中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (20): 3220-3224.doi: 10.12307/2022.624
• 组织构建细胞学实验 cytology experiments in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
受损脊髓神经轴突再生过程中Nogo-A/NgR及 NGF/TrkA 信号通路的交互作用
杨 林1,邬 瑶1,周宾宾2
- 1江西省丰城市中医院,江西省丰城市 330038;2广西中医药大学第一附属医院,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530000
Interaction of Nogo-A/NgR signaling pathway and NGF/TrkA signaling pathway during the regeneration of injured spinal cord nerve axons
Yang Lin1, Wu Yao1, Zhou Binbin2
- 1Fengcheng Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fengcheng 330038, Jiangxi Province, China; 2the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
生长相关蛋白43(Growth associated protein-43,GAP-43):是一种胞膜类磷酸蛋白,是神经元再生可塑性的标志蛋白,参与轴突新生与各阶段联系发生的关键过程,对于中枢神经再生具有重要意义。正常情况下GAP-43处于低表达水平,当神经轴突损伤发生时GAP-43表达水平升高。
轴突再生:神经损伤后的轴突再生是一个复杂的多因素调节过程。胶质细胞包绕轴突形成髓鞘,髓鞘是神经组织固有的特化结构,具有增强轴突信号传导特别是动作电位沿着有髓神经纤维跳跃式传导作用。损伤部位再生轴突重新被激活的胶质细胞包裹而形成髓鞘,是神经功能得到恢复的生物学基础。
背景:生长相关蛋白43是一种胞膜类磷酸蛋白,是神经元再生可塑性的标志蛋白,参与轴突新生与各阶段联系发生的关键过程,对于中枢神经再生具有重要意义。
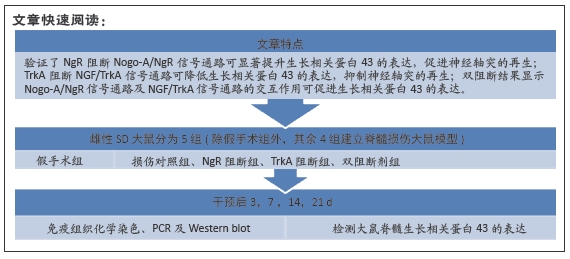
目的:通过观察Nogo-A/NgR 信号通路及 NGF/TrkA 信号通路的交互作用对生长相关蛋白43表达的影响,探讨脊髓损伤后神经再生恢复机制。
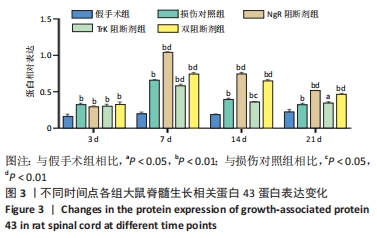
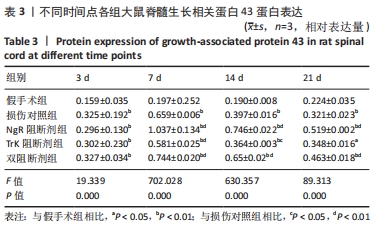
方法:将 120 只 SD 大鼠随机分为 5 组:NgR 阻断组、TrkA 阻断组、双阻断剂组、损伤对照组和假手术组。假手术组大鼠进行椎板切除术(不损伤脊髓);其余各组建立脊髓损伤大鼠模型。造模成功后立即注射阻断剂,NgR 阻断组大鼠在脊髓损伤后的损伤节段注射25 μL NgR 阻断剂 NEP1-40和 25 μL生理盐水;TrkA 阻断组大鼠在相应部位注射25 μL TrkA 阻断剂 K252a和25 μL生理盐水;双阻断剂组大鼠相应部位注射25 μL NgR 阻断剂 NEP1-40 和25 μL TrkA 阻断剂 K252a;损伤对照组和假手术组大鼠注射50 μL生理盐水。于干预后3,7,14,21 d分别取大鼠脊髓组织,通过免疫组织化学、PCR和Western blot检测大鼠脊髓组织生长相关蛋白43的mRNA及蛋白表达。
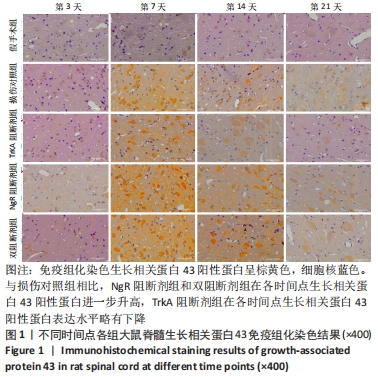
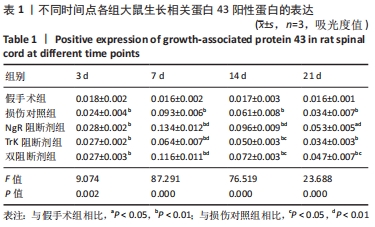
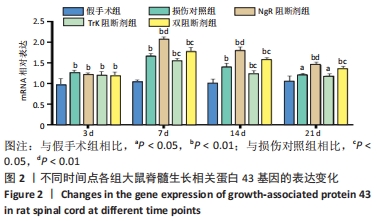
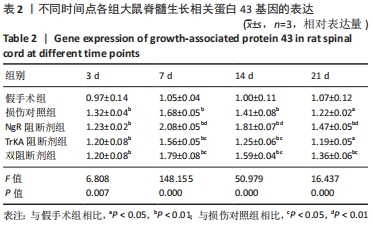
结果与结论:①免疫组化、PCR及Western blot结果显示,NgR 阻断组、TrkA 阻断组、双阻断剂组、损伤对照组的生长相关蛋白43 mRNA及蛋白表达水平较假手术组提高;NgR 阻断组、双阻断剂组的生长相关蛋白43 mRNA及蛋白表达水平较损伤对照组高,在第7,14天差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05或< 0.01);TrkA 阻断组的生长相关蛋白43 mRNA及蛋白表达水平较损伤对照组降低,在第7,14天差异有显著性意义 (P < 0.05或< 0.01);②结果表明,NgR 阻断证明Nogo-A/NgR 信号通路可显著提升生长相关蛋白43的表达,促进神经轴突的再生;TrkA 阻断证明NGF/TrkA 信号通路可降低生长相关蛋白43的表达,抑制神经轴突的再生;NgR 和TrkA 双阻断结果显示Nogo-A/NgR 信号通路及 NGF/TrkA 信号通路的交互作用可促进生长相关蛋白43的表达。
缩略语:神经生长因子:nerve growth factor,NGF;酪氨酸激酶A:tyrosine kinase,TrkA;神经生长抑制因子A:neurite outgrowth inhibitor A,Nogo-A;神经生长抑制因子受体:neurite growth inhibitor receptor,NgR
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4279-377X (杨林)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: