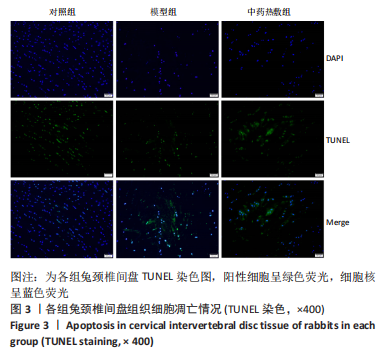
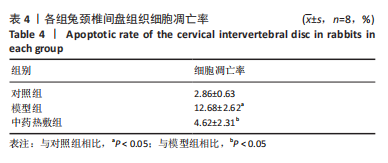
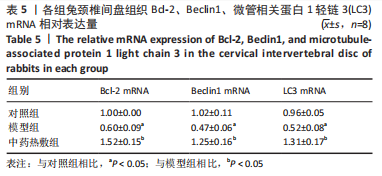
[1] 岳寿伟,魏慧,邵山.颈椎病评估与康复治疗进展[J].中国康复医学杂志,2019,34(11):1273-1277.
[2] HOY D, MARCH L, WOOLF A, et al. The global burden of neck pain: estimates from the global burden of disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(7):1309-1315.
[3] HURWITZ EL, LI D, GUILLEN J, et al. Variations in Patterns of Utilization and Charges for the Care of Neck Pain in North Carolina, 2000 to 2009: A Statewide Claims’ Data Analysis. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2016; 39(4):240-251.
[4] SKILLGATE E, PICO-ESPINOSA OJ, HALLQVIST J, et al. Healthy lifestyle behavior and risk of long duration troublesome neck pain or low back pain among men and women: results from the Stockholm Public Health Cohort. Clin Epidemiol. 2017;9:491-500.
[5] DING F, SHAO ZW, YANG SH, et al. Role of mitochondrial pathway in compression-induced apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells. Apoptosis. 2012;17(6):579-590.
[6] HE R, WANG Z, CUI M, et al. HIF1A Alleviates compression-induced apoptosis of nucleus pulposus derived stem cells via upregulating autophagy. Autophagy. 2021;17(11):3338-3360.
[7] GONG C, ZHANG HH. Autophagy as a potential therapeutic target in intervertebral disc degeneration. Life Sci. 2021;273:119266.
[8] WANG D, HE X, WANG D, et al. Quercetin Suppresses Apoptosis and Attenuates Intervertebral Disc Degeneration via the SIRT1-Autophagy Pathway. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:613006.
[9] ZHANG S, LIANG W, ABULIZI Y, et al. Quercetin Alleviates Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Modulating p38 MAPK-Mediated Autophagy. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:6631562.
[10] ZHENG Z, WANG ZG, CHEN Y, et al. Spermidine promotes nucleus pulposus autophagy as a protective mechanism against apoptosis and ameliorates disc degeneration. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22(6):3086-3096.
[11] JIANG W, ZHANG X, HAO J, et al. SIRT1 protects against apoptosis by promoting autophagy in degenerative human disc nucleus pulposus cells. Sci Rep. 2014;4:7456.
[12] 杨帏勋,李威廷,苏菲德.中医针灸结合中药热敷治疗颈椎病疼痛的效果[J].中医临床研究,2019,11(31):50-51.
[13] 张桂平.中药热敷治疗颈椎病的临床疗效及护理观察[J]. 中国医药指南,2019,17(28):208-209.
[14] 余家阔,吴毅文,戴先进,等.颈椎病生物力学发病机制实验研究[J]. 安徽医科大学学报,1990(1):47-51.
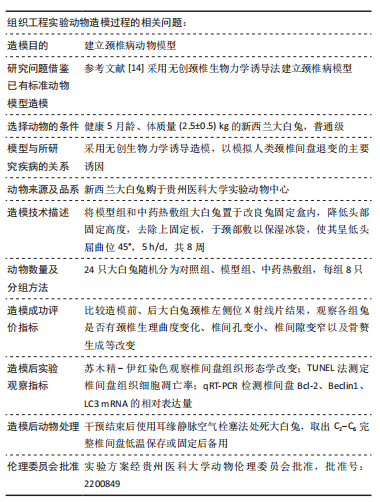
[15] 徐银琴,高航,王光义.通痹方热敷对颈椎病家兔颈部痛阈和椎间盘退变的影响[J].贵州医科大学学报,2020,45(3):298-303.
[16] MASUDA K, AOTA Y, MUEHLEMAN C, et al. A novel rabbit model of mild, reproducible disc degeneration by an anulus needle puncture: correlation between the degree of disc injury and radiological and histological appearances of disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(1):5-14.
[17] 李跃兵,王焕梅.向贤德教授针药结合治疗神经根型颈椎病临床经验撷菁[J]. 湖南中医药大学学报,2019,39(12):1503-1506.
[18] 丁明明,陈文莉,戴益辉,等.简述中药热奄包的临床应用近况[J].江西中医药,2019,50(8):72-74.
[19] 牛明镜,王顺云.中医综合疗法治疗神经根型颈椎病97例[J].中医正骨,2012,24(3):61-62.
[20] 常献,陈斌,李长青.髓核细胞老化机制研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(1):40-42.
[21] 孟祥宇,夏建龙,杨挺,等.椎间盘退变的机制及修复[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(11):1768-1773..
[22] 李文举, 李亦梅. 椎间盘退变机制研究现状及生物治疗展望[J]. 中国骨与关节外科,2014,7(1):66-69.
[23] PENG B, DEPALMA MJ. Cervical disc degeneration and neck pain. J Pain Res. 2018;11:2853-2857.
[24] 苏树燕,黄瑞滨,周晓柔,等.颈椎曲度变直对青年人颈椎间盘早期退变的影响:基于56例磁共振T2-mapping[J]. 分子影像学杂志, 2020,43(2):296-299.
[25] 李沅骋,李开平,宋子琪,等.长期低头位与寒湿刺激建立颈型颈椎病动物模型的研究[J].中华中医药学刊:1-20[2022-05-14].
[26] HASCHTMANN D, STOYANOV JV, GEDET P, et al. Vertebral endplate trauma induces disc cell apoptosis and promotes organ degeneration in vitro. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(2):289-299.
[27] 邹璟,姜梦雅,李解,等.细胞凋亡参与电针对退变椎间盘保护作用的研究[J]. 时珍国医国药,2017,28(9):2271-2273.
[28] AVIN-WITTENBERG T. Autophagy and its role in plant abiotic stress management. Plant Cell Environ. 2019;42(3):1045-1053.
[29] HU YX, HAN XS, JING Q. Autophagy in Development and Differentiation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1206:469-487.
[30] MIZUSHIMA N, KOMATSU M. Autophagy: renovation of cells and tissues. Cell. 2011;147(4):728-741.
[31] D’ARCY MS. Cell death: a review of the major forms of apoptosis, necrosis and autophagy. Cell Biol Int. 2019;43(6):582-592.
[32] RYTER SW, MIZUMURA K, CHOI A. The Impact of Autophagy on Cell Death Modalities. Int J Cell Biol. 2014;2014(1):502676.
[33] HE C, ZHU H, LI H, et al. Dissociation of Bcl-2–Beclin1 Complex by Activated AMPK Enhances Cardiac Autophagy and Protects Against Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis in Diabetes. Diabetes. 2013;62(4):1270-1281.
[34] NAKASHIMA A, AOKI A, KUSABIRAKI T, et al. Role of autophagy in oocytogenesis, embryogenesis, implantation, and pathophysiology of pre-eclampsia. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2017;43(4):633-643.
[35] GRILO AL, MANTALARIS A. Apoptosis: A mammalian cell bioprocessing perspective. Biotechnol Adv. 2019;37(3):459-475.
[36] GARCÍA-SÁEZ AJ. The secrets of the Bcl-2 family. Cell Death Differ. 2012; 19(11):1733-1740.
[37] SUN T, LI X, ZHANG P, et al. Acetylation of Beclin 1 inhibits autophagosome maturation and promotes tumour growth. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7215.
[38] ZHANG TW, LI ZF, DONG J, et al. The circadian rhythm in intervertebral disc degeneration: an autophagy connection. Exp Mol Med. 2020; 52(1):31-40.
[39] 孙忠人,栾逸先,尹洪娜,等. 夹脊电针通过调控细胞死亡治疗脊髓损伤的相关机制研究进展[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2021,36(4):2213-2215.
[40] 赵军,师建平,党赢.椎动脉型颈椎病的血管内皮细胞自噬与血瘀气虚关系探讨[J]. 中医学报,2021,36(6):1184-1186.
[41] LIU Y, SHI L, QIU W, et al. Ferulic acid exhibits anti-inflammatory effects by inducing autophagy and blocking NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Mol Cell Toxicol. 2022;18(4):509-519.
[42] WU C, CHEN H, ZHUANG R, et al. Betulinic acid inhibits pyroptosis in spinal cord injury by augmenting autophagy via the AMPK-mTOR-TFEB signaling pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17(4):1138-1152.
[43] 蔡慧倩, 粟胜勇, 张熙, 等. 温和灸对神经根型颈椎病大鼠脊髓Beclin-1/Bcl-2表达的影响[J]. 针刺研究,2020,45(10):799-805.
[44] ZHAO K, ZHANG Y, LIANG K, et al. Methylation of microRNA-129-5P modulates nucleus pulposus cell autophagy by targeting Beclin-1 in intervertebral disc degeneration. Oncotarget. 2017;8(49):86264-86276.
[45] 徐银琴, 史红美, 王光义. 通痹方热敷联合针刺治疗对退变椎间盘细胞凋亡相关基因Caspase-3、Bcl-2 mRNA的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(5):713-718.
[46] 徐银琴,王光义.通痹方热奄包外敷对家兔退变颈椎间盘细胞凋亡相关基因Caspase-3和Bcl-2 mRNA的影响[J].贵州医科大学学报, 2020,45(4):438-443. |