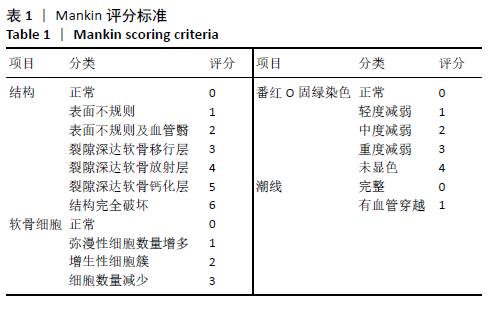
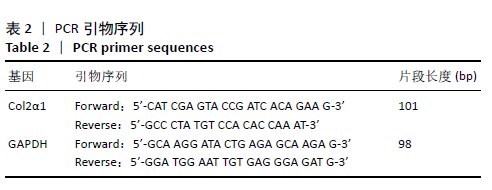
[1] KOLASINSKI SL, NEOGI T, HOCHBERG MC, et al. 2019 American College of Rheumatology/Arthritis Foundation Guideline for the Management of Osteoarthritis of the Hand, Hip, and Knee. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72(2):220-233.
[2] IIJIMA H, SHIMOURA K, AOYAMA T, et al. Low Back Pain as a Risk Factor for Recurrent Falls in People with Knee Osteoarthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2020;73(3):328-335.
[3] 朱路,王贵林.生姜油对关节炎小鼠细胞因子和T细胞亚群的影响[J].长江大学学报(自科版)医学卷,2009,6(4):97-99+2.
[4] BARTELS EM, FOLMER VN, BLIDDAL H, et al. Efficacy and safety of ginger in osteoarthritis patients: a meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(1):13-21.
[5] RICKY ANDY SETYAWAN, SRI TASMINATUN. Efektivitas Krim Ekstrak Zingiber officinale Linn.var.rubrum sebagai Penurun Nyeri Sendi pada Lansia. Mutiara Medika. 2013;13(2):105-110.
[6] CHIEN TY, HUANG SK, LEE CJ, et al. Antinociceptive and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Zerumbone against Mono-Iodoacetate-Induced Arthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(2):249.
[7] ABDEL-RAHMAN RF, ABD-ELSALAM RM, AMER MS, et al. Manjarix attenuated pain and joint swelling in a rat model of monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis. Food Funct. 2020;11(9):7960-7972.
[8] 林丽莎. 印尼与中国生姜对比研究[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2015.
[9] ILIC NM, DEY M, POULEV AA, et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of grains of paradise (Aframomum melegueta Schum) extract. J Agric Food Chem. 2014;62(43):10452-10457.
[10] 马玉峰,祁印泽,王庆甫,等.关节内注射药物建立骨性关节炎动物模型研究进展[J].中国骨伤,2015,28(1):90-95.
[11] 陈婷,姚玲,柯大智,等.生姜乙醇提取物改善果糖所致大鼠脂肪肝的作用机制研究[J].中药新药与临床药理,2016,27(1):28-33.
[12] KUROKI H, NAKAGAWA Y, MORI K, et al. Acoustic stiffness and changein plug cartilage over time after autologous osteochondral grafting: correlation between ultrasound signal intensity and histological score in a rabbit model. Arthritis Res Ther. 2004;6(6):492-504.
[13] 徐叔云, 卞如濂, 陈修. 药理实验方法学 [M]. 北京:人民卫生出版社,1982.
[14] LITWIC A, EDWARDS MH, DENNISON EM, et a1. Epidemiology and burden of osteoarthritis. Br Med Bull. 2013;105:185-199.
[15] CAMPO GM, AVENOSO A, CAMPO S, et a1. Molecular size hyaluronan differently modulates toll-like receptor-4 in LPS-induced inflammation in mouse chondrocytes. Biochimie. 2010;92(2):204-215.
[16] GOLDRING MB, OTERO M, PLUMB DA, et al. Roles of inflammatory and anabolic cytokines in cartilage metabolism: signals and multiple effectors converge upon MMP-13 regulation in osteoarthritis.Eur Cell Mater. 2011;21:202-220.
[17] WOODELL-MAY JE.Role of Inflammation and the Immune System in the Progression of Osteoarthritis.J Orthop Res. 2020;38(2):253-257.
[18] HASEEB A, ANSARI MY, HAQQI TM. Harpagoside suppresses IL-6 expression in primary human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. J Orthop Res. 2017;35(2):311-320.
[19] ROWAN AD, KOSHY PJ, SHINGLETON WD, et al. Synergistic effects of glycoprotein 130 binding cytokines in combination with interleukin-1 on cartilage collagen breakdown. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44(7): 1620-1632.
[20] ANSARI MY, AHMAD N, HAQQI TM. Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: Role of polyphenols. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;129:110452.
[21] SINGH R, AHMED S, ISLAM N, et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits interleukin-1beta-induced expression of nitric oxide synthase and production of nitric oxide in human chondrocytes: suppression of nuclear factor kappaB activation by degradation of the inhibitor of nuclear factor kappaB. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46(8):2079-2086.3
[22] AHMAD N, ANSARI MY, HAQQI TM. Role of iNOS in osteoarthritis: Pathological and therapeutic aspects. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(10): 6366-6376.
[23] GOLDRING MB, GOLDRING SR . Osteoarthritis. J Cell Physiol. 2007; 213(3):626-634.
[24] SCHULZ JM, BIRMINGHAM TB, ATKINSON HF, et al. Are we missing the target? Are we aiming too low? What are the aerobic exercise prescriptions and their effects on markers of cardiovascular health and systemic inflammation in patients with knee osteoarthritis? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2020;54(13): 771-775.
[25] WEI W, HE S, WANG Z, et al. LINC01534 Promotes the Aberrant Metabolic Dysfunction and Inflammation in IL-1β-Simulated Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes by Targeting miR-140-5p. Cartilage. 2019;16:1947603519888787.
[26] 杨威,石继祥,卢明.骨性关节炎发病机制的研究进展[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2019,19(8):84-85+87.
[27] 姚血明,宁乔怡,孙运花,等.姜酚治疗类风湿关节炎的研究进展[J].贵阳中医学院学报,2018,40(1):94-96.
[28] JALALI M, MAHMOODI M, MOOSAVIAN SP, et al. The effects of ginger supplementation on markers of inflammatory and oxidative stress: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Phytother Res. 2020;34(8):1723-1733.
[29] RONDANELLI M, FOSSARI F, VECCHIO V, et al. Clinical trials on pain lowering effect of ginger: A narrative review Phytother Res. 2020; 34(11):2843-2856.
[30] RONDANELLI M, RIVA A, ALLEGRINI P, et al. The Use of a New Food-Grade Lecithin Formulation of Highly Standardized Ginger (Zingiber officinale) and Acmella oleracea Extracts for the Treatment of Pain and Inflammation in a Group of Subjects with Moderate Knee Osteoarthritis. J Pain Res. 2020;13:761-770.
[31] MOZAFFARI-KHOSRAVI H, NADERI Z, DEHGHAN A, et al. Effect of Ginger Supplementation on Proinflammatory Cytokines in Older Patients with Osteoarthritis: Outcomes of a Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. J Nutr Gerontol Geriatr. 2016;35(3):209-218.
[32] ARYANTI PI, HARYANTO J, ULFIANA E. Red Ginger (Zingiber officinale var. rubrum) Massage Reduces Stiffness and Functional Disability in Elderly with Osteoarthritis. Jurnal Ners. 2018;(13):2.
[33] ABUSARAH J, BENABDOUNE H, SHI Q, et al. Elucidating the Role of Protandim and 6-Gingerol in Protection Against Osteoarthritis. J Cell Biochem. 2017;118(5):1003-1013.
[34] 李永津,林涌鹏,侯宇,等.龙鳖胶囊与骨髓间充质干细胞移植对膝骨关节炎大鼠软骨修复作用的比较研究[J].广州中医药大学学报,2018,35(1):123-128.
[35] 芦北极,王贵清,刘春磊.髋关节骨性关节炎软骨组织Ⅱ型胶原α1链和激活T细胞核因子1的表达水平及意义[J].中国老年学杂志, 2013,33(3):548-550.
[36] 童洁,廖瑛,陈政宇,等.骨关节炎软骨细胞自噬及丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路的调控[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(20): 3246-3251.
|