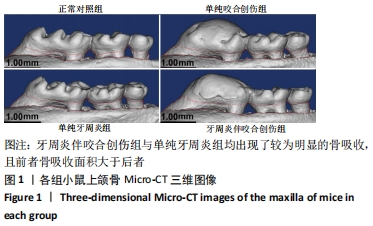
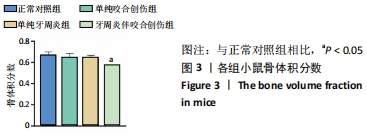
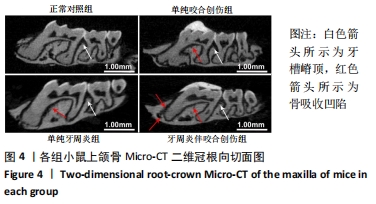
[1] KORNMAN KS. Mapping the pathogenesis of periodontitis: a new look. J Periodontol. 2008;79(8 Suppl):1560-1568.
[2] KHAJURIA DK, PATIL ON, KARASIK D, et al. Development and evaluation of novel biodegradable chitosan based metformin intrapocket dental film for the management of periodontitis and alveolar bone loss in a rat model. Arch Oral Biol. 2018;85:120-129.
[3] VERGNES JN, MAZEVET M. Oral diseases: a global public health challenge. Lancet. 2020;395(10219):186.
[4] Neiderud AM, Ericsson I, Lindhe J. Probing pocket depth at mobile/nonmobile teeth. J Clin Periodontol. 1992;19(10):754-759.
[5] STILLMAN PR. What is Traumatic Occlusion and How Can it be Diagnosed and Corrected? .The Journal of the American Dental Association. 1925;12( 11): 1330-1338.
[6] SINGH DK, JALALUDDIN M, RAJEEV R, et al. Trauma from occlusion: The overstrain of the supporting structures of the teeth. Indian J Dent Sci.2017;9(2):126-132.
[7] 毕良佳.牙周炎与咬合创伤[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2010,3(1): 7-11.
[8] NAKATSU S, YOSHINAGA Y, KURAMOTO A, et al. Occlusal trauma accelerates attachment loss at the onset of experimental periodontitis in rats. J Periodontal Res. 2014;49(3):314-322.
[9] YOSHINAGA Y, UKAI T, ABE Y, et al. Expression of receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand relates to inflammatory bone resorption, with or without occlusal trauma, in rats. J Periodontal Res. 2007;42(5):402-409.
[10] PAN W, YANG L, LI J, et al. Traumatic occlusion aggravates bone loss during periodontitis and activates Hippo-YAP pathway. J Clin Periodontol. 2019;46(4):438-447.
[11] 毕振宇.Wistar大鼠咬合创伤模型牙周与颞下颌关节毛细血管铸型研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2014.
[12] 牛临生,安丽,安阳.大鼠正畸咬合创伤模型牙周组织变化的研究[J].全科口腔医学电子杂志,2016,3(17):1-2,5.
[13] GRAVES DT, FINE D, TENG YT, et al. The use of rodent models to investigate host-bacteria interactions related to periodontal diseases. J Clin Periodontol. 2008;35(2):89-105.
[14] 孔晨.牙周炎动物模型的研究进展[J].医学综述, 2019,25(17): 3344-3349.
[15] CURYLOFO-ZOTTI FA, ELBURKI MS, OLIVEIRA PA, et al. Differential effects of natural Curcumin and chemically modified curcumin on inflammation and bone resorption in model of experimental periodontitis. Arch Oral Biol. 2018;91:42-50.
[16] BLASCO-BAQUE V, GARIDOU L, POMIÉ C, et al. Periodontitis induced by Porphyromonas gingivalis drives periodontal microbiota dysbiosis and insulin resistance via an impaired adaptive immune response. Gut. 2017;66(5):872-885.
[17] KANTARCI A, HASTURK H, VAN DYKE TE. Animal models for periodontal regeneration and peri-implant responses. Periodontol 2000. 2015; 68(1):66-82.
[18] WEI W, XIAO X, LI J, et al. Activation of the STAT1 Pathway Accelerates Periodontitis in Nos3-/- Mice. J Dent Res. 2019;98(9):1027-1036.
[19] 姜宁,罗远,潘杰.局部抑制TLR2对牙周炎小鼠牙槽骨吸收的影响[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2018,28(2):69-72,68.
[20] 徐娟.牙龈卟啉单胞菌对慢性牙周炎致病作用的相关毒力因子研究进展[J].西北国防医学杂志,2020,41(5):321-325.
[21] 尹敏,冯伟,金巧霞,等.慢性牙周炎患者牙龈卟啉单胞菌感染与NLRP3、IL-1β、IL-18在牙周膜细胞中的表达研究[J].中华全科医学, 2017,15(7):1102-1104.
[22] LINDHE J, ERICSSON I. The effect of elimination of jiggling forces on periodontally exposed teeth in the dog. J Periodontol. 1982;53(9):562-567.
[23] SOUZA VH, VISENTAINER JEL, ZACARIAS JMV, et al. Association of IL16 polymorphisms with periodontitis in Brazilians: A case- control study. PLoS One. 2020;15(9):e0239101.
[24] BYRNE SJ, DASHPER SG, DARBY IB, et al. Progression of chronic periodontitis can be predicted by the levels of Porphyromonas gingivalis and Treponema denticola in subgingival plaque. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 2009;24(6):469-477.
[25] SANTIAGO E. Parameter on Occlusal Traumatism in Patients With Chronic Periodontitis. J Periodontol. 2000;71 Suppl 5S:873-875.
[26] MIZE TW, SUNDARARAJ KP, LEITE RS, et al. Increased and correlated expression of connective tissue growth factor and transforming growth factor beta 1 in surgically removed periodontal tissues with chronic periodontitis. J Periodontal Res. 2015;50(3):315-319.
[27] KON T, CHO TJ, AIZAWA T, et al. Expression of osteoprotegerin, receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand (osteoprotegerin ligand) and related proinflammatory cytokines during fracture healing. J Bone Miner Res. 2001;16(6):1004-1014.
[28] FARHAT SB, DE SOUZA CM, BRAOSI AP, et al. Complete physical mapping of IL6 reveals a new marker associated with chronic periodontitis. J Periodontal Res. 2017;52(2):255-261.
[29] LIU YC, LERNER UH, TENG YT. Cytokine responses against periodontal infection: protective and destructive roles. Periodontol 2000. 2010; 52(1):163-206.
[30] CHENG R, WU Z, LI M, et al. Interleukin-1β is a potential therapeutic target for periodontitis: a narrative review. Int J Oral Sci. 2020;12(1):2.
[31] EIVAZI M, FALAHI N, EIVAZI N, et al. The Effect of Scaling and Root Planning on Salivary TNF-α and IL-1α Concentrations in Patients with Chronic Periodontitis. Open Dent J. 2017;11:573-580.
[32] WANG L, LUO JY, LI B, et al. Integrin-YAP/TAZ-JNK cascade mediates atheroprotective effect of unidirectional shear flow. Nature. 2016; 540(7634):579-582.
|