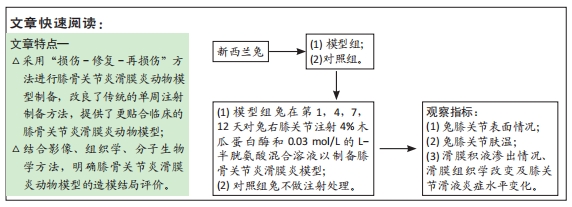
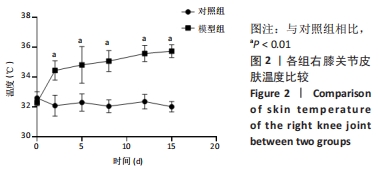
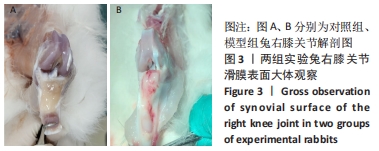
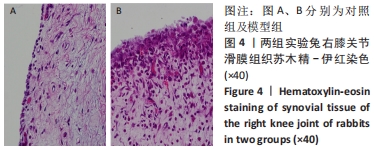
[1] FELSON DT, NIU J, NEOGI T, et al. Synovitis and the risk of knee osteoarthritis: the MOST Study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(3):458-464.
[2] ROEMER FW, GUERMAZI A, ZHANG YQ, et al. Hoffa’s Fat Pad: Evaluation on Unenhanced MR Images as a Measure of Patellofemoral Synovitis in Osteoarthritis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009;192(6):1696-1700.
[3] SCANZELLO CR, GOLDRING SR. The role of synovitis in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Bone. 2012;51(2):249-257.
[4] 中医骨伤科临床诊疗指南·膝痹病(膝骨关节炎)[J].康复学报,2019,29(3):1-7.
[5] ATUKORALA I, KWOH CK, GUERMAZI A, et al. Synovitis in knee osteoarthritis: a precursor of disease? Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(2):390-395.
[6] LOEUILLE D, RAT AC, GOEBEL JC, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging in osteoarthritis: which method best reflects synovial membrane inflammation? Correlations with clinical, macroscopic and microscopic features. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2009;17(9):1186-1192.
[7] DE LANGE-BROKAAR JE, IOAN-FACSINAY A, YUSUF E, et al. Evolution of synovitis in osteoarthritic knees and its association with clinical features. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(11):1867-1874.
[8] TSAI HC, CHEN TL, CHEN Y, et al. Traumatic osteoarthritis-induced persistent mechanical hyperalgesia in a rat model of anterior cruciate ligament transection plus a medial meniscectomy. J Pain Res. 2018;11:41-50.
[10] DAI S, LIANG T, FUJII T, et al. Increased elastic modulus of the synovial membrane in a rat ACLT model of osteoarthritis revealed by atomic force microscopy. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2020;53(11):e10058.
[9] BURKE CJ, ALIZAI H, BELTRAN LS, et al. MRI of synovitis and joint fluid. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2019;49(6):1512-1527.
[11] 廖八根, 徐勇, 高鹏吉. 中医外治法干预运动创伤性膝关节炎模型兔膝关节滑膜中碱性成纤维细胞生长因子的表达[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008,12(11):2047-2050.
[12] RIIS RGC. Assessing synovitis with conventional static and dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in knee osteoarthritis. Dan Med J. 2018;65(4):B5464.
[13] YUN SJ, LIM Y, JIN W, et al. Validity of Radiograph-Based Infrapatellar Fat Pad Opacity Grading for Assessing Knee Synovitis: Correlation With Contrast-Enhanced MRI. Am J Roentgenol. 2017;209(6):1321-1330.
[14] GOLDRING MB. The role of cytokines as inflammatory mediators in osteoarthritis: Lessons from animal models. Connect Tissue Res. 1999;40(1):1-11.
[15] GOWLER PRW, MAPP PI, BURSTON JJ, et al. Refining surgical models of osteoarthritis in mice and rats alters pain phenotype but not joint pathology. Plos One. 2020;15(9):e0239663.
[16] WANG X, JIN XZ, BLIZZARD L, et al. Associations Between Knee Effusion-synovitis and Joint Structural Changes in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol. 2017;44(11):1644-1651.
[17] MATHIESSEN A, CONAGHAN PG. Synovitis in osteoarthritis: current understanding with therapeutic implications. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):18.
[18] 孙鲁宁, 赵燕华, 黄桂成, 等. 木瓜蛋白酶诱导膝关节骨关节炎模型兔滑膜病理变化与药物注射时间的关系[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(50):9311-9313.
[19] 张康乐, 郭珈宜, 刘源, 等. 低浓度木瓜蛋白酶诱导兔早期膝骨关节炎滑膜炎症的时间曲线[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(36):5787-5792.
[20] 符静泉, 许立拔, 胡超, 等. 木瓜蛋白酶水溶液小鼠尾静脉注射急性毒性反应的实验研究[J].广西医科大学学报,2015,32(6):908-911.
[21] BARBOSA GM, CUNHA JE, RUSSO TL, et al. Thirty days after anterior cruciate ligament transection is sufficient to induce signs of knee osteoarthritis in rats: pain, functional impairment, and synovial inflammation. Inflamm Res. 2020;69(3):279-288.
[22] 李宁, 吴建民, 刘晓, 等. 马铃薯外敷药膏对兔膝关节创伤性滑膜炎IL-1β和TNF-α的影响[J].时珍国医国药,2018,29(4):832-833.
[23] SIEKER JT, PROFFEN BL, WALLER KA, et al. Transcriptional profiling of synovium in a porcine model of early post-traumatic osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(8): 2128-2139.
[24] SELLAM J, BERENBAUM F. The role of synovitis in pathophysiology and clinical symptoms of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010;6(11):625-635.
[25] HAYASHI D, ROEMER FW, KATUR A, et al. Imaging of Synovitis in Osteoarthritis: Current Status and Outlook. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2011;41(2):116-130.
[26] YUSUF E, KORTEKAAS MC, WATT I, et al. Do knee abnormalities visualised on MRI explain knee pain in knee osteoarthritis? A systematic review. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70(1):60-67.
[27] ROEMER FW, GUERMAZI A, FELSON DT, et al. Presence of MRI-detected joint effusion and synovitis increases the risk of cartilage loss in knees without osteoarthritis at 30-month follow-up: the MOST study. Ann Rheum Dis., 2011;70(10):1804-1809.
[28] MATHIESSEN A, SLATKOWSKY-CHRISTENSEN B, KVIEN TK, et al. Ultrasound-detected inflammation predicts radiographic progression in hand osteoarthritis after 5 years. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(5):825-830.
[29] 李慧英, 孟东方, 苏建光. 四妙散干预兔膝关节创伤性滑膜炎白细胞介素-1β和肿瘤坏死因子-α水平的研究[J].中华中医药杂志,2013,28(10):3043-3045.
[30] BERENBAUM F. Osteoarthritis as an inflammatory disease (osteoarthritis is not osteoarthrosis!). Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(1):16-21.
[31] RAHMATI M, MOBASHERI A, MOZAFARI M. Inflammatory mediators in osteoarthritis: A critical review of the state-of-the-art, current prospects, and future challenges. Bone. 2016;85:81-90.
[32] ZHANG RX, REN K, DUBNER R. Osteoarthritis pain mechanisms: basic studies in animal models. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013; 21(9): 1308-1315.
[33] NEES TA, ROSSHIRT N, REINER T, et al. Inflammation and osteoarthritis-related pain. Schmerz. 2019;33(1):4-12.
[34] 朱翔,董扬.膝关节滑膜炎性病变临床特征、诊断和治疗[J].国际骨科学杂志,2011,32(1):65-68.
[35] 邓聪,老锦雄,萧昊民.扶正通阳灸法配合药物治疗老年性膝关节滑膜炎的临床研究[J].上海针灸杂志,2021,40(3):343-346.
|