[1] CHAUSSY C, BRENDEL W, SCHMIEDT E. Extracorporeally induced destruction of kidney stones by shock waves. Lancet. 1980;2(8207):1265-1268.
[2] SAUERBRUCH T, DELIUS M, PAUMGARTNER G, et al. Fragmentation of gallstones by extracorporeal shock waves. N Engl J Med. 1986;314(13): 818-822.
[3] XU ZH, JIANG Q, CHEN DY, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave treatment in nonunions of long bone fractures. Int Orthop. 2009;33(3):789-793.
[4] SUN J, GAO F, WANG Y, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy is effective in treating chronic plantar fasciitis: a meta-analysis of RCTs. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(15):e6621.
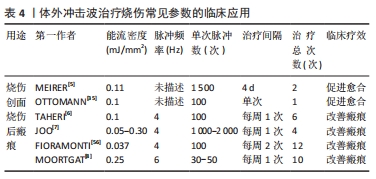
[5] MEIRER R, KAMELGER FS, PIZA-KATZER H. Shock wave therapy: an innovative treatment method for partial thickness burns. Burns. 2005; 31(7):921-922.
[6] TAHERI P, KHOSRAWI S, MAZAHERI M, et al. Effect of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on improving burn scar in patients with burnt extremities in Isfahan, Iran. J Res Med Sci. 2018;23:81.
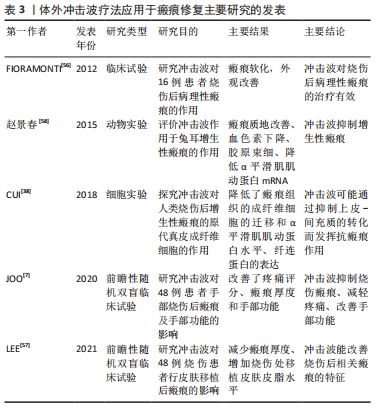
[7] JOO SY, LEE SY, CHO YS, et al. Clinical utility of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on hypertrophic scars of the hand caused by burn injury: a prospective, randomized, double-blinded study. J Clin Med. 2020;9(5):1376.
[8] MOORTGAT P, ANTHONISSEN M, VAN DAELE U, et al. The effects of shock wave therapy applied on hypertrophic burn scars: a randomised controlled trial. Scars Burn Heal. 2020;6:1006867704.
[9] TARNUZZER RW, SCHULTZ GS. Biochemical analysis of acute and chronic wound environments. Wound Repair Regen. 1996;4(3):321-325.
[10] FINNERTY CC, JESCHKE MG, BRANSKI LK, et al. Hypertrophic scarring: the greatest unmet challenge after burn injury. Lancet. 2016;388 (10052):1427-1436.
[11] WOLFRAM D, TZANKOV A, PULZL P, et al. Hypertrophic scars and keloids-a review of their pathophysiology, risk factors, and therapeutic management. Dermatol Surg. 2009;35(2):171-181.
[12] COTSARELIS G. Epithelial stem cells: a folliculocentric view. J Invest Dermatol. 2006;126(7):1459-1468.
[13] SPIEKSTRA SW, BREETVELD M, RUSTEMEYER T, et al. Wound-healing factors secreted by epidermal keratinocytes and dermal fibroblasts in skin substitutes. Wound Repair Regen. 2007;15(5):708-717.
[14] 邢更彦,张浩冲,刘水涛,等.中国骨肌疾病体外冲击波疗法指南(2019年版)[J].中国医学前沿杂志(电子版),2019,11(4):1-10.
[15] DYMAREK R, HALSKI T, PTASZKOWSKI K, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy as an adjunct wound treatment: a systematic review of the literature. Ostomy Wound Manage. 2014;60(7):26-39.
[16] HAYASHI D, KAWAKAMI K, ITO K, et al. Low-energy extracorporeal shock wave therapy enhances skin wound healing in diabetic mice: a critical role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Wound Repair Regen. 2012;20(6):887-895.
[17] WEIHS AM, FUCHS C, TEUSCHL AH, et al. Shock wave treatment enhances cell proliferation and improves wound healing by ATP release-coupled extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) activation. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(39):27090-27104.
[18] INGBER DE. Cellular mechanotransduction: putting all the pieces together again. Faseb J. 2006;20(7):811-827.
[19] 盛炜,张丽,李美蓉,等.体外冲击波疗法促进组织修复及再生的机制综述[J].解放军医学院学报,2020,41(6):638-643.
[20] WANG N, TYTELL JD, INGBER DE. Mechanotransduction at a distance: mechanically coupling the extracellular matrix with the nucleus. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10(1):75-82.
[21] CHIEN S. Mechanotransduction and endothelial cell homeostasis: the wisdom of the cell. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007;292(3): H1209-H1224.
[22] INGBER DE. The riddle of morphogenesis: a question of solution chemistry or molecular cell engineering? Cell. 1993;75(7):1249-1252.
[23] HOLFELD J, TEPEKOYLU C, REISSIG C, et al. Toll-like receptor 3 signalling mediates angiogenic response upon shock wave treatment of ischaemic muscle. Cardiovasc Res. 2016;109(2):331-343.
[24] KIM IG, LEE JY, LEE DS, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy combined with vascular endothelial growth factor-C hydrogel for lymphangiogenesis. J Vasc Res. 2013;50(2):124-133.
[25] ZINS SR, AMARE MF, TADAKI DK, et al. Comparative analysis of angiogenic gene expression in normal and impaired wound healing in diabetic mice: effects of extracorporeal shock wave therapy. Angiogenesis. 2010;13(4):293-304.
[26] 赵景春,咸春静,于家傲,等.体外冲击波疗法对促进创面血管生成及愈合作用的研究进展[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版), 2014,9(1):71-75.
[27] MARIOTTO S, DE PRATI AC, CAVALIERI E, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in inflammatory diseases: molecular mechanism that triggers anti-inflammatory action. Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(19):2366-2372.
[28] HOLFELD J, TEPEKOYLU C, KOZARYN R, et al. Shockwave therapy differentially stimulates endothelial cells: implications on the control of inflammation via toll-Like receptor 3. Inflammation. 2014;37(1):65-70.
[29] DAVIS TA, STOJADINOVIC A, ANAM K, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy suppresses the early proinflammatory immune response to a severe cutaneous burn injury. Int Wound J. 2009;6(1):11-21.
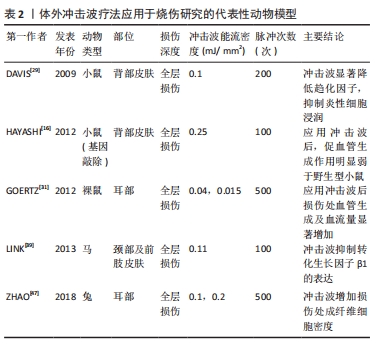
[30] WANG CJ, WANG FS, YANG KD, et al. Shock wave therapy induces neovascularization at the tendon-bone junction. A study in rabbits. J Orthop Res. 2003;21(6):984-989.
[31] GOERTZ O, LAUER H, HIRSCH T, et al. Extracorporeal shock waves improve angiogenesis after full thickness burn. Burns. 2012;38(7): 1010-1018.
[32] KISCH T, SORG H, FORSTMEIER V, et al. Remote effects of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on cutaneous microcirculation. J Tissue Viability. 2015;24(4):140-145.
[33] SCHADEN W, THIELE R, KOLPL C, et al. Shock wave therapy for acute and chronic soft tissue wounds: a feasibility study. J Surg Res. 2007; 143(1):1-12.
[34] WANG FS, YANG KD, WANG CJ, et al. Shockwave stimulates oxygen radical-mediated osteogenesis of the mesenchymal cells from human umbilical cord blood. J Bone Miner Res. 2004;19(6):973-982.
[35] OTTOMANN C, STOJADINOVIC A, LAVIN PT, et al. Prospective randomized phase II trial of accelerated reepithelialization of superficial second-degree burn wounds using extracorporeal shock wave therapy. Ann Surg. 2012;255(1):23-29.
[36] ASCHERMANN I, NOOR S, VENTURELLI S, et al. Extracorporal shock waves activate migration, proliferation and inflammatory pathways in fibroblasts and keratinocytes, and improve wound healing in an open-label, single-arm study in patients with therapy-refractory chronic leg ulcers. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;41(3):890-906.
[37] SUHR F, DELHASSE Y, BUNGARTZ G, et al. Cell biological effects of mechanical stimulations generated by focused extracorporeal shock wave applications on cultured human bone marrow stromal cells. Stem Cell Res. 2013;11(2):951-964.
[38] CUI HS, HONG AR, KIM JB, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy alters the expression of fibrosis-related molecules in fibroblast derived from human hypertrophic scar. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(1):124.
[39] LINK KA, KOENIG JB, SILVEIRA A, et al. Effect of unfocused extracorporeal shock wave therapy on growth factor gene expression in wounds and intact skin of horses. Am J Vet Res. 2013;74(2):324-332.
[40] DJEDOVIC G, KAMELGER FS, JESCHKE J, et al. Effect of extracorporeal shock wave treatment on deep partial-thickness burn injury in rats: a pilot study. Plast Surg Int. 2014;2014:495967.
[41] FINNERTY CC, JESCHKE MG, BRANSKI LK, et al. Hypertrophic scarring: the greatest unmet challenge after burn injury. Lancet. 2016;388 (10052):1427-1436.
[42] MAUCK MC, SHUPP JW, WILLIAMS F, et al. Hypertrophic scar severity at autograft sites is associated with increased pain and itch after major thermal burn injury. J Burn Care Res. 2018;39(4):536-544.
[43] GERDESMEYER L, MAIER M, HAAKE M, et al. Physical-technical principles of extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT). Orthopade. 2002;31(7):610-617.
[44] SPEED CA. Extracorporeal shock-wave therapy in the management of chronic soft-tissue conditions. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86(2):165-171.
[45] KIM DH, HAN SH, SUH HS, et al. Benefits of extracorporeal shock waves for keloid treatment: a pilot study. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33(4):e13653.
[46] SAGGINI R, SAGGINI A, SPAGNOLI AM, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy: an emerging treatment modality for retracting scars of the hands. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2016;42(1):185-195.
[47] ZHAO JC, ZHANG BR, HONG L, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy with low-energy flux density inhibits hypertrophic scar formation in an animal model. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41(4):1931-1938.
[48] ZHAO JC, ZHANG BR, SHI K, et al. Lower energy radial shock wave therapy improves characteristics of hypertrophic scar in a rabbit ear model. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(1):933-939.
[49] TAKAHASHI N, OHTORI S, SAISU T, et al. Second application of low-energy shock waves has a cumulative effect on free nerve endings. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;443:315-319.
[50] FRICOVA J, ROKYTA R. The effects of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on pain patients. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2015;36(2):161-164.
[51] D’AGOSTINO MC, CRAIG K, TIBALT E, et al. Shock wave as biological therapeutic tool: from mechanical stimulation to recovery and healing, through mechanotransduction. Int J Surg. 2015;24(Pt B):147-153.
[52] 赵胜超,陈永亮,吴博,等.体外冲击波治疗增生性瘢痕的研究进展及机制探讨[J].中国烧伤创疡杂志,2019,31(2):149-152.
[53] CHO YS, JOO SY, CUI H, et al. Effect of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on scar pain in burn patients: a prospective, randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(32):e4575.
[54] 黎景波,曹海燕,肖啸,等.综合康复结合冲击波治疗对下肢烧伤后增生性瘢痕患者疼痛程度及下肢功能的影响[J].中国实用医药, 2019,14(24):184-185.
[55] 廖曼霞,曹海燕,易先锋,等.冲击波联合综合康复治疗对下肢烧伤后增生性瘢痕的疗效观察[J].中国康复,2016,31(2):141-143.
[56] FIORAMONTI P, CIGNA E, ONESTI MG, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the management of burn scars. Dermatol Surg. 2012;38(5): 778-782.
[57] LEE SY, JOO SY, CHO YS, et al. Effect of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for burn scar regeneration: a prospective, randomized, double-blinded study. Burns. 2021;47(4):821-827.
[58] 赵景春.体外冲击波抑制兔耳增生性瘢痕的实验研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2015.
[59] SHI L, LI Z, WANG P, et al. Irritant contact dermatitis following extracorporeal shockwave therapy: a case report. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. doi: 10.21037/apm-20-1830.
|