[1]黄峻.中国心力衰竭流行病学特点和防治策略[J].中华心脏与心律电子杂志,2015,3(2):81-88.
[2]NGUYEN TP, QU Z, WEISS JN. Cardiac fibrosis and arrhythmogenesis: the road to repair is paved with perils. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014;70:83-91.
[3]GYöNGYöSI M, WINKLER J, RAMOS I, et al. Myocardial fibrosis: biomedical research from bench to bedside. Eur J Heart Fail. 2017; 19(2):177-191.
[4]王友华,马美,田振军.心肌梗死后的心功能改善:有氧运动干预发挥效应新视角[J].中国运动医学杂志,2019,38(7):624-629.
[5]贾丽晔,郭琪,王鹏程,等.运动疗法对心血管疾病患者的影响和作用机理研究进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2016,22(9):1041-1044.
[6]KATSURA H, KANEMARU A, YAMADA K, et al. Long-term effectiveness of an inpatient pulmonary rehabilitation program for elderly COPD patients: Comparison between young-elderly and old-elderly groups. Respirology. 2004;9(2):230-236.
[7]OLDRIDGE NB, GUYATT GH, FISCHER ME, et al. Cardiac rehabilitation after myocardial infarction. Combined experience of randomized clinical trials.JAMA. 1988;260(7):945-950.
[8]YANCY CW, JESSUP M, BOZKURT B, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines.Circulation. 2013; 128(16):1810-1852.
[9]DERUMEAUX G, ICHINOSE F, RAHER MJ, et al. Myocardial alterations in senescent mice and effect of exercise training: a strain rate imaging study.Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2008;1(3):227-234.
[10]LI Y, CAI X, GUAN Y, et al. Adiponectin Upregulates MiR-133a in Cardiac Hypertrophy through AMPK Activation and Reduced ERK1/2 Phosphorylation.PLoS One. 2016;11(2):e0148482.
[11]王世强,李丹,刘奥峰.运动改善疾病所致心肌纤维化研究进展[J].中国运动医学杂志,2019,38(3):220-227.
[12]BOSTRöM P, WU J, JEDRYCHOWSKI M P, et al. A PGC1-alpha- dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature. 2012;481(7382):463-468.
[13]WRANN CD, WHITE JP, SALOGIANNNIS J, et al. Exercise Induces Hippocampal BDNF through a PGC-1 alpha/FNDC5 Pathway. Cell Metab. 2013;18(5):649-659.
[14]ROCA-RIVADA A, CASTELAO C, SENIN L L, et al. FNDC5/irisin is not only a myokine but also an adipokine.PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e60563.
[15]MATSUO Y, GLEITSMANN K, MANGER N, et al. Fibronectin type III domain containing 5 expression in skeletal muscle in chronic heart failure-relevance of inflammatory cytokines. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2015;6(1):62-72.
[16]NGUYEN TP, QU Z, WEISS JN. Cardiac fibrosis and arrhythmogenesis: The road to repair is paved with perils. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014;70:83-91
[17]YUE Y, MENG K, PU Y, et al. Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) mediates cardiac fibrosis and induces diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017;133:124-130.
[18]RAO Z, WANG S, BUNNER WP, et al. Exercise induced Right Ventricular Fibrosis is Associated with Myocardial Damage and Inflammation. Korean Circ J. 2018;48(11):1014-1024.
[19]KUUSISTO J, KARJA V, SIPOLA P, et al. Low-grade inflammation and the phenotypic expression of myocardial fibrosis in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Heart. 2012l;98(13):1007-1013.
[20]CALLIS TE, PANDYA K, SEOK HY, et al. MicroRNA-208a is a regulator of cardiac hypertrophy and conduction in mice. J Clin Invest. 2009;119(9):2772-2786.
[21]PEDERSEN BK, FEBBRAIO MA. Muscles, exercise and obesity: skeletal muscle as a secretory organ. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2012;8(8): 457-465.
[22]SANCHIS-GOMAR F, PEREZ-QUILIS C. The p38-PGC-1alpha- irisin-betatrophin axis: Exploring new pathways in insulin resistance. Adipocyte. 2014;3(1):67-68.
[23]AYDIN S, KULOGLU T, AYDIN S, et al.Cardiac, skeletal muscle and serum irisin responses to with or without water exercise in young and old male rats: cardiac muscle produces more irisin than skeletal muscle. Peptides. 2014;52:68-73.
[24]ARONIS KN, MORENO M, POLYZOS SA, et al. Circulating irisin levels and coronary heart disease: association with future acute coronary syndrome and major adverse cardiovascular events. Int J Obes (Lond). 2015;39(1):156-161.
[25]陈聪毅,王冠捷.运动诱发鸢尾素对肥胖合并间歇性低氧引起心肌纤维化的影响[J].大专体育学刊,2017,19(3)DOI:10.5297/ser.1903.006
[26]LEE P, LINDERMAN JD, SMITH S, et al.Irisin and FGF21 are cold-induced endocrine activators of brown fat function in humans.Cell Metab. 2014;19(2):302-309.
[27]MIYAMOTO-MIKAMI E, SATO K, KURIHARA T, et al. Endurance training-induced increase in circulating irisin levels is associated with reduction of abdominal visceral fat in middle-aged and older adults. PLoS One. 2015;10(3):e0120354.
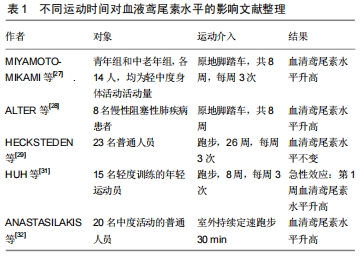
[28]ALTER P, VAN DE SAND K, NELL C, et al. Airflow limitation in COPD is associated with increased left ventricular wall stress in coincident heart failure. Respir Med. 2015;109(9):1131-1137.
[29]HECKSTEDEN A, WEGMANN M, STEFFEN A, et al. Irisin and exercise training in humans - Results from a randomized controlled training trial. BMC Med. 2013;11:235.
[30]SCHARHAG-ROSENBERGER F, MEYER T, WEGMANN M, et al. Irisin does not mediate resistance training-induced alterations in resting metabolic rate. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2014;46(9):1736-1743.
[31]HUH JY, MOUGIOS V, SKRAPARLIS A, et al. Irisin in response to exercise in humans with and without metabolic syndrome.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100(3):E453-457.
[32]ANASTASILAKIS AD, POLYZOS SA, SARIDAKIS ZG, et al. Circulating irisin in healthy, young individuals: day-night rhythm, effects of food intake and exercise, and associations with gender, physical activity, diet, and body composition.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(9): 3247-3255.
[33]DASKALOPOULOU SS, COOKE AB, GOMEZ YH, et al.Plasma irisin levels progressively increase in response to increasing exercise workloads in young,healthy, active subjects. Eur J Endocrinol. 2014; 171(3):343-352.
[34]NORHEIM F, LANGLEITE TM, HJORTH M, et al. The effects of acute and chronic exercise on PGC-1α, irisin and browning of subcutaneous adipose tissue in human. FEBS J. 2014;281(3):739-749.
[35]IJIRI N, KANAZAWA H, ASAI K, et al. Irisin, a newly discovered myokine, is a novel biomarker associated with physical activity in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respirology. 2015;20(4):612-617.
[36]HEW-BUTLER T, LANDIS-PIWOWAR K, BYRD G, et al.Plasma irisin in runners and nonrunners: no favorable metabolic associations in humans. Physiol Rep. 2015;3(1). pii: e12262.
[37]TSUCHIYA Y, ANDO D, GOYoto K, et al. High-intensity exercise causes greater irisin response compared with low-intensity exercise under similar energy consumption. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2014;233(2): 135-140.
[38]XIE C, ZHANG Y, TRAN TD, et al. Irisin Controls Growth, Intracellular Ca2+ Signals, and Mitochondrial Thermogenesis in Cardiomyoblasts. PLoS One. 2015;10(8):e0136816.
[39]WANG YB. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in heart development and diseases. Circulation. 2007;116(12):1413-1423.
[40]WINBANKS CE, WEEKS KL, THOMSON RE, et al. Follistatin-mediated skeletal muscle hypertrophy is regulated by Smad3 and mTOR independently of myostatin. J Cell Biol. 2012; 197(7):997-1008.
[41]谢平,李汇华.心肌素与心血管疾病的研究进展[J].基础医学与临床,2008, 28(10):1103-1106.
[42]CLEMENT S, STOUFFS M, BETTOL E, et al.Expression and function of alpha-smooth muscle actin during embryonic-stem-cell-derived cardiomyocyte differentiation. J Cell Sci. 2007;120(Pt 2):229-238.
[43]LI M, WANG N, GONG HQ, et al. Ca²⁺ signal-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy through activation of myocardin.Gene. 2015;557(1):43-51.
[44]YOSHIDA T, SINHA S, DANDRE F, et al. Myocardin is a key regulator of CArG-dependent transcription of multiple smooth muscle marker genes. Circ Res. 2003;92(8):856-864.
[45]XING W, ZHANG TC, CAO D, et al.Myocardin induces cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Circ Res. 2006;98(8):1089-1097.
[46]WANG H, ZHAO YT, ZHANG S, et al. Irisin plays a pivotal role to protect the heart against ischemia and reperfusion injury. J Cell Physiol. 2017;232(12):3775-3785.
[47]ZHANG YZ, MU Q, ZHOU Z, et al. Protective Effect of Irisin on Atherosclerosis via Suppressing Oxidized Low Density Lipoprotein Induced Vascular Inflammation and Endothelial Dysfunction. PLoS One. 2016;11(6):e0158038.
[48]AKHMEDOV AT, RYBIN V, MARIN-GARCIA J. Mitochondrial oxidative metabolism and uncoupling proteins in the failing heart. Heart Fail Rev. 2015;20(2):227-249.
[49]PENG J, DENG X, HUANG W, et al. Irisin protects against neuronal injury induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation in part depends on the inhibition of ROS-NLRP3 inflammatory signaling pathway. Mol Immunol. 2017;91:185-194.
[50]DOENST T, NGUYEN TD, ABEL ED, et al. Cardiac metabolism in heart failure-implications beyond ATP production. Circ Res. 2013; 113(6):709-724.
[51]NAKAHIRA K, HASPEL JA, RATHINAM VA, et al. Autophagy proteins regulate innate immune responses by inhibiting the release of mitochondrial DNA mediated by the NALP3 inflammasome. Nat Immunol. 2011r;12(3):222-230.
[52]YE X, SHEN Y, NI C, et al. Irisin reverses insulin resistance in C2C12 cells via the p38-MAPK-PGC-1 alpha pathway. Peptides. 2019;119: 170120.
[53]MA ST, ZHANG Y, WANG Q, et al. Ablation of uncoupling protein 2 exacerbates salt-induced cardiovascular and renal remodeling associated with enhanced oxidative stress. Int J Cardiol. 2014;175(1): 206-210.
[54]MCLEOD CJ, AZIZ A, HOYT RF JR, et al. Uncoupling proteins 2 and 3 function in concert to augment tolerance to cardiac ischemia.J Biol Chem. 2005;280(39):33470-33476.
[55]HASLIP M, DOSTANIC I, HUANG Y, et al. Endothelial uncoupling protein 2 regulates mitophagy and pulmonary hypertension during intermittent hypoxia.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015;35(5):1166-1178.
[56]MA S, WANG Q, ZHANG Y, et al. Transgenic overexpression of uncoupling protein 2 attenuates salt-induced vascular dysfunction by inhibition of oxidative stress. Am J Hypertens. 2014;27(3):345-354.
[57]GAO YH, GAO HB, DI NN, et al. Effects of beta3-adrenergic receptor antagonist on myocardial UCP2 expression and energy metabolism in chronic heart failure rats. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2013l;29(4):376-379, 384.
[58]CHEN K, XU Z, LIU Y, et al.Irisin protects mitochondria function during pulmonary ischemia/reperfusion injury. Sci Transl Med. 2017;9(418). pii: eaao6298.
|