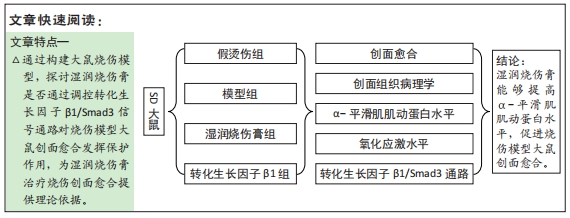
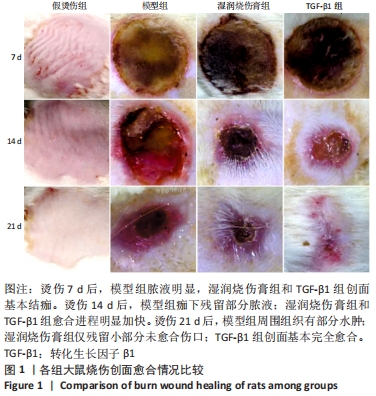
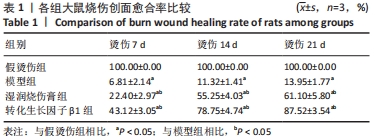
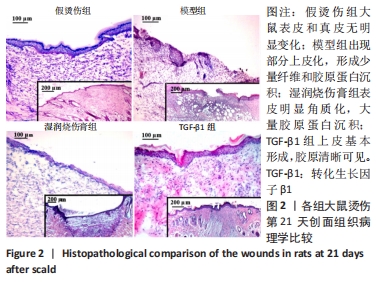
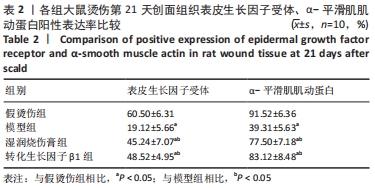
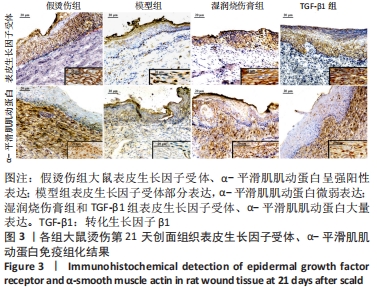
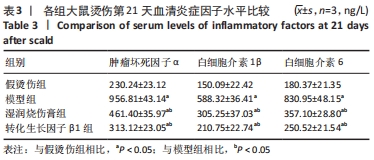
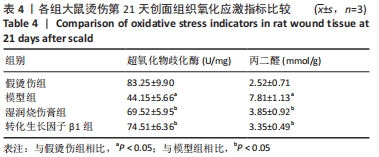
[1] JESCHKE MG, PECK MD. Burn care of the elderly. J Burn Care Res. 2017;38(3): e625-e628.
[2] 李蓉, 宋志芳. 心理弹性的心理支持方案用于面部深度烧伤美容患者的临床研究[J].中国健康心理学杂志,2018,26(9):1337-1340.
[3] SON B, LEE S, KIM H, et al. Low dose radiation attenuates inflammation and promotes wound healing in a mouse burn model. J Dermatol Sci. 2019;96(2):81-89.
[4] LEILA R, JAFAR SR, RAZIYEH K, et al. Skin Burns: Review of Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Approaches. Wounds. 2019;31(12):308-315.
[5] DU HY, ZHOU YW, LIANG X, et al. CCN1 accelerates re-epithelialization by promoting keratinocyte migration and proliferation during cutaneous wound healing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;505(4):966-972.
[6] 冯志芳. 湿润烧伤膏治疗烧伤创面患者的效果分析[J]. 中国医学创新,2019, 16(20):105-108.
[7] 杨新蕾, 许建允, 孟红阳. 湿润烧伤膏治疗供皮区残余创面的疗效观察[J]. 当代医学,2021,27(12):121-122.
[8] 梁吉星. 湿润烧伤膏治疗深Ⅱ度烧伤效果及对血清炎症因子的影响[J]. 中医药临床杂志,2019,31(8):1571-1573.
[9] 张丽艳. 湿润烧伤膏(MEBO)对糖尿病皮肤溃疡小鼠抗氧化作用及机制研究[D]. 沈阳:辽宁中医药大学,2019.
[10] JIANG TC, WANG ZY, SUN J. Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes stimulate cutaneous wound healing mediates through TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):198-207.
[11] JI YY, ZHANG AJ, CHEN XB, et al. Sodium humate accelerates cutaneous wound healing by activating TGF-beta/Smads signaling pathway in rats. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2016;6(2):132-140.
[12] 张萍, 蒋仕秋, 陈雪莲, 等. 基于TGF-β1/Smad3信号通路观察rb-bFGF在糖尿病大鼠烧伤创面愈合中的作用机制[J]. 疑难病杂志,2020,19(6):617-622+631.
[13] 张攀攀, 王培仁, 唐巍. 表皮生长因子联合封闭式负压引流对四肢深Ⅱ度烧伤患者创面愈合及ICAM-1、EGF的影响[J]. 中国合理用药探索,2021,18(1):96-100.
[14] ANGGOROWATI N, KURNIASARI CR, DAMAYANTI K, et al. Histochemical and immunohistochemical study of α-SMA, collagen, and PCNA in epithelial ovarian neoplasm. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2017;18(3):667-671.
[15] PUTRA A, ALIF I, HAMRA N, et al. MSC-released TGF-beta regulate alpha-SMA expression of myofibroblast during wound healing. J Stem Cells Regen Med. 2020;16(2):73-79.
[16] 卢孔君. 表皮生长因子和维甲酸复方柔性脂质体软膏的制备及烧伤愈合的研究[D]. 杭州:浙江大学,2019.
[17] SIMONETTI O, LUCARINI G, ORLANDO F, et al. Role of Daptomycin on Burn Wound Healing in an Animal Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infection Model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017;61(9):e00606-e00617.
[18] 刘昕, 孙毅海, 唐深, 等. 输尿管热损伤后TGF-β亚型及α-平滑肌肌动蛋白表达的实验研究[J]. 微创医学,2019,14(4):412-414+429.
[19] 王雪欣, 张明谏, 李小兵. 严重烧伤患者锌缺乏与补锌治疗研究进展[J]. 中华烧伤杂志,2018,34(1):57-59.
[20] HERNANDEZ P, BULLER D, MITCHELL T, et al. Severe Burn-Induced Inflammation and Remodeling of Achilles Tendon in a Rat Model. Shock. 2018;50(3):346-350.
[21] ZHOU XQ, RUAN QF, YE ZQ, et al. Resveratrol accelerates wound healing by attenuating oxidative stress-induced impairment of cell proliferation and migration. Burns. 2021;47(1):133-139.
[22] ZHANG DM, WANG BL, SUN YJ, et al. Injectable Enzyme-Based Hydrogel Matrix with Precisely Oxidative Stress Defense for Promoting Dermal Repair of Burn Wound. Macromol Biosci. 2020;20(6):e2000036.
[23] 董小鹏, 于博. 生肌玉红膏对深Ⅱ度烧伤模型大鼠创面氧化应激水平影响的实验研究[J]. 中国卫生标准管理,2016,7(22):124-125.
[24] 巩文艺, 韩冬. 黄芪多糖对严重烧伤大鼠心肌组织氧化应激和炎症反应的影响[J]. 中国中医急症,2016,25(6):1005-1007+1022.
[25] 徐汤灵, 林谋俊, 何勇, 等. 花椒籽油对大鼠烧伤模型促创面愈合和血清炎症因子的调节作用[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志,2020,36(13):1821-1824.
[26] KANG JH, JUNG MY, YIN X, et al. Cell-penetrating peptides selectively targeting SMAD3 inhibit profibrotic TGF-β signaling. J Clin Invest. 2017;127(7):2541-2554.
[27] 刘筱, 伍伟明, 尹婷, 等. 美洲大蠊提取液对大鼠难愈合创面TGF-β表达的影响[J]. 中医药导报,2018,24(6):9-12.
[28] MENG XL, GAO XX, CHEN XX. Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells exert anti-fibrotic action on hypertrophic scar-derived fibroblasts in co-culture by inhibiting the activation of the TGF β1/Smad3 pathway. Exp Ther Med. 2021;21(3):210
[29] YAN G, RU Y, WU K, et al. GOLM1 promotes prostate cancer progression through activating PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling. Prostate. 2018;78(3):166-177.
[30] GUO J, FANG Y, JIANG F, et al. Neohesperidin inhibits TGF-beta1/Smad3 signaling and alleviates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019;864:172712.
[31] LIU N, FENG J, LU X, et al. Isorhamnetin Inhibits Liver Fibrosis by Reducing Autophagy and Inhibiting Extracellular Matrix Formation via the TGF-beta1/Smad3 and TGF-beta1/p38 MAPK Pathways. Mediators Inflamm. 2019;2019:6175091.
[32] LOBODA A, SOBCZAK M, JOZKOWICZ A, et al. TGF-beta1/Smads and miR-21 in Renal Fibrosis and Inflammation. Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:8319283.
[33] XU H, LI F. miR-127 aggravates myocardial failure by promoting the TGF-beta1/Smad3 signaling. Mol Med Rep. 2019;20(3):2500.
[34] 郑晨果, 陈念昭, 黄盈, 等. 痔愈喷剂对大鼠创面TGF-β1表达的影响[J]. 中华中医药学刊,2015,33(1):165-167+17-18.
|