中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (32): 5162-5170.doi: 10.12307/2021.219
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
促炎因子及基质金属蛋白酶在骨关节炎发病机制及相关治疗中的地位和作用
范重山1,孙明帅1,韩文朝1,2
- 1河南中医药大学,河南省郑州市 451200;2河南中医药大学附属医院(濮阳市中医院) ,河南省濮阳市 457000
-
收稿日期:2020-10-16修回日期:2020-10-20接受日期:2020-11-09出版日期:2021-11-18发布日期:2021-07-26 -
通讯作者:韩文朝,硕士生导师,主任医师,河南中医药大学,河南省郑州市 451200;河南中医药大学附属医院(濮阳市中医院) ,河南省濮阳市 457000 -
作者简介:范重山,男,1994年生,河南省郸城县人,汉族,河南中医药大学在读硕士,医师,主要从事中医药防治骨关节病的研究
Proinflammatory factors and matrix metalloproteinases: status and roles in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis
Fan Chongshan1, Sun Mingshuai1, Han Wenchao1, 2
- 1Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 451200, Henan Province, China; 2Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine (Puyang Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine), Puyang 457000, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2020-10-16Revised:2020-10-20Accepted:2020-11-09Online:2021-11-18Published:2021-07-26 -
Contact:Han Wenchao, Master’s supervisor, Chief physician, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 451200, Henan Province, China; Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine (Puyang Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine), Puyang 457000, Henan Province, China -
About author:Fan Chongshan, Master candidate, Physician, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 451200, Henan Province, China
摘要:
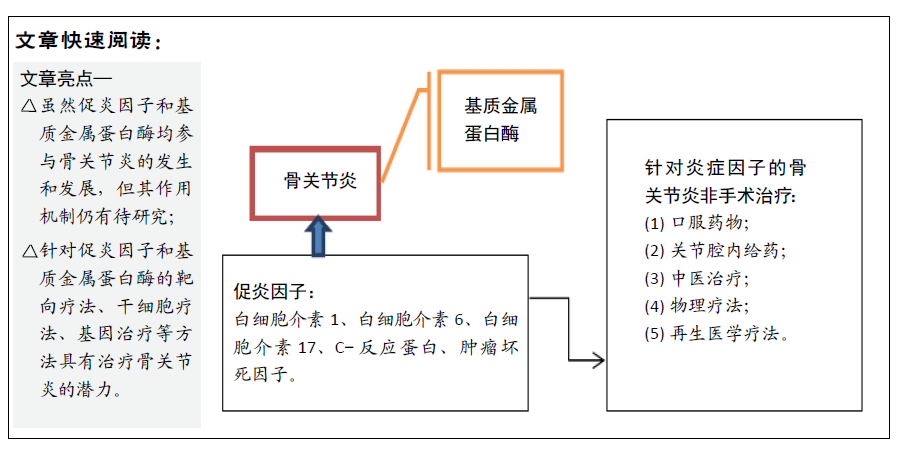
文题释义:
骨关节炎治疗:轻中度骨关节炎主要通过口服或者关节内注射镇痛药、抗炎药以及营养物质等缓解病情;重度骨关节炎可通过关节置换手术进行治疗。
正常关节中炎症因子的作用:在正常关节中软骨细胞的凋亡和增殖以及细胞外基质降解和合成均处于动态平衡中,其中白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素17、C-反应蛋白、肿瘤坏死因子α等多种细胞因子参与这种动态平衡。
背景:虽然已经提出了一些与骨关节炎相关的危险因素,包括遗传易感性、衰老、肥胖、关节结构及力线异常等,但骨关节炎的发病机制在很大程度上仍不清楚。
目的:综述国内外相关文献,总结促炎因子及基质金属蛋白酶在骨关节炎中的作用机制及相关治疗进展。
方法:第一作者以“骨关节炎,白细胞介素1,白细胞介素6,白细胞介素17,C-反应蛋白,肿瘤坏死因子α,基质金属蛋白酶,治疗”为中文检索词,以“osteoarthritis,Interleukin-1,Interleukin-6,Interleukin-17,C-reactive protein,tumor necrosis factor-α,matrix metalloproteinase,treatment”为英文检索词,检索1990年1月以来PubMed和中国知网数据库收录的基础及临床研究。
结果与结论:①骨关节炎是一种由多种因素导致的关节疾病,发病机制复杂,主要受到多种信号通路的调控,其中炎症细胞因子及基质金属蛋白酶在骨关节炎发病机制中的作用已经越来越明显,调控着骨关节炎的发生和发展,但仍需要更深入的研究探讨;②相信在不远的将来,明确骨关节炎的致病机制,探究新型的治疗手段,特别是干细胞疗法、基因治疗等方法的引入,有望使今后对骨关节炎的治疗和预防更具针对性。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
范重山, 孙明帅, 韩文朝. 促炎因子及基质金属蛋白酶在骨关节炎发病机制及相关治疗中的地位和作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(32): 5162-5170.
Fan Chongshan, Sun Mingshuai, Han Wenchao. Proinflammatory factors and matrix metalloproteinases: status and roles in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(32): 5162-5170.
2.1.1 感染、损伤或手术 多种细菌和病毒感染骨关节后,会导致某些类型骨关节炎的发展,软骨撕裂、关节脱臼、韧带损伤以及关节畸形者发生骨关节炎的风险更高。2017年的一项回顾性队列研究显示,发生前交叉韧带撕裂和外侧半月板损伤者在10年内发生骨关节炎的风险提升1.5倍[4];滑膜炎也与手部骨关节炎影像学进展有关[5]。关节中软骨细胞失去基质保护和营养后会发生退变和死亡[6],浅表的软骨损伤后24 h内,其周围软骨细胞的分裂、基质合成、分解代谢酶活性均明显。关节内组织和机械力学应力之间的复杂相互作用导致半月板挤压,其可能参与骨关节炎的发生发展。
2.1.2 肥胖或超重 肥胖一直被认为是引发膝关节炎的危险因素之一,超重和肥胖患者罹患骨关节炎的风险更大,同时其也会恶化骨关节炎的进程。关节是人体负重部位,当体质量增加后,其负荷随之增加,因而加大发生关节损伤的可能。有荟萃分析显示,肥胖或超重者发生膝骨关节炎的风险是正常体质量者的2.96倍,且体质量指数越高,膝关节炎的风险越大[6],因而控制体质量是预防骨关节炎的重要措施。妇女在10年内减重≥5 kg,可能降低50%发生膝骨关节炎的风险[7];维持越长时间的高体质量指数,发生膝骨关节炎的风险也越高[8]。高脂血症也是新发手部骨关节炎的独立危险因素[9]。罗美杰等[10]的一项整群抽样调查结果显示,膝关节炎患者的体质量指数越大,其西安大略和麦克马斯特大学骨关节炎指数越高,且患者发生跌倒的风险也越高。
2.1.3 慢性劳损 骨性关节炎更多见于慢性损伤,尤其是长期的劳损,包括长期行走或者端坐姿势不正确,以及过度负重。在从事各种体育项目的运动员中膝骨关节炎的发病率可达16%-95%[11],主要是由于运动员长时间的运动训练和高强度的训练负荷使膝关节受到反复冲击,引起关节软骨负荷改变及损伤,导致骨赘形成,增加远期骨性关节炎的发病风险。
2.1.4 先天性骨骼和软组织畸形 骨性关节炎与患者先天性骨骼和软组织畸形导致的关节不稳也有很大关联,例如髋关节发育不良患者先天髋关节解剖结构异常,在生长发育过程中髋臼对股骨头的覆盖逐渐减少,髋臼和股骨头的匹配度下降,造成髋关节生物力学长期异常,最终将发展成为髋关节骨关节炎[12]。研究发现某些骨关节炎患者肢体外观虽正常,但存在肢体扭转畸形,于是提出了扭转畸形与骨关节炎关系的新课题,人们发现膝内翻、膝外翻、足外翻、足内翻等患者成年后常有膝、髋的骨关节炎存在[13]。
2.1.5 基因 骨关节炎被认为是一种多基因疾病,有研究认为基因对骨关节炎的影响超过65%。WARNER等[14]的全基因组关联分析研究已确定了21种独立的骨关节炎易感基因位点。ALDH1A2基因rs4238326多态性可能与非创伤性膝骨关节炎易感性有关[15];TACR1基因多态性rs11688000与有症状骨关节炎的风险降低有关[16];COMT基因多态性Val158Met与髋骨关节炎相关的疼痛有关[17]。LI等[18]发现骨关节炎小鼠脊髓前角细胞中miRNA-146a与步态平衡能力相关。早发性严重性骨关节炎的发生与Ⅱ型胶原前蛋白突变有关[19]。
2.1.6 其他 女性比男性更容易发生骨关节炎,尤其在50岁以后。在男性和女性的组织发育过程中以及整个生命周期中,膝盖组织都受到性激素的调节,尽管绝经与女性骨关节炎严重程度增加有关,但仅全身性雌激素不能解释观察到的性别差异。除了膝骨关节炎的患病率增加之外,女性通常比男性更痛苦,且对其功能和生活质量的影响更大[20],雌激素替代疗法可显著减少髋骨关节炎以及膝骨关节炎的发生[21]。软骨组织成分暴露后可引发自身免疫反应,从而增加蛋白降解及炎症,造成软骨进一步损伤,进而使更多的软骨组织暴露于免疫系统中,形成恶性级联反应[22-25]。
2.2 促炎症细胞因子在骨关节炎发病中的作用 承受高机械负荷的正常关节中软骨细胞的凋亡和增殖以及细胞外基质降解和合成均处于动态平衡中,其中白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素17、C-反应蛋白、肿瘤坏死因子α等多种细胞因子参与这种动态平衡。大量研究认为这些因子均可参与骨关节炎的发展,发生炎症反应的软骨细胞会产生MMP,从而引起软骨降解,进而使骨关节炎进展。
2.2.1 白细胞介素1 白细胞介素1是分子质量为17 kD的细胞因子,可由巨噬细胞、软骨细胞、滑膜细胞、单核巨噬细胞等多种细胞产生,有白细胞介素1α和白细胞介素1β两种亚型,二者有25%同源性,以前体形式分泌出来,在白细胞介素转换酶作用下,转换成活性白细胞介素1。软骨细胞膜上分布有可结合白细胞介素1的受体,高水平的白细胞介素1与软骨细胞膜上受体结合,通过信息传递系统,将改变的信息输送到细胞内,从而干扰了软骨细胞的正常代谢活性,如抑制软骨细胞表型的分化[26]、诱导软骨细胞凋亡[27]、抑制软骨细胞增殖[28];白细胞介素1还可诱导MMP表达并促使其活化,引起软骨基质降解[29];白细胞介素1对滑膜的影响可刺激滑膜细胞释放中性蛋白酶和前列腺素E2,引起滑膜炎症和促进骨吸收[30]。许多研究在动物模型和体外培养方面实验证实白细胞介素1在骨关节炎的发病进程中起着关键作用。研究证实动物关节腔内注射重组的白细胞介素1可以成功诱发膝骨关节炎,再现白细胞介素1对关节软骨的破坏作用[31]。LANDSBERG等[32]将骨关节炎患者膝关节软骨细胞及滑膜细胞进行体外培养,其合成的白细胞介素1α和白细胞介素1β水平均升高。郑剑平等[33]的研究表明,膝骨关节炎患者关节液及血清中存在大量白细胞介素1,显著高于正常对照组,且膝骨关节炎患者的病程越长,症状越重,关节滑液中白细胞介素1含量增多就越显著。但是VAN DALEN等[34]研究认为,白细胞介素1α和白细胞介素1β不参与胶原酶诱导骨关节炎的滑膜炎症和软骨破坏,提示其他介质参与了关节损伤。因此,有关白细胞介素1对关节破坏的确切作用机制还需深入研究。
2.2.2 白细胞介素6 白细胞介素6于20世纪80年代被克隆出来,首次被证明能促进T淋巴细胞和B淋巴细胞的活化,并调节炎症相关的急性期反应。白细胞介素6是一种加速关节降解和骨关节炎进程的关键炎症因子,白细胞介素6升高可用于预测骨关节炎。骨关节炎患者的外周血中存在高水平的白细胞介素6和其他细胞因子,并且在骨关节炎动物模型中也可以检测到高水平的白细胞介素6[35]。一项前瞻性研究显示,如果个体的体质量指数较高,并且循环血清中白细胞介素6水平增加,则更容易被诊断为膝骨关节炎[36]。白细胞介素6也被证明是低氧诱导因子2α诱导的实验性骨关节炎小鼠中MMP-13
表达的关键介质[37],并影响软骨基质的合成代谢过程[38]。白细胞介素6可增加骨关节炎的严重程度,抑制白细胞介素6/Stat3信号可减缓实验性骨关节炎的进展[39-40]。MOKTAR等[41]观察膝骨关节炎患者关节软骨中白细胞介素6 mRNA水平,并与同一患者的正常软骨进行比较,21例患者中有12例软骨中白细胞介素6 mRNA表达上调,其余白细胞介素
6 mRNA表达下调。统计分析显示,骨关节炎患者的白细胞介素6 mRNA水平与正常软骨相比差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。膝关节软骨中白细胞介素6 mRNA水平出现个体间差异的原因可能是,白细胞介素6作为一种分解代谢因子,其表达可能受到其他细胞因子的影响。白细胞介素6在骨关节炎中的表达调控尚不完全清楚,这些结果将刺激更多的关于白细胞介素6作为潜在治疗靶点的研究。
2.2.3 白细胞介素17 白细胞介素17是近年发现的一种主要由CD4+辅助性T细胞17(Th17)合成及分泌的细胞因子家族,通过与细胞表面相应受体结合而发挥对机体的调控作用。白细胞介素17能刺激组织、细胞合成并释放中性粒细胞趋化因子、炎性细胞因子、MMP及破骨细胞分化因子等诱导局部组织炎症反应。WANG等[42]评价白细胞介素17对兔膝关节的影响,将实验兔右膝作为对照组,左膝随机分为4组,即Hulth组和3个白细胞介素17组(1,10,50 ng组);术后12周时,采用X射线片分析、组织学评价和聚合酶链反应分析软骨退变相关标志物的mRNA表达水平。与Hulth组一样,10 ng和50 ng白细胞介素17组表现出典型的骨关节炎表现,与Hulth法诱导的骨关节炎相似。NA等[43]的研究表明,白细胞介素17通过调节骨关节炎小鼠模型中的几种炎症递质加速软骨和小肠的破坏,在骨关节炎的发生发展中起着重要作用。BAI等[44]采用聚合酶链反应-限制性片段长度多态性分析方法,对594例膝骨关节炎患者和576例健康对照者白细胞介素17A rs2275913和白细胞介素17F rs763780进行多态性检测,结果表明白细胞介素17基因多态性可能与膝骨关节炎的高危发生有关。SNELLING等[45]的临床研究显示晚期膝、髋关节骨关节炎患者滑液中白细胞介素17水平明显升高,骨关节炎患者血清和滑液中的白细胞介素17水平与影像学图像病变严重程度也呈正相关,以白细胞介素17为基础对患者进行分层,可以确定那些对靶向治疗反应灵敏的患者。另外,白细胞介素17可抑制软骨细胞合成蛋白聚糖,并促进细胞基质蛋白酶的产生[46]。白细胞介素17在骨关节炎疾病发生和发展中所起的作用已基本肯定,但其作用途径以及其与症状的关系尚未完全明确,从分子水平阐明骨关节炎的发病途径以及针对该途径的免疫治疗都有待于进一步探索。
2.2.4 C-反应蛋白 骨关节炎患者血清C-反应蛋白水平升高,除了提示全身炎症外,C-反应蛋白本身也可能在骨关节炎的发生发展中起作用。KOZIJN等[47]在人类C-反应蛋白转基因小鼠模型中评估了C-反应蛋白本身是否参与了代谢性骨关节炎的发展,结果显示,在高脂饲料诱导的代谢功能障碍背景下,C-反应蛋白高表达通过增加了软骨退变和骨赘生而加重骨关节炎。CONROZIER等[48]研究数据表明,快速破坏性髋关节骨性关节炎可能与一定程度的炎症有关,这些炎症反应可通过血清C-反应蛋白水平的显著性增加来反映。ZHANG[49]的研究显示,血清C-反应蛋白水平与膝关节炎的发生相关,C-反应蛋白浓度增高的患者可能有发生膝关节炎的可能性。然而,C-反应蛋白水平升高与膝关节炎进展无关;此外,膝关节炎患者疼痛程度越高,C-反应蛋白浓度越高。高敏C-反应蛋白是急性时相反应的一种下游介质,具有免疫调节功能,目前的高敏C-反应蛋白试剂盒可检测出更低浓度的C-反应蛋白,能为临床应用提供更多有价值的参考信息,可以预测骨关节炎病变发生、发展和预后[50-51]。上述这些发现提示选择性地针对C-反应蛋白活性的干预措施可以改善代谢性骨关节炎的发展。
2.2.5 肿瘤坏死因子α 肿瘤坏死因子α是一种促炎性细胞因子,在骨关节炎的发病机制中起重要作用[52]。CHEN等[53]进行的一项研究证明,白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α增加了关节软骨僵硬和收缩功能受损的风险。血清白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α水平与老年人膝关节骨关节炎相关[54];在体外,促炎性因子白细胞介素1β和/或肿瘤坏死因子α上调软骨细胞亚群中MMP-1,3 mRNA,促使骨关节炎发病[55]。有研究表明,膝骨关节炎患者肿瘤坏死因子α mRNA表达量是健康对照组的1.56倍;肿瘤坏死因子α水平与骨关节炎分级一致,MMP-13水平升高与西安大略和麦克马斯特大学骨关节炎指数有显著相关性[56]。基于这些观察结果,肿瘤坏死因子α可能为骨关节炎的病因研究提供线索。肿瘤坏死因子α能促进Ⅱ型胶原和蛋白多糖的分解代谢,从而损害软骨细胞外基质的完整性和组织稳态。一些研究表明,肿瘤坏死因子α诱导软骨细胞死亡,并阻碍软骨祖细胞的迁移[57-58],种族分层分析显示亚洲人对肿瘤坏死因子αrs1800629易感,增加了患骨关节炎的风险[59]。
2.3 MMP在骨关节炎发病中的作用 MMP是水解细胞外基质的一种蛋白水解酶,被认为是机体生理重建和病理破坏的主要基础因素之一,在软骨基质大分子细胞分裂中起重要作用,破坏关节软骨细胞外基质结构和功能的完整性。MMP是酶活性依赖锌离子的蛋白酶超家族[60],根据其结构域结构、序列相似性和底物的特异性,可分为胶原酶、基质溶解素和明胶酶等亚家族。此文主要介绍与骨关节炎关系密切的几种常见的MMP。
2.3.1 MMP-1 MMP-1是成纤维细胞型胶原酶,基因位于11号染色体(11q22.3)长臂上,在软骨细胞、成纤维细胞、上皮细胞、内皮细胞、肿瘤细胞等细胞中表达[61]。病理条件下,MMP-1表达水平明显升高,降解细胞外基质胶原蛋白并介导软骨破坏[62-64]。MMP-1在骨关节炎软骨细胞中的表达高于正常软骨细胞,提示MMP-1在骨关节炎发病机制中起主导作用[65]。Ⅱ型胶原是关节软骨细胞外基质的一个重要成分,能够为关节软骨提供张力强度,并维持蛋白多糖和水分所形成的膨胀压。大量实验表明,约60%的骨关节炎患者关节液中会产生碱性磷酸钙结晶,这些结晶可以刺激关节软骨和滑膜组织中MMP-1的合成,进而破坏细胞外基质的动态平衡[66]。为探讨MMP-1表达量与骨关节炎软骨降解程度的关系,WU等[67]观察兔前交叉韧带横断模型骨关节炎进展过程中MMP-1在软骨和滑膜中的水平和分布,结果显示,MMP-1参与了兔前交叉韧带横断模型骨关节炎的形成,其表达量与软骨降解程度有关,滑膜MMP-1表达的增加滞后于软骨,提示骨关节炎的病理来源于软骨,但滑膜炎也可能参与软骨的降解,尤其是骨关节炎的中晚期。HWANG等[68]的临床研究表明,骨关节炎患者早期滑液中MMP-1浓度较高,且随着骨关节炎的发展而降低。以上研究显示,MMP-1降解关节软骨细胞外基质,造成软骨的病理性破坏,进而引起骨关节炎的发生。
2.3.2 MMP-13 MMP-13是导致软骨退行性改变的关键酶,被认为是骨关节炎发病过程中发生退行性改变的主要因素。由于MMP-13在骨关节炎患者的关节和关节软骨中明显过度表达,而在正常成人组织中几乎无法检测到,因此备受关注。众所周知,MMP-13在骨关节炎关节中起着细胞外基质降解酶的作用[69-70]。在实验性小鼠骨关节炎模型中,MMP-13水平与骨关节炎早期发生软骨细胞肥大分化有关[71],其过度表达可通过过度细胞外基质降解诱导骨关节炎的发生[72]。在临床样本中,MMP-13在骨关节炎过程的不同阶段异常表达,在骨关节炎早期软骨中MMP-13表达上调,在骨关节炎晚期MMP-13表达下调[73]。祁雷[74]采用膝关节内侧副韧带离断+内侧半月板切除的方法建立动物骨关节炎模型,MMP-13和ADAMTS-5在骨关节炎发病过程中的不同时期表达水平有明显变化,可作为骨关节炎防治研究的评价指标。李跃军等[75]研究认为MMP-13和β-catenin在骨关节炎组滑膜组织中均表现为高表达状态,两者在骨关节炎与非骨关节炎组表达差异有显著性意义,MMP-13与β-catenin在参与骨关节炎软骨退变和滑膜炎症反应等病理变化过程中密切相关。因此,MMP-13是软骨降解网络中的一个中心节点[76],因此有必要了解MMP-13在骨关节炎发病中的作用。
2.3.3 其他 MMP-2参与细胞外基质降解,它能够降解Ⅰ,Ⅳ,Ⅴ、Ⅶ,Ⅹ型胶原、层粘连蛋白、弹性蛋白、纤维连接蛋白和蛋白多糖[77],研究表明,不同原因导致的骨关节炎表现为关节滑膜细胞MMP-2的分泌量和活性增高[78]。MMP-9又称为明胶酶B,从人类巨噬细胞中纯化而来,许伟朋[79]的研究表明肿瘤坏死因子α、前列腺素E2和MMP-9在轻度骨关节炎组滑膜中的表达较正常组明显增多,重度骨关节炎组较轻度骨关节炎组明显增多,与骨关节炎患者的病程长短、病情严重程度呈正相关性。肿瘤坏死因子α及前列腺素E2均能上调MMP-9的表达,致使MMPs/基质金属蛋白酶抑制剂1比例失衡,引起软骨基质的破坏,参与骨关节炎发病及渐进性加重。MMP-3又称为基质溶解酶1,由滑膜内皮细胞产生,可通过降解细胞外多糖直接作用于软骨基质。CHU等[80]研究发现骨关节炎实验兔血清和关节液中MMP-3水平明显增高,可有效判断膝骨关节炎的严重程度。
2.4 针对炎症因子的骨关节炎非手术治疗进展
2.4.1 口服药物治疗 国际骨关节炎学会制定的《膝关节骨关节炎非手术治疗指南》推荐用非固醇抗炎药(尤其是特异性的环氧化酶2抑制剂)控制病情,“指南”还推荐了生物制剂、软骨保护剂及细胞移植等新技术[81],但生物制剂、细胞移植因其治疗费用及各级医院医疗水平限制在临床并不普及。非类固醇抗炎药有双氯芬酸钠、塞来昔布及美洛昔康等,它们能够通过阻断一些特殊的合成路径,减少关节内的炎症因子含量,以及促进软骨基质蛋白聚糖合成,从而很好地缓解骨关节炎患者的关节疼痛。双氯芬酸钠目前主要有2种给药途径,口服和局部给药已被确立为标准治疗方法之一。一般来说,口服非类固醇抗炎药的耐受性良好;然而,一项叙述性综述表明,局部给药比口服双氯芬酸钠具有更好的耐受性,不良反应较小,特别是口服给药后有胃肠道出血的副反应[82]。此外,对于一些有潜在风险和不良反应史的患者,局部给药被认为是治疗肌肉骨骼疼痛的合理选择[83]。一项荟萃分析显示塞来昔布治疗(每天口服200 mg)可显著改善骨关节炎的疼痛和功能。然而,与安慰剂对照组相比,塞来昔布在10-13周治疗后会发生更严重的胃肠道不良反应,尤其是腹痛[84]。动物模型证实10 mg/kg的美洛昔康是降低骨关节炎大鼠肿瘤坏死因子α水平的潜在剂量,其对动物疼痛的抑制可能与肿瘤坏死因子α水平降低有关[85]。Hussain等[86]评估白藜芦醇作为美洛昔康的佐剂对90 d内疼痛和功能活动的影响,并监测肝肾功能、血脂和血液学指标。临床和生化指标表明,500 mg/d的白藜芦醇作为美洛昔康的佐剂,对膝骨关节炎患者而言安全和耐受性良好,在治疗膝骨关节炎疼痛和改善身体功能方面优于美洛昔康。
此外,一系列新的骨关节炎治疗药物,如双醋瑞因、多西环素等,都是针对不同炎症因子、MMP的治疗药物[87-88]。但应该认识到,这些抗炎症因子药物的不良反应始终困扰着骨关节炎患者的治疗,可根据情况适当加用胃肠黏膜保护剂、质子泵抑制剂等保护胃肠,建议长期服用患者定期复查肝肾功能。以硫酸氨基葡萄糖为代表的氨基葡萄糖类药物,不仅能发挥软骨修复作用,还有一定的炎症因子抑制作用[89-90]。如动物口服硫酸氨基葡萄糖后,关节滑液中的肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β便会显著下降,又如氨基葡萄糖联合其他药物可以使多种炎症因子的含量显著下降,关节功能得以明显改善[91-92]。与此同时,该药较少的不良反应反映了临床治疗的安全性。
2.4.2 关节腔内给药 关节腔内注射使用药物有透明质酸、糖皮质激素及自体富血小板血浆等。陈波等[93]采用透明质酸钠注射治疗膝骨关节炎患者,治疗4周后,膝骨关节炎严重性指数评分明显降低,白细胞介素1β水平也明显低于对照组,可见透明质酸钠在改善老年膝骨关节炎患者病情、减轻炎性递质水平方面可发挥积极作用。关节腔内直接注射糖皮质激素的目的也是为了抑制炎症因子的产生[94],而且这种治疗方法联合非类固醇抗炎药更加直接、疗效更加突出。杨彦飞等[95]研究显示,对轻度或X射线片退变Ⅰ,Ⅱ级膝骨关节炎患者,关节腔注射透明质酸钠或透明质酸钠+复方倍他米松注射液均有效,注射透明质酸钠+复方倍他米松注射液效果优于单独注射透明质酸钠;对于中度患者,单独注射透明质酸钠无效,透明质酸钠+复方倍他米松注射液注射有效;对于重度或X射线片退变Ⅲ,Ⅳ级患者,单独注射透明质酸钠或透明质酸钠+复方倍他米松注射液注射均无效。但是临床应用糖皮质激素有许多不良反应,其不仅可以缓解症状,而且也能加重软骨磨损,主要是激素不利于钙和磷的吸收,以及降低疼痛敏感性[96]。富血小板血浆是患者自身全血离心分离出的富含多种生长因子的血小板浓缩物,多用于膝骨关节炎早期治疗。曾佳森等[97]研究显示膝关节腔内注射自体富血小板血浆与透明质酸钠,近期效果类似,治疗6,12个月后临床效果优于透明质酸钠,能有效改善患者的疼痛,控制病情的迁延,降低分解性细胞因子(白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、MMP-9、MMP-13、肿瘤坏死因子α)表达水平。
2.4.3 中医治疗 由于中医药疗法疗效可靠、不良反应少等优势,在国内的临床实践中占有一席之地。中药复方制剂以及单方和有效成分均能通过调节相关细胞因子、生物活性分子、蛋白酶表达及血液循环等因素改善关节炎症状,影响软骨细胞代谢,防止或延缓关节软骨退变。同样针灸和推拿等疗法也能通过影响局部关节代谢,改善软骨损伤,减轻关节疼痛,对骨关节炎发挥治疗作用。夏璇等[98]研究表明痹祺胶囊可以更好地改善膝骨关节炎患者的关节僵硬和功能状态,可以更好地改善未合并服用止痛药患者的膝关节影像学结果。槲皮素是一种存在于多种植物的五羟基黄酮类化合物,研究发现槲皮素可减轻关节软骨损伤,缓解关节肿胀,抑制血清中MMP-9、MMP-13和白细胞介素1β的表达,在骨关节炎动物模型中起到保护关节软骨的作用[99]。KANZAKI等[100]将40例有症状的膝骨性关节炎患者随机分为2组,分别给予膳食补充剂(每天1 200 mg氨基葡萄糖、60 mg硫酸软骨素和
45 mg槲皮素苷)或安慰剂,治疗和随访持续16周,结果显示膳食补充剂在减轻膝骨关节炎相关临床症状方面比安慰剂更有效。此外,软骨代谢生物标志物分析显示,在随访期间,膳食组的Ⅱ型胶原合成/降解平衡有改善的趋势。在一项随机、开放、平行、对照的临床研究中,139例膝骨关节炎患者被随机分配2组,接受500 mg姜黄素胶囊3次/d,或50 mg双氯芬酸片2次/d,共28 d[101];在第14,28天,姜黄素治疗组的疼痛严重程度和膝关节损伤和骨关节炎评分与双氯芬酸组相似,差异无显著性意义;在第7天,与双氯芬酸相比,服用姜黄素患者的肠胃气胀发作次数明显减少(P < 0.01);第28天,姜黄素具有减肥作用和抗溃疡作用(P < 0.01);姜黄素组患者均不需要H2阻断剂,双氯芬酸组有19例需要H2阻断剂(P < 0.01);姜黄素组的不良反应明显较少,姜黄素在膝骨关节炎患者中表现出更好的耐受性,结果可见姜黄素可作为膝骨关节炎患者非类固醇抗炎药不良反应的替代治疗方案。另外一项为期12周的多中心、随机、双盲、安慰剂对照、平行的研究方案,旨在评估杜仲提取物对轻度骨关节炎患者的疗效和安全性;将招募100例轻度骨关节炎患者按1∶1的比例随机分为2组,一组接受杜仲提取物12周,另一组接受安慰剂12周,通过目测类比评分、西安大略和麦克马斯特大学骨关节炎指数、健康状况调查简表和实验室测试结果进行评估,这项临床试验有望为杜仲提取物治疗轻度骨关节炎的有效性和安全性提供证据[102]。HU等[103]研究表明,中药复方杜仲补骨颗粒能有效提高美洛昔康的疗效,且杜仲与美洛昔康联合用药优于单用美洛昔康。韩国学者PARK等[104]探讨了三七、地黄、刺五加的水溶性提取物治疗膝骨关节炎6周的安全性和有效性,结果显示其能有效改善疼痛和关节功能。
针灸能够有效减轻骨关节炎患者的疼痛,并改善其关节功能。有基础及临床研究对于针灸在骨关节炎中的机制进行探索,认为针灸可能通过刺激相关炎性因子通路,调节细胞因子水平,改善骨关节炎的炎症反应,从而发挥治疗作用[105]。在兔关节软骨中的研究也证实,温针灸通过抑制软骨细胞凋亡,减少细胞中尿激酶型纤溶酶原激活物生成,进而阻断MMP的活化,保护骨关节炎中的关节软骨[106],同样温针灸减轻膝骨关节炎大鼠的炎性损伤可能基于减少软骨组织中ROCK、p-LIMK1和p-Cofilin的表达[107],以及降低滑膜组织中肿瘤坏死因子α表达,并抑制软骨中Wnt3a和β-catenin蛋白表达[108]。基于90例膝骨关节炎患者的随机对照研究也证实,经外奇穴温针灸是通过降低关节液肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1和一氧化氮水平来改善患者关节软骨损伤[109]。汪国翔等[110]将72例膝骨关节炎患者随机分为滞动针法组和药物组(n=36),滞动针法组以犊鼻、内膝眼、足三里、阳陵泉、阴陵泉、血海、梁丘、鹤顶为主要穴位,施以滞动针法,留针30 min,1次/d;药物组口服塞来昔布胶囊,200 mg/次,1次/d;两组均以14 d为1个疗程,每个疗程间休息2 d,连续治疗2个疗程;结果显示,滞动针法可有效缓解膝骨关节炎患者疼痛症状、改善关节功能,作用和口服塞来昔布胶囊相当。因此说明针灸治疗骨关节炎也是通过调节多种细胞因子、减轻关节软骨损伤从而达到治疗的目的。推拿具有行气止痛、活血通络、荣润关节、舒筋活络等功效,可改善膝骨关节炎患者膝关节疼痛、僵硬、活动受限以及异常步态等临床症状。此外,CHEN等[111]研究发现艾灸和针刺治疗均能减轻膝骨关节炎的症状,且艾灸疗效优于针刺,其作用机制可能与降低患者血清炎性因子和氧化应激因子水平有关。动物研究发现,推拿还能通过提高膝骨关节炎关节液中氧自由基的清除能力,改善关节软骨形态与功能,发挥对骨关节炎的防治作用[112]。
2.4.4 物理疗法 物理疗法适用于骨关节炎的慢性期,对亚急性期疼痛有较好的缓解作用,还能增加局部血液循环,减轻滑膜炎症,使软骨得到充分的营养,延缓软骨的退行性变。物理治疗是早期无严重增生、关节畸形患者的有效治疗方法。DEYLE等[113]的研究表明,手法物理治疗和监督性运动相结合可改善膝关节骨关节炎患者的功能,并可能延迟或避免手术干预的需要。ZHONG等[114]观察小剂量体外冲击波疗法对Kellgren Lawrence Ⅱ级或Ⅲ级骨关节炎患者膝关节疼痛、下肢功能及软骨改变的疗效,结果显示,4周小剂量体外冲击波疗法治疗轻中度膝关节骨性关节炎患者的疼痛缓解和功能改善优于安慰剂,但对关节软骨有一定的负面影响。
2.4.5 再生医学疗法 在过去的30年里,软骨组织工程已经从治疗关节软骨的局部病变发展到针对骨关节炎的治疗策略,细胞疗法对于关节软骨损伤的修复具有重要意义。间充质干细胞具有自我更新和定向分化的潜能,能够修复软骨组织,抑制软骨细胞分泌炎性因子,还可以在体内定向分化成软骨细胞,这为间充质干细胞治疗骨关节炎提供了理论依据。基于间充质干细胞的细胞疗法为骨关节炎的治疗及逆转软骨破坏带来了希望,其能抑制T效应细胞和其他免疫细胞,同时激活调节性T细胞,减少促炎细胞因子的产生,从而抑制炎症和减轻疼痛。白朝奇等[115]学者应用关节镜清理术联合自体骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗膝骨关节炎,能显著减轻患者疼痛程度,下调患侧膝关节液内炎症递质(白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α、前列腺素E2)的释放,改善患侧膝关节功能。CHAHAL等[116]的研究表明,骨髓间充质干细胞治疗可使骨关节炎患者疼痛和症状得到全面改善,并减少滑膜炎症。BASTOS 等[117]比较了有无富血小板血浆的骨髓间充质干细胞关节内注射与皮质类固醇关节内注射治疗膝骨关节炎的临床和实验室结果,显示3组患者在随访12个月时膝关节损伤及骨关节病治疗效果评分均有显著改善;与皮质类固醇组相比,骨髓间充质干细胞组和骨髓间充质干细胞+富血小板血浆组的膝关节损伤及骨关节病治疗效果评分改善率最高,说明关节内注射骨髓间充质干细胞可有效改善膝骨关节炎的功能,减轻症状。另外,有研究表明,间充质干细胞旁分泌的营养因子是间充质干细胞治疗骨关节炎的重要机制之一,作为遗传信息载体的外泌体参与许多疾病生理过程,可能在关节组织修复治疗中发挥作用[118-119]。
基因疗法是指通过将编码抗炎因子或生长因子等基因转导入关节内的细胞(关节软骨细胞或滑膜细胞),从而改善关节退行性变和抑制炎症反应来保护关节内环境,修复损伤的关节软骨。将目的基因导入关节软骨细胞或滑膜细胞来进行基因治疗是目前的趋势[120-121],骨关节炎的基因治疗正从实验室走向临床,随着有效目的基因的筛选、安全高效的载体和基因长期表达等问题的逐步解决,将有望治愈骨关节炎。

| [1] BLAGOJEVIC M, JINKS C, JEFFERY A, et al. Risk factors for onset of osteoarthritis of the knee in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18(1):24-33. [2] LIU-BRYAN R, TERKELTAUB R. Emerging regulators of the inflammatory process in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11(1):35-44. [3] MEHANA EE, KHAFAGA AF, EL-BLEHI SS.The role of matrix metalloproteinases in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: An updated review. Life Sci. 2019;234:116786. [4] SANDERS TL, PAREEK A, KREMERS HM, et al. Long-term follow-up of isolated ACL tears treated without ligament reconstruction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(2):493-500. [5] DAMMAN W, LIU R, BLOEM JL, et al. Bone marrow lesions and synovitis on MRI associate with radiographic progression after 2 years in hand osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(1):214-217. [6] BLAGOJEVIC M, JINKS C, JEFFERY A, et al. Risk factors for onset of osteoarthritis of the knee in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18(1):24-33. [7] CHRISTENSEN R, BARTELS EM, ASTRUP A, et al. Effect of weight reduction in obese patients diagnosed with knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66(4):433-439. [8] WILLS AK, BLACK S, COOPER R, et al. Life course body mass index and risk of knee osteoarthritis at the age of 53 years: evidence from the 1946 British birth cohort study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71(5):655-660. [9] FREY N, HÜGLE T, JICK SS, et al. Hyperlipidaemia and incident osteoarthritis of the hand: a population-based case-control study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(7):1040-1045. [10] 罗美杰,董伟芹,董胜莲,等.老年膝关节骨关节炎患者体重指数对关节症状的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2020,40(3):632-634. [11] GOUTTEBARGE V, INKLAAR H, BACKX F, et al. Prevalence of osteoarthritis in former elite athletes: a systematic overview of the recent literature. Rheumatol Int. 2015;35(3):405-418. [12] WYLES CC, HEIDENREICH MJ, JENG J, et al. The John Charnley Award: Redefining the Natural History of Osteoarthritis in Patients With Hip Dysplasia and Impingement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017;475(2):336-350. [13] KRACKOW KA, MANDEVILLE DS, RACHALA SR, et al. Torsion deformity and joint loading for medial knee osteoarthritis. Gait Posture. 2011; 33(4):625-629. [14] WARNER SC, VALDES AM. Genetic association studies in osteoarthritis: is it fairytale? Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2017;29(1):103-109. [15] CHU M, ZHU X, WANG C, et al. The rs4238326 polymorphism in ALDH1A2 gene potentially associated with non-post traumatic knee osteoarthritis susceptibility: a two-stage population-based study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(7):1062-1067. [16] WARNER SC, WALSH DA, LASLETT LL, et al. Pain in knee osteoarthritis is associated with variation in the neurokinin 1/substance P receptor (TACR1) gene. Eur J Pain. 2017;21(7):1277-1284. [17] VAN MEURS JB, UITTERLINDEN AG, STOLK L, et al. A functional polymorphism in the catechol-O-methyltransferase gene is associated with osteoarthritis-related pain. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(2):628-629. [18] LI X, GIBSON G, KIM JS, et al. MicroRNA-146a is linked to pain-related pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Gene. 2011;480(1-2):34-41. [19] ALA-KOKKO L, BALDWIN CT, MOSKOWITZ RW, et al. Single base mutation in the type II procollagen gene (COL2A1) as a cause of primary osteoarthritis associated with a mild chondrodysplasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990;87(17):6565-6568. [20] ZHANG W, NUKI G, MOSKOWITZ RW, et al. OARSI recommendations for the management of hip and knee osteoarthritis: part III: Changes in evidence following systematic cumulative update of research published through January 2009. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18(4):476-499. [21] HURLEY MV. The role of muscle weakness in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1999;25(2):283-vi. [22] KIM HT, LO MY, PILLARISETTY R. Chondrocyte apoptosis following intraarticular fracture in humans. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2002;10(9): 747-749. [23] YUAN GH, MASUKO-HONGO K, KATO T,et al. Immunologic intervention in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(3):602-611. [24] SCANZELLO CR, UMOH E, PESSLER F, et al. Local cytokine profiles in knee osteoarthritis: elevated synovial fluid interleukin-15 differentiates early from end-stage disease. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2009;17(8):1040-1048. [25] 郭明,安高,封桂英,等.CD4+ T细胞亚群在类风湿性关节炎中的研究进展[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2014,30(9):1004-1007. [26] TEW SR, LI Y, POTHACHAROEN P, TWEATS LM, et al. Retroviral transduction with SOX9 enhances re-expression of the chondrocyte phenotype in passaged osteoarthritic human articular chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2005;13(1):80-89. [27] HÉRAUD F, HÉRAUD A, HARMAND MF.Apoptosis in normal and osteoarthritic human articular cartilage. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000;59(12): 959-965. [28] 闫虎,苏友新,林学义. IL-1β诱导新西兰大白兔膝关节退变软骨细胞的体外培养及鉴定[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2014,34(1):81-86. [29] 黄媛霞,徐海斌,郭春.IL-1β和MMP-13在兔骨关节炎模型软骨和滑液中的表达[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2017,38(4):507-511,528. [30] 武豪杰,王晓,张明辉,等. 白细胞介素1β和基质金属蛋白酶-9在兔膝关节骨性关节炎模型滑膜中的表达及意义[J].中华实验外科杂志,2016,33(3):741-743. [31] D’SOUZA AL, MASUDA K, OTTEN LM, et al. Differential effects of interleukin-1 on hyaluronan and proteoglycan metabolism in two compartments of the matrix formed by articular chondrocytes maintained in alginate. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2000;374(1):59-65. [32] LANDESBERG R, TAKEUCHI E, PUZAS JE. Differential activation by cytokines of mitogen-activated protein kinases in bovine temporomandibular-joint disc cells. Arch Oral Biol. 1999;44(1):41-48. [33] 郑剑平,利春时.白细胞介素-1在骨性关节炎的水平及作用[J].中国实用医药,2009,4(15):5-7. [34] VAN DALEN SC, BLOM AB, SLÖETJES AW, et al. Interleukin-1 is not involved in synovial inflammation and cartilage destruction in collagenase-induced osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017; 25(3):385-396. [35] 曾惠琼,黄新民,伍少霞,等.膝骨关节炎与外周血IL-4、IL-6、IL-17A的相关性分析[J].风湿病与关节炎,2019,8(6):17-19,23. [36] LIVSHITS G, ZHAI G, HART DJ, et al. Interleukin-6 is a significant predictor of radiographic knee osteoarthritis: The Chingford Study. Arthritis and rheumatism. 2009;60(7):2037-2045. [37] RYU JH, YANG S, SHIN Y, et al. Interleukin-6 plays an essential role in hypoxia-inducible factor 2alpha-induced experimental osteoarthritic cartilage destruction in mice. Arthritis and rheumatism. 2011;63(9):2732-2743. [38] POREE B, KYPRIOTOU M, CHADJICHRISTOS C, et al. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and/or soluble IL-6 receptor down-regulation of human type II collagen gene expression in articular chondrocytes requires a decrease of Sp1.Sp3 ratio and of the binding activity of both factors to the COL2A1 promoter. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(8):4850-4865. [39] LATOURTE A, CHERIFI C, MAILLET J, et al. Systemic inhibition of IL-6/Stat3 signalling protects against experimental osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(4):748-755. [40] NASI S, SO A, COMBES C. Interleukin-6 and chondrocyte mineralisation act in tandem to promote experimental osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(7):1372-1379. [41] MOKTAR NM, YUSOF HM, YAHAYA NH, et al. The transcript level of interleukin-6 in the cartilage of idiopathic osteoarthritis of knee. Clin Ter. 2010;161(1):25-28. [42] WANG Z, ZHENG C, ZHONG Y, et al. Interleukin-17 Can Induce Osteoarthritis in Rabbit Knee Joints Similar to Hulth’s Method. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:2091325. [43] NA HS, PARK JS, CHO KH, et al. Interleukin-1-Interleukin-17 Signaling Axis Induces Cartilage Destruction and Promotes Experimental Osteoarthritis. Front Immunol. 2020;11:730. [44] BAI Y, GAO S, LIU Y, et al. Correlation between Interleukin-17 gene polymorphism and osteoarthritis susceptibility in Han Chinese population.BMC Med Genet. 2019;20(1):20. [45] SNELLING SJ, BAS S, PUSKAS GJ, et al. Presence of IL-17 in synovial fluid identifies a potential inflammatory osteoarthritic phenotype. PLoS One. 2017;12(4):e0175109. [46] CHEN B, DENG Y, TAN Y, et al. Association between severity of knee osteoarthritis and serum and synovial fluid interleukin 17 concentrations. J Int Med Res. 2014;42(1):138-144. [47] KOZIJN AE, TARTJIONO MT, RAVIPATI S, et al.Human C-reactive protein aggravates osteoarthritis development in mice on a high-fat diet.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019;27(1):118-128. [48] CONROZIER T, CHAPPUIS-CELLIER C, RICHARD M, et al. Increased serum C-reactive protein levels by immunonephelometry in patients with rapidly destructive hip osteoarthritis. Rev Rhum Engl Ed. 1998;65(12):759-765. [49] ZHANG J. Meta-analysis of serum C-reactive protein and cartilage oligomeric matrix protein levels as biomarkers for clinical knee osteoarthritis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):22. [50] WEN L, SHIN MH, KANG JH, et al. The value of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in hand and knee radiographic osteoarthritis: data from the Dong-gu Study. Clin Rheumatol. 2018;37(4):1099-1106. [51] 刘建华,赵海勇,温芳,等.炎性细胞因子在膝骨关节炎中的表达及与高敏C反应蛋白和红细胞沉降率的相关性[J].天津医药,2020, 48(1):55-58. [52] EL-TAHAN RR, GHONEIM AM, EL-MASHAD N. TNF-alpha gene polymorphisms and expression.Springerplus. 2016;5:1508. [53] CHEN C, XIE J, RAJAPPA R, et al. Interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha increase stiffness and impair contractile function of articular chondrocytes. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 2015;47: 121-129. [54] STANNUS O, JONES G, CICUTTINI F, et al. Circulating levels of IL-6 and TNF-alpha are associated with knee radiographic osteoarthritis and knee cartilage loss in older adults. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18: 1441-1447. [55] KUNISCH E, KINNE RW, ALSALAMEH RJ, et al. Pro-inflammatory IL-1beta and/or TNF-alpha up-regulate matrix metalloproteases-1 and -3 mRNA in chondrocyte subpopulations potentially pathogenic in osteoarthritis: in situ hybridization studies on a single cell level. Int J Rheum Dis. 2016; 19:557-566. [56] ÖZLER K, AKTAŞ E, ATAY Ç, et al. Serum and knee synovial fluid matrix metalloproteinase-13 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels in patients with late-stage osteoarthritis. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2016;50(3):356-361. [57] LOPEZ-ARMADA MJ, CARAMES B, LIRES-DEAN M, et al. Cytokines, tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1beta, differentially regulate apoptosis in osteoarthritis cultured human chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006;14:660-669. [58] JOOS H, WILDNER A, HOGREFE C,et al. Interleukin-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibit migration activity of chondrogenic progenitor cells from non-fibrillated osteoarthritic cartilage. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15:R119. [59] CHEN J, WU Y, YU J, et al. Association between tumor necrosis factor alpha rs1800629 polymorphism and risk of osteoarthritis in a Chinese population. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2018;51(8):e7311. [60] CHOWDHURY TT, SCHULZ RM, RAI SS, et al. Biomechanical modulation of collagen fragment-induced anabolic and catabolic activities in chondrocyte/agarose constructs. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12:R82. [61] BRINCKERHOFF CE, RUTTER JL, BENBOW U. Interstitial collagenases as markers of tumor progression. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6:4823-4830. [62] BURRAGE PS, MIX KS, BRINCKERHOFF CE. Matrix metalloproteinases: role in arthritis. Front Biosci. 2006;11:529-543. [63] KASPIRIS A, KHALDI L, GRIVAS TB, et al. Subchondral cyst development and MMP-1 expression during progression of osteoarthritis: an immunohistochemical study. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013;99(5): 523-529. [64] VINCENTI MP, BRINCKERHOFF CE. Transcriptional regulation of collagenase (MMP-1, MMP-13) genes in arthritis: integration of complex signaling pathways for the recruitment of gene-specific transcription factors. Arthritis Res. 2002;4(3):157-164. [65] TETLOW LC, ADLAM DJ, WOOLLEY DE. Matrix metalloproteinase and proinflammatory cytokine production by chondrocytes of human osteoarthritic cartilage: associations with degenerative changes. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44(3):585-594. [66] SUN Y, WENGER L, BRINCKERHOFF CE, et al. Basic calcium phosphate crystals induce matrix metalloproteinase-1 through the Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase/c-Fos/AP-1/metalloproteinase 1 pathway. Involvement of transcription factor binding sites AP-1 and PEA-3. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(2):1544-1552. [67] WU H, DU J, ZHENG Q. Expression of MMP-1 in cartilage and synovium of experimentally induced rabbit ACLT traumatic osteoarthritis: immunohistochemical study. Rheumatol Int. 2008;29(1):31-36. [68] HWANG IY, YOUM YS, CHO SD, et al. Synovial fluid levels of TWEAK and matrix metalloproteinase 1 in patients with osteoarthritis, and associations with disease severity. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2018; 26(1):2309499018760112. [69] KNÄUPER V, LÓPEZ-OTÍN C, SMITH B, et al. Biochemical characterization of human collagenase-3. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:1544-1550. [70] KNAUPER V, COWELL S, SMITH B,et al. The role of the C-terminal domain of human collagenase-3 (MMP-13) in the activation of procollagenase-3, substrate specificity, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase interaction. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:7608-7816. [71] KAMEKURA S, HOSHI K, SHIMOAKA T, et al. Osteoarthritis development in novel experimental mouse models induced by knee joint instability. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2005;13:632-641 [72] NUGENT M. MicroRNAs: exploring new horizons in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2016;24:573-580. [73] SATO T, KONOMI K, YAMASAKI S, et al. Comparative analysis of gene expression profiles in intact and damaged regions of human osteoarthritic cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:808e-817e [74] 祁雷.大鼠骨关节炎模型的建立及软骨组织中MMP13和ADAMTS5的表达[D].合肥:安徽医科大学,2018. [75] 李跃军,朱卫国,方钦正,等.骨关节炎滑膜组织中β-catenin和基质金属蛋白酶13的临床意义[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(16): 2472-2477. [76] PHILIPOT D, GUERIT D, PLATANO D, et al. p16INK4a and its regulator miR-24 link senescence and chondrocyte terminal differentiation-associated matrix remodeling in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16:R58. [77] ALUNNO A, FALCINELLI E, LUCCIOLI F, et al. Platelets Contribute to the Accumulation of Matrix Metalloproteinase Type 2 in Synovial Fluid in Osteoarthritis. Thromb Haemost. 2017;117(11):2116-2124. [78] GALASSO O, FAMILIARI F, DE GORI M, et al.Recent findings on the role of gelatinases (matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9) in osteoarthritis. Adv Orthop. 2012;2012:834208. [79] 许伟朋. TNF-α、PGE2和MMP-9在膝骨关节炎骨膜中的表达及意义[D].郑州:郑州大学,2012. [80] CHU XQ, WANG JJ, DOU LD, et al. Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein and matrix metalloproteinase-3 expression in the serum and joint fluid of a reversible osteoarthritis rabbit model. Genet Mol Res. 2015; 14(4):14207-14215. [81] MCALINDON TE, BANNURU RR, SULLIVAN MC, et al. OARSI guidelines for the non-surgical management of knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(3):363-388. [82] Tieppo Francio V, Davani S, TOWER Y, et al. Oral Versus Topical Diclofenac Sodium in the Treatment of Osteoarthritis. J Pain Palliat Care Pharmacother. 2017; 31(2):113-120. [83] WADSWORTH LT, KENT JD, HOLT RJ. Efficacy and safety of diclofenac sodium 2% topical solution for osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled, 4 week study. Curr Med Res Opin. 2016;32(2):241-250. [84] XU C, GU K, YASEN Y, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Celecoxib Therapy in Osteoarthritis: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(20):e3585. [85] KHOTIB J, UTAMI NW, GANI MA, et al.The change of proinflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor α level in the use of meloxicam in rat model of osteoarthritis.J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2019. [86] HUSSAIN SA, MAROUF BH, ALI ZS, et al. Efficacy and safety of co-administration of resveratrol with meloxicam in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a pilot interventional study. Clin Interv Aging. 2018;13: 1621-1630. [87] ALEGRÍA A, IRARRÁZAVAL S. Is diacerein an alternative for the treatment of osteoarthritis? Medwave. 2017;17(8):e7041. [88] ZHANG X, DENG XH, SONG Z, et al. Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibition With Doxycycline Affects the Progression of Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Rupture: Evaluation in a New Nonsurgical Murine ACL Rupture Model. Am J Sports Med. 2020;48(1):143-152. [89] BRUYÈRE O, ALTMAN RD, REGINSTER JY. Efficacy and safety of glucosamine sulfate in the management of osteoarthritis: Evidence from real-life setting trials and surveys. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2016; 45(4 Suppl):S12-17. [90] SAENGNIPANTHKUL S, WAIKAKUL S, ROJANASTHIEN S, et al. Differentiation of patented crystalline glucosamine sulfate from other glucosamine preparations will optimize osteoarthritis treatment. Int J Rheum Dis. 2019;22(3):376-385. [91] LUBIS AMT, SIAGIAN C, WONGGOKUSUMA E, et al. Comparison of Glucosamine-Chondroitin Sulfate with and without Methylsulfonylmethane in Grade I-II Knee Osteoarthritis: A Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. Acta Med Indones. 2017;49(2):105-111. [92] GRZANNA MW, AU RY, AU AY, et al. Avocado/Soybean Unsaponifiables, Glucosamine and Chondroitin Sulfate Combination Inhibits Proinflammatory COX-2 Expression and Prostaglandin E2 Production in Tendon-Derived Cells. J Med Food. 2020;23(2):139-146. [93] 陈波,郭祥,钟海波,等.透明质酸钠对老年膝骨性关节炎患者关节滑液IL-1β的影响及其机制[J].中国老年学杂志,2019,39(11): 2705-2707. [94] 范步新.四种药物对兔骨关节炎模型关节液中白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α和一氧化氮水平的影响[D].北京:首都医科大学, 2004. [95] 杨彦飞,周新,周静,等.透明质酸联合糖皮质激素关节腔注射治疗膝关节骨关节炎的短期疗效[J].中华骨科杂志,2020,40(10): 644-652. [96] 董钧,李波.糖皮质激素治疗骨关节炎致软骨损伤后的诊疗体会[J].中国医药指南,2015,13(6):146. [97] 曾佳森,张亚勤,周亮,等.富血小板血浆对膝骨关节炎相关细胞因子的影响[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2020,14(2): 137-143. [98] 夏璇,王焕锐,吕媛,等.痹祺胶囊治疗膝骨关节炎的临床疗效及影像学评价[J].中草药,2020,51(13):3518-3522. [99] FANG L, SHI XF, SUN HY, et al. Effects of Exosomes Derived from miR-486 Gene Modified Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Biological Characteristics of Rat Cardiomyocytes. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2018;26(5):1531-1537. [100] KANZAKI N, SAITO K, MAEDA A, et al. Effect of a dietary supplement containing glucosamine hydrochloride, chondroitin sulfate and quercetin glycosides on symptomatic knee osteoarthritis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Sci Food Agric. 2012;92(4):862-869. [101] SHEP D, KHANWELKAR C, GADE P,et al. Safety and efficacy of curcumin versus diclofenac in knee osteoarthritis: a randomized open-label parallel-arm study. Trials. 2019;20(1):214. [102] AHN HY, CHO JH, NAM D, et al. Efficacy and safety of Cortex Eucommiae (Eucommia ulmoides Oliver) extract in subjects with mild osteoarthritis: Study protocol for a 12-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(50):e18318. [103] HU CX, HU KY, WANG JF. Potential role of the compound Eucommia bone tonic granules in patients with osteoarthritis and osteonecrosis: A retrospective study. World J Clin Cases. 2020;8(1):46-53. [104] PARK SH, KIM SK, SHIN IH, et al. Effects of AIF on Knee Osteoarthritis Patients: Double-blind, Randomized Placebo-controlled Study. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009;13(1):33-37. [105] 戴超然,何奕坤,吴辉辉,等.不同针灸疗法干预关节炎炎症反应的机制研究进展[J].天津中医药,2020,37(7):836-840. [106] 李春,刘娣,张艳玲,等.基于纤溶酶途径介导的软骨细胞外基质损伤机制研究温针灸治疗膝骨性关节炎的作用机理[J].辽宁中医杂志,2020,47(2):187-190,223. [107] 彭锐,李静,李佳,等.温针灸对膝骨关节炎大鼠软骨组织ROCK/LIMK1/Cofilin通路的影响[J].针刺研究,2020,45(2):105-110. [108] 黄娜,赵娜.温针灸对膝骨关节炎大鼠滑膜组织肿瘤坏死因子水平及软骨中Wnt3a, β-catenin蛋白表达影响的研究[J].新中医,2020, 52(3):124-127. [109] 周荣生.经外奇穴温针灸对膝骨关节炎患者关节液TNF-α, IL-1及NO水平的影响[J].光明中医,2020,35(10):1528-1530. [110] 汪国翔,邓凯烽,廖子龙,等.滞动针法对膝骨关节炎患者关节功能及关节液中相关细胞因子的影响[J].针刺研究,2020,45(7):564-568,573. [111] CHEN Y, WANG RQ, LIU JX, et al. Effect of moxibustion on inflammatory factors and oxidative stress factors in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2020;40(9):913-917. [112] CAI GW, LI J, XU XJ, et al. Effect of acupoint heat-sensitive moxibustion intervention on serum osteopontin and matrix metalloproteinase-3 in patients with acute knee pain. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2013;38(6):488-492. [113] DEYLE GD, HENDERSON NE, MATEKEL RL, et al. Effectiveness of manual physical therapy and exercise in osteoarthritis of the knee.A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 2000;132(3):173-181. [114] ZHONG Z, LIU B, LIU G, et al. A Randomized Controlled Trial on the Effects of Low-Dose Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy in Patients With Knee Osteoarthritis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2019;100(9):1695-1702. [115] 白朝奇,封鹏,张雪艳,等.关节镜清理联合自体骨髓间充质干细胞移植对膝骨关节炎患者疼痛程度、炎症介质及膝关节功能的影响[J].海南医学,2020,31(17):2203-2206. [116] CHAHAL J, GÓMEZ-ARISTIZÁBAL A, SHESTOPALOFF K, et al. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Treatment in Patients with Osteoarthritis Results in Overall Improvement in Pain and Symptoms and Reduces Synovial Inflammation. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019;8(8): 746-757. [117] BASTOS R, MATHIAS M, ANDRADE R, et al. Intra-articular injection of culture-expanded mesenchymal stem cells with or without addition of platelet-rich plasma is effective in decreasing pain and symptoms in knee osteoarthritis: a controlled, double-blind clinical trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28(6):1989-1999. [118] WANG Y, YU D, LIU Z, et al. Exosomes from embryonic mesenchymal stem cells alleviate osteoarthritis through balancing synthesis and degradation of cartilage extracellular matrix. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):189. [119] TOFIÑO-VIAN M, GUILLÉN MI, PÉREZ DEL CAZ MD, et al. Microvesicles from Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells as a New Protective Strategy in Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;47(1):11-25. [120] BONDESON J, LAUDER S, WAINWRIGHT S, et al. Adenoviral gene transfer of the endogenous inhibitor IkappaBalpha into human osteoarthritis synovial fibroblasts demonstrates that several matrix metalloproteinases and aggrecanases are nuclear factor-kappaB-dependent. J Rheumatol. 2007;34(3):523-533. [121] CHEN LX, LIN L, WANG HJ, et al. Suppression of early experimental osteoarthritis by in vivo delivery of the adenoviral vector-mediated NF-kappaBp65-specific siRNA.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008;16(2):174-184. |
| [1] | 龙桂月, 李冬冬, 廖红兵. 磷酸钙骨水泥/聚乳酸羟基乙酸降解产物促进小鼠单核细胞破骨向分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1193-1198. |
| [2] | 宋荷花, 魏在荣. 糖尿病的周围神经病变:研究与治疗[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1278-1285. |
| [3] | 李 龙, 李光第, 石 豪, 邓柯淇. 环状RNA作为内源性竞争RNA参与调控骨性关节炎的发生[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(5): 751-757. |
| [4] | 张 键, 林坚平, 周 钢, 王本超, 吴永昌. 全外显子测序盘状半月板的病因学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(2): 192-199. |
| [5] | 唐余敬, 蓝奉军, 李光第, 汪 建, 刘日光. 钙离子在慢性氟中毒发病机制中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(17): 2745-2753. |
| [6] | 王欣欣, 王景信. 间充质干细胞源性外泌体治疗继发性淋巴水肿[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(10): 1603-1609. |
| [7] | 张玉娟, 原一桐, 杜若琛, 田 峰, 付 媛, 王春芳. miR-31促进骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖和迁移[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(1): 66-71. |
| [8] | 胡 伟, 谢兴奇, 屠冠军. 骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体改善脊髓损伤后血脊髓屏障的完整性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 992-998. |
| [9] | 李嘉骏, 夏 天, 刘佳敏, 陈 锋, 陈豪特, 卓映宏, 吴炜锋. 淫羊藿苷调控成骨信号相关通路治疗激素性股骨头缺血性坏死的分子机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(5): 780-785. |
| [10] | 刘伊依, 邱俊强, 衣龙燕, 周财亮. 接受抗阻训练中老年人白细胞介素6与C-反应蛋白变化的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(5): 804-812. |
| [11] | 刘 进, 李 振, 郝慧琴, 王 泽, 赵彩虹, 芦文静. 二妙散水提物调控胶原诱导性关节炎大鼠成纤维样滑膜细胞增殖、迁移和炎性因子的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(5): 688-693. |
| [12] | 殷婷婷, 杜大勇, 蒋知新, 柳 杨, 刘奇林, 李运田. 粒细胞集落刺激因子改善急性心肌梗死模型大鼠的心肌纤维化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(5): 730-735. |
| [13] | 生卫北, 熊 奡, 刘 苏, 邓嘉鹏, 翁 鉴, 于 斐, 陈英奇, 曾 晖. 磷酸肌酸改性壳聚糖水凝胶干预大鼠骨髓源性巨噬细胞极化和炎症因子的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(31): 5040-5046. |
| [14] | 梁浩然, 周 新, 杨彦飞, 牛文杰, 宋文杰, 任智远, 王薛丁, 刘 洋, 段王平. 青壮年股骨颈骨折内固定后股骨头坏死的发病机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(3): 456-460. |
| [15] | 刘 珂, 范海霞, 王 宏, 程焕芝, 耿海霞. 胶原纤维和基质金属蛋白酶9在大鼠正畸牙根吸收中的表达及意义[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(27): 4288-4292. |
骨关节炎是力学因素和生物学因素作用下软骨合成和降解偶联失衡的结果,目前研究认为,软骨组织基质金属蛋白酶(matrix metalloproteinase,MMP)的异常增高可能是导致软骨细胞外基质合成与降解失衡的重要原因。另外,软骨不论以何种形式发生退变,都离不开炎症递质的作用。通过调控炎症因子及MMP的表达,参与许多骨关节炎相关事件,包括软骨细胞外基质合成与降解失衡、软骨细胞凋亡以及滑膜炎症等[2-3]。文章基于促炎因子和MMP调控骨关节炎的进展作一综述,为今后骨关节炎的研究和防治提供新思路。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
1.2 入选标准
纳入标准:①文章所述内容与炎症因子和MMP调控骨关节炎密切相关;②同一领域选择近期发表或在权威杂志上发表的文章。
排除标准:①合并有关节肿瘤、类风湿性关节炎等疾病的研究;②推测性结论,缺乏说服力的研究;③重复性研究。
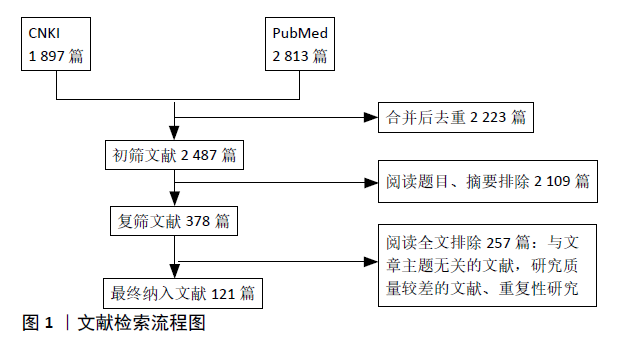
1.3 质量评估 计算机初检获得4 710篇文献,通过阅读文题和摘要筛选,排除重复性研究以及内容不相关的文献,最后纳入121篇文献进行分析,中文文献24篇,英文文献97篇。文献检索流程见图1。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程

文题释义:
骨关节炎治疗:轻中度骨关节炎主要通过口服或者关节内注射镇痛药、抗炎药以及营养物质等缓解病情;重度骨关节炎可通过关节置换手术进行治疗。
正常关节中炎症因子的作用:在正常关节中软骨细胞的凋亡和增殖以及细胞外基质降解和合成均处于动态平衡中,其中白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素17、C-反应蛋白、肿瘤坏死因子α等多种细胞因子参与这种动态平衡。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
骨关节炎是力学因素和生物学因素作用下软骨合成和降解偶联失衡的结果,目前研究认为,软骨组织基质金属蛋白酶的异常增高可能是导致软骨细胞外基质合成与降解失衡的重要原因。另外,软骨不论以何种形式发生退变,都离不开炎症介质的作用。通过调控炎症因子及基质金属蛋白酶的表达,参与许多骨关节炎相关事件,包括软骨细胞外基质合成与降解失衡、软骨细胞凋亡以及滑膜炎症等。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||