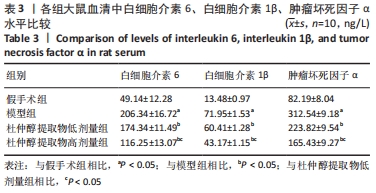
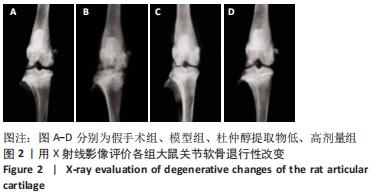
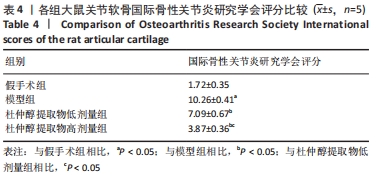
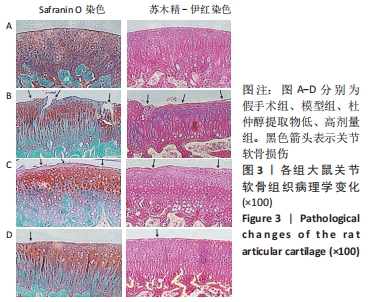
[1] CHENG F, YAN FF, LIU YP, et al. Dexmedetomidine inhibits the NF-κB pathway and NLRP3 inflammasome to attenuate papain-induced osteoarthritis in rats. Pharm Biol. 2019;57(1):649-659.
[2] ABRAMOFF B, CALDERA FE. Osteoarthritis: Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options. Med Clin North Am. 2020; 104(2):293-311.
[3] PIAO S, DU W, WEI Y, et al. Protectin DX attenuates IL-1β-induced inflammation via the AMPK/NF-κB pathway in chondrocytes and ameliorates osteoarthritis progression in a rat model. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;78(1):1-9.
[4] WOODELL-MAY JE, SOMMERFELD SD. Role of Inflammation and the Immune System in the Progression of Osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(2):253-257.
[5] LI L, HAIQING L, WEIMEI S, et al. Insights into the action mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine in osteoarthritis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017(1):1-13.
[6] HE X, WANG JH, LI MX, et al. Eucommia ulmoides Oliv.: Ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology of an important traditional Chinese medicine. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;151(1):78-92.
[7] XIE GP, JIANG N, WANG SN, et al. Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. bark aqueous extract inhibits osteoarthritis in a rat model of osteoarthritis. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015; 162(1):148-154.
[8] SIMS NA. The JAK1/STAT3/SOCS3 axis in bone development, physiology, and pathology. Exp Mol Med. 2020;52(8):1185-1197.
[9] 林奇生,邹学农,曾瑞芬,等.杜仲醇提取物通过RhoA/ROCK信号通路调控大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化作用研究[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2019, 21(2):26-30
[10] 吴大雷,周守恒,闫健伟,等.杜仲醇提取物可促进根尖周炎模型大鼠骨组织的愈合[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(23):3685-3689.
[11] FENG K, CHEN Z, PENGCHENG L, et al. Quercetin attenuates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis via SIRT1/AMPK-mediated inhibition of ER stress in rat chondrocytes and prevents the progression of osteoarthritis in a rat model. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(10):18192-18205.
[12] GERWIN N, BENDELE AM, GLASSON S, et al. The OARSI histopathology initiative - recommendations for histological assessments of osteoarthritis in the rat. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18(3):S24-34.
[13] WANG BW, JIANG Y, YAO ZL, et al. Aucubin protects chondrocytes against IL-1β-induced apoptosis in vitro and inhibits osteoarthritis in mice model. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019;13(1):3529-3538.
[14] XIA T, GAO R, ZHOU G, et al. Trans-Cinnamaldehyde Inhibits IL-1β-Stimulated Inflammation in Chondrocytes by Suppressing NF-κB and p38-JNK Pathways and Exerts Chondrocyte Protective Effects in a Rat Model of Osteoarthritis. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019(1):1-12.
[15] GRÄSSEL S, MUSCHTER D. Recent advances in the treatment of osteoarthritis. F1000Res. 2020;9:F1000 Faculty Rev-325.
[16] DING ZJ, LIANG C, WANG X, et al. Antihypertensive Activity of Eucommia Ulmoides Oliv: Male Flower Extract in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020;2020(1):1-6.
[17] WANG JY, CHEN XJ, ZHANG L, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. male flower extract on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation. Chin Med J (Engl). 2019;132(3):319-328.
[18] ROHDEWALD PJ. Review on Sustained Relief of Osteoarthritis Symptoms with a Proprietary Extract from Pine Bark, Pycnogenol. J Med Food. 2018;21(1):1-4.
[19] SUN G, BA CL, GAO R, et al. Association of IL-6, IL-8, MMP-13 gene polymorphisms with knee osteoarthritis susceptibility in the Chinese Han population. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(2):1-15.
[20] MEHANA EE, KHAFAGA AF, EL-BLEHI SS. The role of matrix metalloproteinases in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: An updated review. Life Sci. 2019;234(1):116786.
[21] CHARLIER E, DEROYER C, CIREGIA F, et al. Chondrocyte dedifferentiation and osteoarthritis (OA). Biochem Pharmacol. 2019;165(1):49-65.
[22] MAZUR CM, WOO JJ, YEE CS, et al. Osteocyte dysfunction promotes osteoarthritis through MMP13-dependent suppression of subchondral bone homeostasis. Bone Res. 2019;7(1):1-17.
[23] ZENG R, LU X, LIN J, et al. FOXM1 activates JAK1/STAT3 pathway in human osteoarthritis cartilage cell inflammatory reaction. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021;246(6):644-653.
[24] JIANG M, HE J, GU H, et al. Protective effect of resveratrol on obesity-related osteoarthritis via alleviating JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway is independent of SOCS3. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020;388(1):114871.
[25] MOHAMED EA, SAYED WM. Implication of JAK1/STAT3/SOCS3 Pathway in Aging of Cerebellum of Male Rat: Histological and Molecular study. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1): 8840.
[26] ANDOH A, SHIOYA M, NISHIDA A, et al. Expression of IL-24, an activator of the JAK1/STAT3/SOCS3 cascade, is enhanced in inflammatory bowel disease. J Immunol. 2009;183(1):687-695.
[27] HE L, TIAN L. Downregulation of miR-409-3p suppresses LPS-induced inflammation in human bronchial epithelial cells through SOCS3/JAK1/STAT3 signaling: The implication for bronchopneumonia. Mol Med Rep. 2021;23(3):190.
[28] OSUKA K, USUDA N, AOYAMA M, et al. Expression of the JAK/STAT3/SOCS3 signaling pathway in herniated lumbar discs. Neurosci Lett. 2014;569:55-58.
[29] LI XD, LI XM, GU JW, et al. MiR-155 regulates lymphoma cell proliferation and apoptosis through targeting SOCS3/JAK-STAT3 signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21(22):5153-5159.
[30] LIU H, FENG XD, YANG B, et al. Dimethyl fumarate suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma progression via activating SOCS3/JAK1/STAT3 signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(8):4713-4725.
[31] EID RA, ALKHATEEB MA, ELEAWA S, et al. Cardioprotective effect of ghrelin against myocardial infarction-induced left ventricular injury via inhibition of SOCS3 and activation of JAK2/STAT3 signaling. Basic Res Cardiol. 2018;113(2):13.
[32] LI M, ZHENG R, YUAN FL. MiR-410 affects the proliferation and apoptosis of lung cancer A549 cells through regulation of SOCS3/JAK-STAT signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(18): 5987-5993.
[33] KURDI M, BOOZ GW. Can the protective actions of JAK-STAT in the heart be exploited therapeutically? Parsing the regulation of interleukin-6-type cytokine signaling. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2007;50(2):126-141.
[34] BOYLE K, ZHANG JG, NICHOLSON SE, et al. Deletion of the SOCS box of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3) in embryonic stem cells reveals SOCS box-dependent regulation of JAK but not STAT phosphorylation. Cell Signal. 2009;21(3):394-404.
[35] LIANG Y, JIN Y, LI Y. Expression of JAKs/STATs pathway molecules in rat model of rapid focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Pediatr Nephrol. 2009;24(9):1661-1671.
|