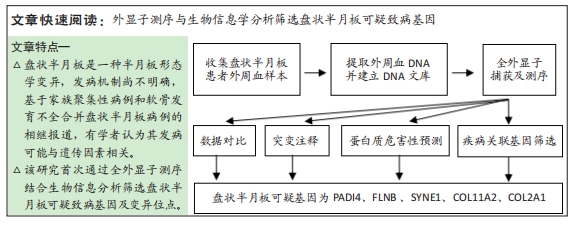
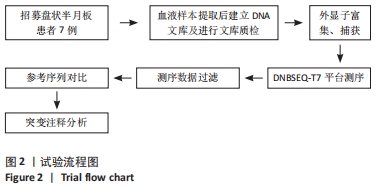
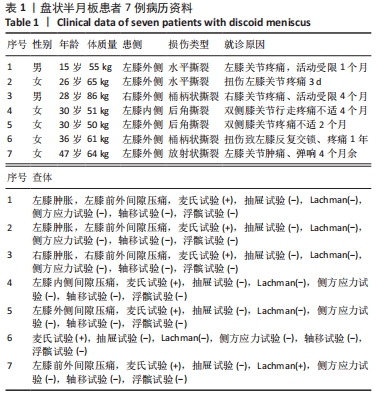
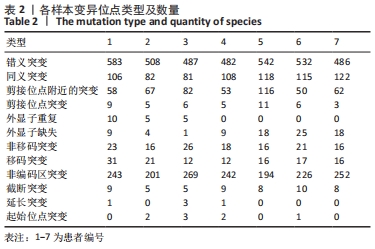
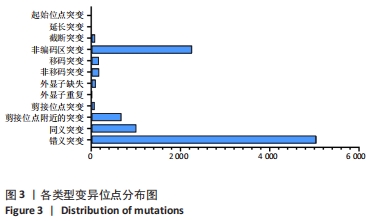
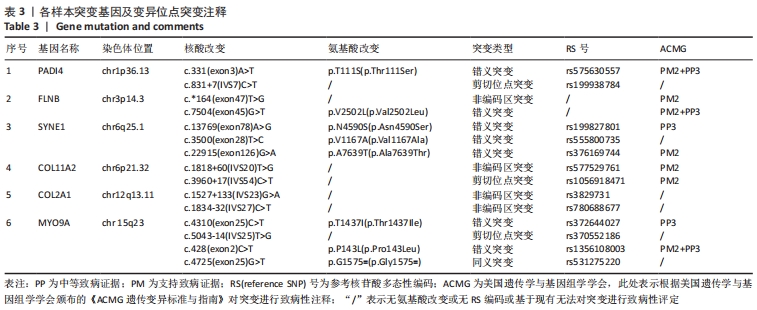
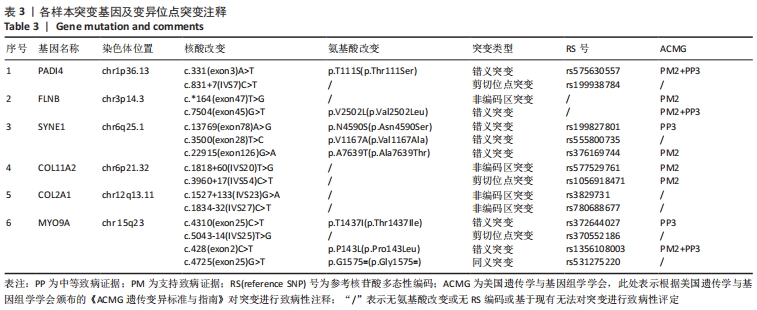
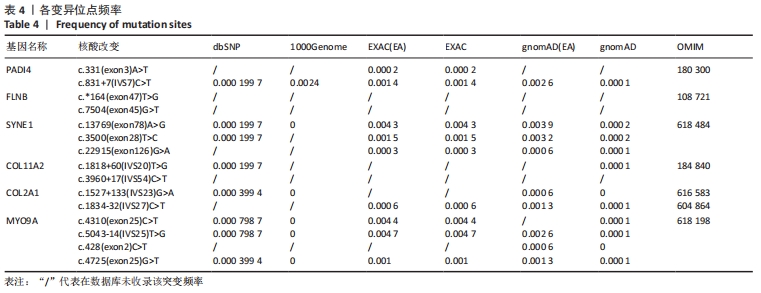
[1] WATANABE M, TAKEDA S, IKEUCHI H. Atlas of arthroscopy. Tokyo: Igaku-Shoin,1978:88.
[2] MASQUIJO JJ, BERNOCCO F, PORTA J. Discoid meniscus in children and adolescents: Correlation between morphology and meniscal tears. Rev Esp Cir Ortop Traumatol (Engl Ed). 2019;63(1):24-28.
[3] SMILLIE IS. The congenital discoid meniscus. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1948; 30B(4):671-682.
[4] KAPLAN EB. Discoid lateral meniscus of the knee joint; nature, mechanism, and operative treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1957;39-A(1):77-87.
[5] 吴柏年,陈作人,陆凯,等.胎儿半月板及胫骨髁形态观察与测量[J].浙江医学,1994,16(5):13-14.
[6] AHMED ALI R, MCKAY S. Familial discoid medial meniscus tear in three members of a family: a case report and review of literature. Case Rep Orthop. 2014;2014:285675.
[7] 陈峰,杨波.盘状半月板病因学研究现状与进展[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2016,9(1):80-83.
[8] 钟宏彬. BGISEQ-500、Hiseq 4000和Hiseq X Ten三个测序平台之间外显子测序数据比较分析[D].广州:华南理工大学,2018.
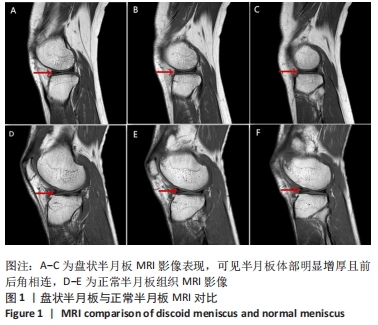
[9] 赵福香. 膝关节盘状半月板的MRI表现以及MRI诊断盘状半月板的标准研究[J].现代医用影像学,2019,28(5):1073-1074.
[10] 王淑丽,王林森,王植.膝关节盘状半月板类型及损伤的MRI分析[J].临床放射学杂志,2004,23(1):66-69.
[11] SAAVEDRA M, SEPÚLVEDA M, JESÚS TUCA M, et al. Discoid meniscus: current concepts. EFORT Open Rev. 2020;5(7):371-379.
[12] KOCHER MS, LOGAN CA, KRAMER DE. Discoid Lateral Meniscus in Children: Diagnosis, Management, and Outcomes. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2017;25(11):736-743.
[13] KIM JH, AHN JH, KIM JH, et al. Discoid lateral meniscus: importance, diagnosis, and treatment. J Exp Orthop. 2020;7(1):81.
[14] CHOI YH, SEO YJ, HA JM, et al. Collagenous Ultrastructure of the Discoid Meniscus: A Transmission Electron Microscopy Study. Am J Sports Med. 2017;45(3):598-603.
[15] BISICCHIA S, BOTTI F, TUDISCO C. Discoid lateral meniscus in children and adolescents: a histological study. J Exp Orthop. 2018;5(1):39.
[16] AYDIN KABAKÇI AD, BÜYÜKMUMCU M, AKIN D, et al. Morphological structure and variations of fetal lateral meniscus: the significance in convenient diagnosis and treatment. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(10):3364-3373.
[17] KIM JH, BIN SI, LEE BS, et al. Does discoid lateral meniscus have inborn peripheral rim instability? Comparison between intact discoid lateral meniscus and normal lateral meniscus. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2018;138(12):1725-1730.
[18] YANG SJ, DING ZJ, LI J, et al. Factors influencing postoperative outcomes in patients with symptomatic discoid lateral meniscus. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):551.
[19] GRIMM NL, PACE JL, LEVY BJ, et al. Demographics and Epidemiology of Discoid Menisci of the Knee: Analysis of a Large Regional Insurance Database. Orthop J Sports Med. 2020;8(9):2325967120950669.
[20] ATAY OA, PEKMEZCI M, DORAL MN, et al. Discoid meniscus: an ultrastructural study with transmission electron microscopy. Am J Sports Med. 2007;35(3):475-478.
[21] CUI JH, MIN BH. Collagenous fibril texture of the discoid lateral meniscus. Arthroscopy. 2007;23(6):635-641.
[22] Papadopoulos A, Kirkos JM, Kapetanos GA. Histomorphologic study of discoid meniscus. Arthroscopy. 2009;25(3):262-268.
[23] YANG X, SHAO D. Bilateral discoid medial Meniscus: Two case reports. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(15):e15182.
[24] FARLETT J, WOOD JR. Ipsilateral Medial and Lateral Discoid Menisci: A Rare Combination of Infrequent Anatomic Variants. J Clin Imaging Sci. 2020;10:11.
[25] 陈佳.腰椎间盘退变和先天性脊柱侧凸相关基因关联分析和致病性研究[D].北京:北京协和医学院,2018.
[26] 赵春霞,崔映宇,陈义汉.核膜血影重复蛋白研究进展[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,2014,41(4):337-344.
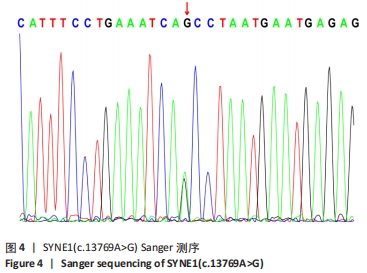
[27] GAMA MT, HOULE G, NOREAU A, et al. SYNE1 mutations cause autosomal-recessive ataxia with retained reflexes in Brazilian patients. Mov Disord. 2016;31(11):1754-1756.
[28] WIETHOFF S, HERSHESON J, BETTENCOURT C, et al. Heterogeneity in clinical features and disease severity in ataxia-associated SYNE1 mutations. J Neurol. 2016;263(8):1503-1510.
[29] KIM JS, KIM AR, YOUN J, et al. Identifying SYNE1 ataxia and extending the mutational spectrum in Korea. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2019;58: 74-78.
[30] INDELICATO E, NACHBAUER W, FAUTH C, et al. SYNE1-ataxia: Novel genotypic and phenotypic findings. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2019;62: 210-214.
[31] WANG Y, CAO R, YANG W, et al. SP1-SYNE1-AS1-miR-525-5p feedback loop regulates Ang-II-induced cardiac hypertrophy. J Cell Physiol. 2019; 234(8):14319-14329.
[32] ZHAO T, MA Y, ZHANG Z, et al. Young and early-onset dilated cardiomyopathy with malignant ventricular arrhythmia and sudden cardiac death induced by the heterozygous LDB3, MYH6, and SYNE1 missense mutations. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2021;26(4): e12840.
[33] CHEN Z, REN Z, MEI W, et al. A novel SYNE1 gene mutation in a Chinese family of Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy-like. BMC Med Genet. 2017;18(1):63.
[34] 陈祖芝.伴有SYNE1基因新突变的Emery-Dreifuss肌营养不良症家系基因突变特点分析[D].郑州:郑州大学,2017.
[35] 何梅.人核纤层蛋白病秀丽隐杆线虫模型的建立和机制研究[D].哈尔滨:东北林业大学,2018.
[36] 赵丹华,赵运涛,杨旭,等. X连锁遗传的Emery-Dreifuss肌营养不良一家系的临床、病理及基因突变特点[J].中国神经免疫学和神经病学杂志,2017,24(3):197-200.
[37] HARTMAN MA, FINAN D, SIVARAMAKRISHNAN S, et al. Principles of unconventional myosin function and targeting. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2011;27:133-155.
[38] O’CONNOR E, PHAN V, CORDTS I, et al. MYO9A deficiency in motor neurons is associated with reduced neuromuscular agrin secretion. Hum Mol Genet. 2018;27(8):1434-1446.
[39] O’CONNOR E, TÖPF A, MÜLLER JS, et al. Identification of mutations in the MYO9A gene in patients with congenital myasthenic syndrome. Brain. 2016;139(Pt 8):2143-2153.
[40] MCMACKEN G, WHITTAKER RG, EVANGELISTA T, et al. Congenital myasthenic syndrome with episodic apnoea: clinical, neurophysiological and genetic features in the long-term follow-up of 19 patients. J Neurol. 2018;265(1):194-203.
[41] YIŞ U, BECKER K, KURUL SH, et al. Genetic Landscape of Congenital Myasthenic Syndromes From Turkey: Novel Mutations and Clinical Insights. J Child Neurol. 2017;32(8):759-765.
[42] TSAI CY, HSIEH SC, LIU CW, et al. The Expression of Non-Coding RNAs and Their Target Molecules in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Molecular Basis for Rheumatoid Pathogenesis and Its Potential Clinical Applications. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(11):5689.
[43] BADILLO-SOTO MA, RODRÍGUEZ-RODRÍGUEZ M, PÉREZ-PÉREZ ME, et al. Potential protein targets of the peptidylarginine deiminase 2 and peptidylarginine deiminase 4 enzymes in rheumatoid synovial tissue and its possible meaning. Eur J Rheumatol. 2016;3(2):44-49.
[44] BAWADEKAR M, SHIM D, JOHNSON CJ, et al. Peptidylarginine deiminase 2 is required for tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced citrullination and arthritis, but not neutrophil extracellular trap formation. J Autoimmun. 2017;80:39-47.
[45] 刘玮,吴歆,徐沪济.类风湿关节炎易感基因遗传背景的研究进展[J].诊断学理论与实践,2018,17(3):347-351.
[46] 叶蓓,成宇,司玉莹,等.低氧环境中PADI4促进破骨细胞分化和骨吸收功能的研究[J].现代免疫学,2021,41(5):361-367.
[47] LIU C, TANG W, ZHAO H, et al. The variants at FLNA and FLNB contribute to the susceptibility of hypertension and stroke with differentially expressed mRNA. Pharmacogenomics J. 2021;21(4):458-466.
[48] 徐启明. FLNB基因突变在发育性骨骼畸形中的分子生物学研究[D].北京:北京协和医学院,2018.
[49] 尚小可,郑君,温鹏,等.人类与实验动物半月板解剖及超微结构的比较[J].宁夏医科大学学报,2018,40(10):1231-1234.
[50] 李素萍,金玉霞,杨静,等.COL2A1基因新发突变导致先天性脊柱骨骺发育不良的遗传分析及产前诊断[J].临床检验杂志,2020, 38(12): 919-921,952.
[51] 张铂彦,张悦,刘贺,等.COL2A1基因突变与Ⅱ型胶原蛋白病表型关系的研究进展[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2020,46(3):643-648.
[52] TURLO AJ, MCDERMOTT BT, BARR ED, et al. Gene expression analysis of subchondral bone, cartilage, and synovium in naturally occurring equine palmar/plantar osteochondral disease. J Orthop Res. 2021. doi: 10.1002/jor.25075. Online ahead of print.
[53] LIU Y, WANG L, YANG YK, et al. Prenatal diagnosis of fetal skeletal dysplasia using targeted next-generation sequencing: an analysis of 30 cases. Diagn Pathol. 2019;14(1):76.
[54] XU C, LUO S, WEI L, et al. Integrated transcriptome and proteome analyses identify novel regulatory network of nucleus pulposus cells in intervertebral disc degeneration. BMC Med Genomics. 2021;14(1):40.
[55] YANG X, JIA H, XING W, et al. Genetic variants in COL11A2 of lumbar disk degeneration among Chinese Han population. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019;7(2):e00524.
|