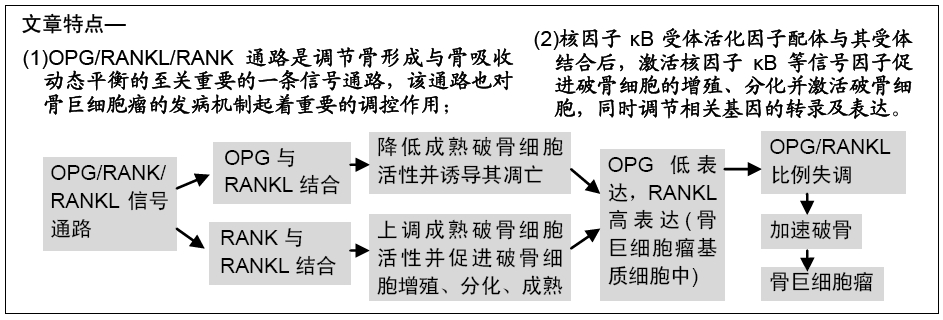
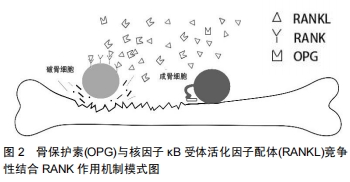
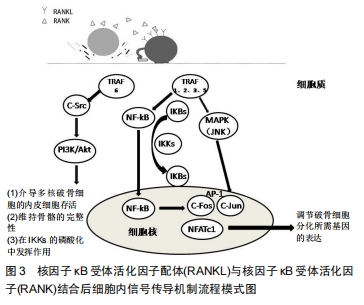
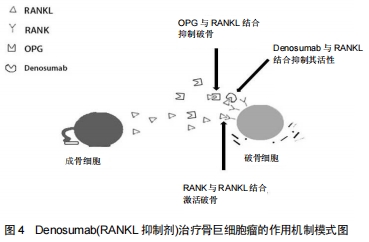
[1]HOFBAUER LC, HEUFELDER AE. Role of receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand and osteoprotegerin in bone cell biology. J Mol Med (Berl). 2001;79(5-6): 243-253.
[2]DEMPSTER DW, LAMBING CL, KOSTENUIK PJ, et al. Role of RANK ligand and denosumab, a targeted RANK ligand inhibitor, in bone health and osteoporosis: a review of preclinical and clinical data. Clin Ther.2012;34(3):521-536.
[3]TYROVOLA JB, SPYROPOULOS MN, MAKOU M,et al. Root resorption and the OPG/RANKL/RANK system: a mini review. J Oral Sci.2008;50(4):367-376.
[4]LIU W, XU C, ZHAO HY, et al. Osteoprotegerin Induces Apoptosis of Osteoclasts and Osteoclast Precursor Cells via the Fas/Fas Ligand Pathway. PLoS One. 2015;10(11): e0142519.
[5]HONMA M, IKEBUCHI Y, KARIYA Y, et al. Regulatory mechanisms of RANKL presentation to osteoclast precursors. Curr Osteoporos Rep.2014;12(1): 115-120.
[6]BAUD'HUIN M, LAMOUREUX F, DUPLOMB L, et al. RANKL, RANK, osteoprotegerin: key partners of osteoimmunology and vascular diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci.2007; 64(18): 2334-2350.
[7]LESKELA HV, KUORILEHTO T, RISTELI J, et al. Congenital pseudarthrosis of neurofibromatosis type 1: impaired osteoblast differentiation and function and altered NF1 gene expression. Bone.2009; 44(2): 243-250.
[8]YAMASHITA T, TAKAHASHI N, UDAGAWA N.New roles of osteoblasts involved in osteoclast differentiation. World J Orthop. 2012;3(11):175-181.
[9]谢冰洁,冯捷,韩向龙.破骨细胞生物学特征的研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(11):1770-1775.
[10]仝晓阳,张玲莉,郭健民,等.运动对骨代谢信号通路影响的研究进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2016,22(12):1425-1429.
[11]SILVA JA, LOPES FERRUCCI D, PERONI LA, et al. Periodontal disease-associated compensatory expression of osteoprotegerin is lost in type 1 diabetes mellitus and correlates with alveolar bone destruction by regulating osteoclastogenesis. Cells Tissues Organs. 2012;196(2): 137-150.
[12]CHEN X, WANG Z, DUAN N, et al. Osteoblast-osteoclast interactions. Connective tissue research. Connect Tissue Res. 2018;59(2):99-107.
[13]ZHANG S, WANG X, LI G, et al. Osteoclast regulation of osteoblasts via RANKRANKL reverse signal transduction in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(4):3994-4000.
[14]KEARNS AE, KHOSLA S, KOSTENUIK PJ. Receptor activator of nuclear factor κB ligand and osteoprotegerin regulation of bone remodeling in health and disease. Endocr Rev.2008;29(2): 155-192.
[15]NG PK, TSUI SK, LAU CP, et al. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein beta is up-regulated in giant cell tumor of bone and regulates RANKL expression. J Cell Biochem.2010;110(2):438-446.
[16]MAK IW, TURCOTTE RE, GHERT M. Parathyroid hormone–related protein (PTHrP) modulates adhesion, migration and invasion in bone tumor cells. Bone.2013;55(1):198-207.
[17]WU PF, TANG JY, LI KH. RANK pathway in giant cell tumor of bone: pathogenesis and therapeutic aspects. Tumour Biol. 2015; 36(2):495-501.
[18]MULPURI K, SONG KM, GOLDBERG MJ, et al. Detection and Nonoperative Management of Pediatric Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip in Infants up to Six Months of Age.J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015;23(3):202-205.
[19]XU SF, ADAMS B, YU XC, et al. Denosumab and giant cell tumour of bone—a review and future management considerations. Current Oncology.2013; 20(5): 442-447.
[20]NOH BJ, PARK YK. Giant cell tumor of bone: updated molecular pathogenesis and tumor biology. Human pathology. 2018;81:1-8.
[21]ROUX S, AMAZIT L, MEDURI G, et al.RANK (receptor activator of nuclear factor κ B) and RANK ligand are expressed in giant cell tumors of bone. Am J Clin Pathol. 2002;117(2):210-216.
[22]ATKINS GJ, BOURALEXIS S, HAYNES DR, et al.Osteoprotegerin inhibits osteoclast formation and bone resorbing activity in giant cell tumors of bone. Bone.2001;28(4): 370-377.
[23]CLEVEN AH, HÖCKER S, BRIAIRE-DE BRUIJN I, et al. Mutation Analysis of H3F3A and H3F3B as a Diagnostic Tool for Giant Cell Tumor of Bone and Chondroblastoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2015; 39(11):1576-1583.
[24]CHENG YY, HUANG L, LEE KM, et al. Bisphosphonates Induce Apoptosis of Stromal Tumor Cells in Giant Cell Tumor of Bone. Calcif Tissue Int. 2004;75(1):71-77.
[25]CHANG SS, SURATWALA SJ, JUNG KM, et al. Bisphosphonates May Reduce Recurrence in Giant Cell Tumor by Inducing Apoptosis.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;(426):103-109.
[26]REID IR, CUNDY T. Osteonecrosis of the jaw. Skeletal Radiol. 2009;38(1):5-9.
[27]BALKE M, CAMPANACCI L, GEBERT C,et al. Bisphosphonate treatment of aggressive primary, recurrent and metastatic Giant Cell Tumour of Bone.BMC Cancer. 2010;10:462.
[28]UDAY S, GASTON CL, ROGERS L, et al. Osteonecrosis of the Jaw and Rebound Hypercalcemia in Young People Treated With Denosumab for Giant Cell Tumor of Bone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103(2):596-603.
[29]BRANSTETTER DG, NELSON SD, MANIVEL JC, et al. Denosumab Induces Tumor Reduction and Bone Formation in Patients with Giant-Cell Tumor of Bone. Clin Cancer Res. 2012; 18(16):4415-4424.
[30]ABE K,YOSHIMURA Y,DEYAMA Y,et al.Effects of bisphosphonates on osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cells. Int J Mol Med. 2012;29(6):1007-1015.
[31]DUFRESNE A, DERBEL O, CASSIER P, et al. Giant-cell tumor of bone, anti-RANKL therapy.Bonekey Rep. 2012;1:149.
[32]THOMAS D, HENSHAW R, SKUBITZ K,et al.Denosumab in patients with giant-cell tumour of bone: an open-label, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11(3):275-280.
[33]MAK IW, EVANIEW N, POPOVIC S, et al. A Translational Study of the Neoplastic Cells of Giant Cell Tumor of Bone Following Neoadjuvant Denosumab.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(15): e127.
[34]ERRANI C, TSUKAMOTO S, MAVROGENIS AF. How safe and effective is denosumab for bone giant cell tumour? Int Orthop. 2017;41(11):2397-2400.
[35]VAN DER HEIJDEN L, DIJKSTRA PDS, BLAY JY, et al. Giant cell tumour of bone in the denosumab era. Eur J Cancer. 2017;77: 75-83.
[36]BROEHM CJ, INWARDS CY, AL-IBRAHEEMI A, et al. Giant Cell Tumor of Bone in Patients 55 Years and Older: A Study of 34 Patients.Am J Clin Pathol. 2018;149(3):222-233.
[37]ENGELLAU J, SEEGER L, GRIMER R, et al. Assessment of denosumab treatment effects and imaging response in patients with giant cell tumor of bone. World J Surg Oncol. 2018;16(1):191.
[38]GONG LH, LIU WF, DING Y, et al. Clinical, radiologic and pathologic features of giant cell tumor of bone treated with denosumab. Zhonghua Bing li Xue Zazhi. 2018;47(6):449-454.
[39]ITKIN B, STRAMINSKY S, DE RONATO G,et al. Prognosis of metastatic giant cell tumor of bone in the pre-denosumab era. A systematic review and a meta-analysis. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2018; 48(7):640-652.
[40]KATO I, FURUYA M, MATSUO K, et al. Giant cell tumours of bone treated with denosumab: histological, immunohistochemical and H3F3A mutation analyses. Histopathology. 2018;72(6):914-922.
[41]YI J, LEE YH, KIM SK, et al. Response evaluation of giant-cell tumor of bone treated by denosumab: Histogram and texture analysis of CT images.J Orthop Sci. 2018;23(3):570-577.
[42]PURI A, GULIA A, HEGDE P, et al. Neoadjuvant denosumab: its role and results in operable cases of giant cell tumour of bone. Bone Joint J. 2019;101-B(2):170-177.
[43]RUTKOWSKI P, GASTON L, BORKOWSKA A, et al. Denosumab treatment of inoperable or locally advanced giant cell tumor of bone - Multicenter analysis outside clinical trial. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2018;44(9):1384-1390.
[44]URAKAWA H, YONEMOTO T, MATSUMOTO S, et al. Clinical outcome of primary giant cell tumor of bone after curettage with or without perioperative denosumab in Japan: from a questionnaire for JCOG 1610 study. World J Surg Oncol. 2018;16(1):160.
[45]WENDLING D, GUILLOT X, SONDAG M, et al. Giant cell tumor of bone under Denosumab treatment. Joint Bone Spine. 2018; 85(4): 491.
[46]SHIBUYA I, TAKAMI M, MIYAMOTO A, et al. In Vitro Study of the Effects of Denosumab on Giant Cell Tumor of Bone: Comparison with Zoledronic Acid.Pathol Oncol Res. 2019;25(1):409-419.
[47]AGARWAL A, LARSEN BT, BUADU LD, et al. Denosumab chemotherapy for recurrent giant-cell tumor of bone: a case report of neoadjuvant use enabling complete surgical resection. Case Rep Oncol Med. 2013;2013:496351.
[48]LOPEZ-POUSA A, MARTIN BROTO J, GARRIDO T, et al. Giant cell tumour of bone: new treatments in development.Clin Transl Oncol. 2015;17(6):419-430.
[49]HAQUE AU, MOATASIM A. Giant cell tumor of bone: a neoplasm or a reactive condition? Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2008;1:489-501.
[50]BALKE M, NEUMANN A, SZUHAI K, et al. A short-term in vivo model for giant cell tumor of bone. BMC cancer. 2011;11:241.
[51]LI GN, WANG SP, XUE X, et al. Monoclonal antibody-related drugs for cancer therapy. Drug Discov Ther. 2013;7(5):178-184.
[52]SIEVERS EL, SENTER PD. Antibody-drug conjugates in cancer therapy.Annu Rev Med. 2013;64:15-29.
[53]PEREZ HL, CARDARELLI PM, DESHPANDE S, et al. Antibody-drug conjugates: current status and future directions. Drug discovery today. 2014;19(7):869-881.
|