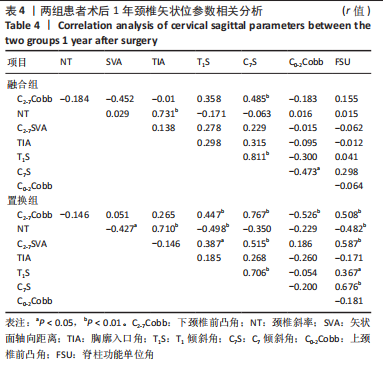
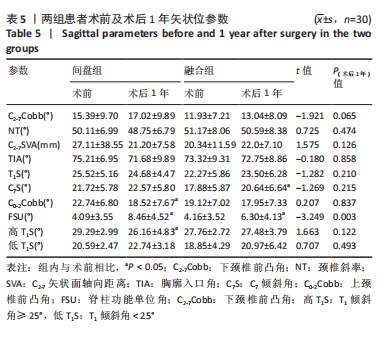
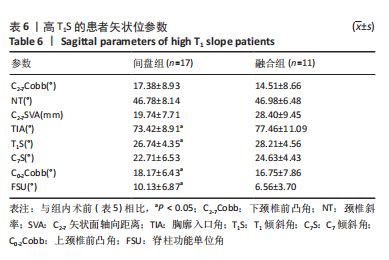
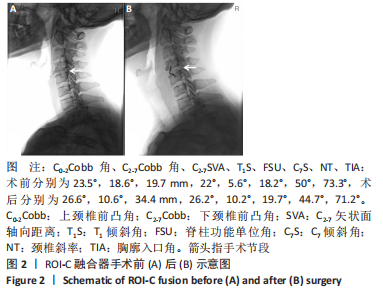
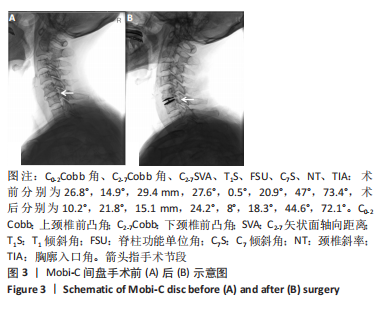
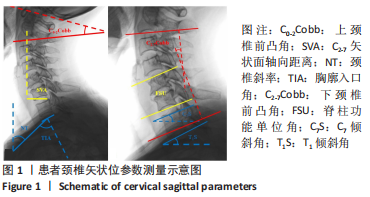
[1] 刘涛, 邱水强, 黄宇峰, 等. 颈前路椎间融合术后矢状位参数变化与临床疗效的相关性研究[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2018,38(2):79-85.
[2] DONG L, XU Z, CHEN X, et al. The change of adjacent segment after cervical disc arthroplasty compared with anterior cervical discectomy and fusion: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Spine J. 2017;17(10):1549-1558.
[3] CHUNG YW, KIM SK, PARK YJ. Differences in the Prevalence of Clinical Adjacent Segment Pathology among Continents after Anterior Cervical Fusion: Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J Clin Med. 2021;10(18):4125.
[4] 徐帅, 朱震奇, 钱亚龙, 等. 颈椎人工椎间盘置换与椎间盘切除融合术后邻近节段退变比较研究的Meta分析[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2017,27(4):296-304.
[5] 陈江, 李晋玉, 郑晨颖, 等. 双节段颈人工椎间盘置换与颈椎间盘切除融合后颈椎矢状位参数的变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021, 25(15):2341-2346.
[6] RAJAKUMAR DV, HARI A, KRISHNA M, et al. Adjacent-level arthroplasty following cervical fusion. Neurosurg Focus. 2017;42(2):E5.
[7] TAMAI K, BUSER Z, PAHOLPAK P, et al. Can C7 Slope Substitute the T1 slope?: An Analysis Using Cervical Radiographs and Kinematic MRIs. Spine. 2018;43(7):520-525.
[8] YANG X, BARTELS RHMA, DONK R, et al. The association of cervical sagittal alignment with adjacent segment degeneration. Eur Spine J. 2020;29(11):2655-2664.
[9] DENARO V, LONGO UG, BERTON A, et al. Favourable outcome of posteriordecompression and stabilization in lordosis for cervical spondylotic myelopathy: the spinal cord “back shift” concept. Eur Spine J. 2015;24(7):826-831.
[10] BUCCI MN, OH D, COWAN RS, et al. The ROI-C zero-profile anchored spacer for anterior cervical discectomy and fusion: biomechanical profile and clinical outcomes. Med Devices (Auckl). 2017;18(10): 61-69.
[11] 宋升, 孙振中, 姜为民, 等. 桥形固定颈椎前路融合器ROI-C在颈椎内固定治疗中的初步疗效分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(44):7127-7132.
[12] 朱彦奇, 王红霞, 曹锐, 等. 零切迹椎间融合器与钛板椎间融合器治疗多节段颈椎病的Meta分析[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2019, 29(9):805-814.
[13] GERILMEZ A, NADERI S. A Novel Perspective for Analyzing Craniocervical Sagittal Balance and Horizontal Gaze. World Neurosurg. 2021;149:e924-e930.
[14] AJELLO M, MARENGO N, PILLONI G, et al. Is It Possible To Evaluate the Ideal Cervical Alignment for Each Patient Needing Surgery? An Easy Rule To Determine the Appropriate Cervical Lordosis in Preoperative Planning. World Neurosurg. 2017;97:471-478.
[15] 赵学千. 中医手法和颈椎间盘置换术治疗颈椎病后颈椎矢状位参数的变化研究[D]. 北京:北京中医药大学,2020:44-46.
[16] 刘静培. 成年人不同曲度颈椎矢状位参数代偿相关性研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2018:7-9.
[17] 张琦, 熊洋, 俞兴, 等. Mobi-C人工间盘联合ROI-C自稳性融合器与单纯ROI-C自稳性融合器治疗双节段颈椎病的中期疗效随访[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(3):397-402.
[18] DMITRIEV AE, CUNNINGHAM BW, HU N, et al. Adjacent level intradiscal pressure and segmental kinematics following a cervical total disc arthroplasty: an in vitro human cadaveric model. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(10):1165-1172.
[19] WEINHOFFER SL, GUYER RD, HERBERT M, et al. Intradiscal pressure measurements above an instrumented fusion. A cadaveric study. Spine. 1995;20(5):526-531.
[20] DEJAEGHER J, WALRAEVENS J, VAN LOON J, et al. 10-year follow-up after implantation of the Bryan Cervical Disc Prosthesis. Eur Spine J. 2017;26(4):1191-1198.
[21] RADCLIFF K, DAVIS RJ, HISEY MS, et al. Long-term Evaluation of Cervical Disc Arthroplasty with the Mobi-C© Cervical Disc: A Randomized, Prospective, Multicenter Clinical Trial with Seven-Year Follow-up. Int J Spine Surg. 2017;11(4):31.
[22] WANG QL, TU ZM, HU P, et al. Long-term Results Comparing Cervical Disc Arthroplasty to Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(1):16-30.
[23] MEHREN C, HEIDER F, SIEPE CJ, et al. Clinical and radiological outcome at 10 years of follow-up after total cervical disc replacement. Eur Spine J. 2017;26(9):2441-2449.
[24] KIM K, HOFFMAN G, BAE H, et al. Ten-Year Outcomes of 1- and 2-Level Cervical Disc Arthroplasty From the Mobi-C Investigational Device Exemption Clinical Trial. Neurosurgery. 2021;88(3):497-505.
[25] WENG C, WANG J, TUCHMAN A, et al. Influence of T1 Slope on the Cervical Sagittal Balance in Degenerative Cervical Spine: An Analysis Using Kinematic MRI. Spine. 2016;41(3):185-190.
[26] SHANG Z, ZHANG Y, ZHANG D, et al. Clinical and Radiological Analysis of Bryan Cervical Artificial Disc Replacement for “Skip” Multi-Segment Cervical Spondylosis: Long-Term Follow-Up Results. Med Sci Monit. 2017;4(23):5254-5263.
[27] KANI KK, CHEW FS. Cervical Disc Arthroplasty: Review and Update for Radiologists. Semin Roentgenol. 2019;54(2):113-123.
[28] 鲍达, 陈兴, 李力韬, 等. Mobi-C人工颈椎间盘置换术对颈椎曲度的影响[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2018,33(7):673-675.
[29] HAYASHI T, DAUBS MD, SUZUKI A, et al. The Compensatory Relationship of Upper and Subaxial Cervical Motion in the Presence of Cervical Spondylosis. Clin Spine Surg. 2016;29(4):E196-200.
[30] 孙东. 上下颈椎矢状位序列和T1 slope相关性的影像学研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2017:6-8.
[31] LEE SH, KIM KT, SEO EM, et al. The influence of thoracic inlet alignment on the craniocervical sagittal balance in asymptomatic adults. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2012;25(2):E41-47.
[32] LI J, ZHANG D, SHEN Y. Impact of cervical sagittal parameters on axial neck pain in patients with cervical kyphosis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020; 15(1):434.
[33] YANG P, LI Y, LI J, et al. Impact of T1 slope on surgical and adjacent segment degeneration after Bryan cervical disc arthroplasty. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2017;13:1119-1125.
[34] LE HUEC JC, THOMPSON W, MOHSINALY Y, et al. Sagittal balance of the spine. Eur Spine J. 2019;28(9):1889-1905.
[35] ZHAO J, JIANG R, YANG Y, et al. Preoperative T1 Slope as a Predictor of Change in Cervical Alignment and Range of Motion After Cervical Disc Arthroplasty. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:5844-5850.
[36] GOEDMAKERS CMW, JANSSEN T, YANG X, et al. Cervical radiculopathy: is a prosthesis preferred over fusion surgery? A systematic review. Eur Spine J. 2020;29(11):2640-2654.
[37] VLEGGEERT-LANKAMP CLA, JANSSEN TMH, VAN ZWET E, et al. The NECK trial: Effectiveness of anterior cervical discectomy with or without interbody fusion and arthroplasty in the treatment of cervical disc herniation; a double-blinded randomized controlled trial. Spine J. 2019;19(6):965-975.
|